
Interpretation:
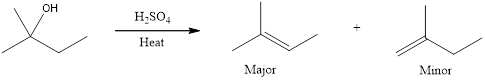
The major product and minor product that is expected has to be drawn when the given compound is heated with concentrated sulfuric acid to give an E1 reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination reactions are the one in which the groups are lost and the saturated bonds are converted to unsaturated bonds. Usually the substitution reaction competes with elimination reaction.
In elimination reaction, the beta proton is removed together with the leaving group to form a double bond.
E1 reaction proceeds through two separate single steps. First step is the formation of carbocation intermediate by loss of leaving group. Second step is the attack of base to lose a proton. E1 stands for unimolecular elimination.
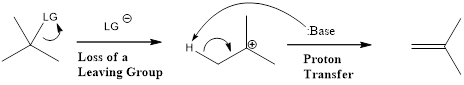
First step is the rate determining step. Hydroxide group is a poor leaving group. Hence, for elimination reaction, a very strong acid is required to protonate the hydroxyl group. When an alcohol is heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, the product obtained is an
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: First Semester Topics
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





