
Concept introduction:
Budget Line: It is defined as the combination of all the goods that a consumer can purchase, exhausting all his income. The formula for the budget line is:
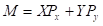
Here,
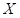 is the quantity of good X.
is the quantity of good X. 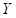 is the quantity of good Y.
is the quantity of good Y. 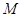 is the total income.
is the total income. 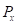 is the
is the price of good X.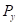 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
Giffen goods: All those goods whose demand increases with an increase in its price is known as Giffen goods.
- It violates the
law of demand which states that when prices increase, the demand for a good decreases. - It has an upward sloping curve which is generally due to the substitution effects.
Example of Giffen good: consider a situation in which a poor guy uses cereals for all the necessary nutrients so, as the price of cereal increases, he demands less of other goods.
Substitution effects: It states that the demand of a good increases if the price of its substitute goods increase and vice versa. Take an example of tea and coffee, if prices of tea increase, then the demand for coffee increases.
Income effects: It states that the demand for normal goods and the income are directly related which means that when income increases, then the demand for normal goods also increase and vice versa.
Inferior goods: It is a type of good in which the demand declines when the income of the consumer increases. Example; demand for potato decreases as income increases because we prefer green vegetables at higher incomes
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK ECONOMICS
- Please give with explanationarrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forwardand u (C1, C2) = 1/2 = f) Derive analytically and show graphically the solution under other util- ity functions such as u (C1, C2) ac₁+bc2 where a, b > 0, u (C1, C2) = ac₁+bc1/2 acbc2 (assume that the agent is sufficiently rich to avoid the corner solution). What of these utility functions reflects best your own preferences (or indicate other utility function that represent your pref- erences).arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





