
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780132915540
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.3, Problem 10P
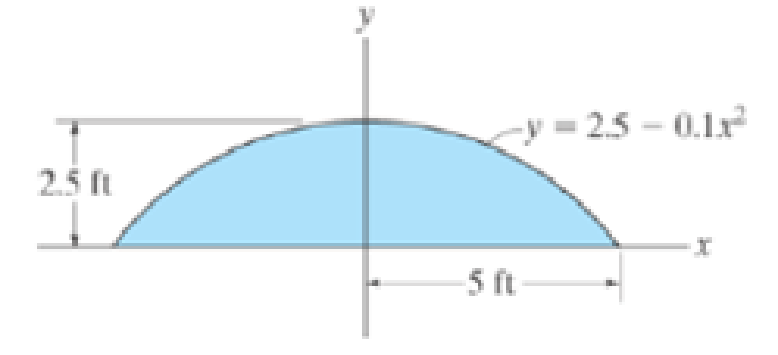
Solve the problem in two ways, using rectangular differential elements, (a) having a thickness dx and (b) having a thickness of dy.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
my ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by step
My ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending moment
Chapter 10 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Ch. 10.3 - Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 1PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 2PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 3PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 6P
Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 10.3 - Determine the moment of inertia of the area about...Ch. 10.3 - Solve the problem in two ways, using rectangular...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 15PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 16PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 17PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 19PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 20PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 21PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 22PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 23PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 24PCh. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the beams...Ch. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the beams...Ch. 10.4 - Determine me moment of inertia of the...Ch. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the...Ch. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the composite...Ch. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the composite...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 27PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 28PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 29PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 30PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 31PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 32PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the beams...Ch. 10.4 - Determine, g, which locates the centroidal axis z...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 36PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 37PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 38PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 39PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 41PCh. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the beams...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 43PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 44PCh. 10.4 - Determine the distance x to the centroid C of the...Ch. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the area about...Ch. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the area about...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 50PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the...Ch. 10.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the...Ch. 10.7 - Determine the product of inertia of the thin strip...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 55PCh. 10.7 - Determine the product of inertia of the shaded...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 57PCh. 10.7 - Determine the product of inertia of the shaded...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 59PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 60PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 62PCh. 10.7 - Determine the product of inertia for the beams...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 64PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 65PCh. 10.7 - Determine the product of inertia of the cross...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 67PCh. 10.7 - For the calculation, assume all comers to be...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 69PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 70PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 71PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 72PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 73PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 74PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 75PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 76PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 77PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 78PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 79PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 80PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 81PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 82PCh. 10.7 - using Mohrs circle.Ch. 10.8 - Determine the moment of inertia of the thin ring...Ch. 10.8 - The material has a constant density .Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 86PCh. 10.8 - Determine the radius of gyration kx of the...Ch. 10.8 - The material has a constant density .Ch. 10.8 - Hint: For integration, use thin plate elements...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 90PCh. 10.8 - Prob. 91PCh. 10.8 - Determine the moment of inertia Iy. The specific...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 93PCh. 10.8 - The total mass of the solid is 1500 kg.Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 95PCh. 10.8 - Prob. 96PCh. 10.8 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 98PCh. 10.8 - 15 lb. and 20 lb, respectively, determine the mass...Ch. 10.8 - The density of the material is 7.85 Mg/m3.Ch. 10.8 - The material has a density of 200kg/m3. Prob....Ch. 10.8 - The pendulum consists of a plate having a weight...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 103PCh. 10.8 - The material has a density of 200kg/m3.Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 105PCh. 10.8 - Determine its mass moment of inertia about the y...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 107PCh. 10.8 - Prob. 108PCh. 10.8 - Prob. 109PCh. 10.8 - Determine the moment of inertia for the shaded...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 111RPCh. 10.8 - Determine the product of inertia of the shaded...Ch. 10.8 - Determine the area moment of inertia of the...Ch. 10.8 - Determine the area moment of inertia of the shaded...Ch. 10.8 - Determine the moment of inertia for the shaded...Ch. 10.8 - Prob. 117RPCh. 10.8 - Prob. 119RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- My ID#016948724 please solve this problems and show me every step clear to follow pleasearrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward[Q2]: The cost information supplied by the cost accountant is as follows:Sales 20,00 units, $ 10 per unitCalculate the (a/ newsale guantity and (b) new selling price to earn the sameVariable cost $ 6 per unit, Fixed Cost $ 30,000, Profit $ 50,000profit ifi) Variable cost increases by $ 2 per unitil) Fixed cost increase by $ 10,000Ili) Variable cost increase by $ 1 per unit and fixed cost reduces by $ 10,000arrow_forward
- can you please help me perform Visual Inspection and Fractography of the attatched image: Preliminary examination to identify the fracture origin, suspected fatigue striation, and corrosion evidences.arrow_forwardcan you please help[ me conduct Causal Analysis (FTA) on the scenario attatched: FTA diagram which is a fault tree analysis diagram will be used to gain an overview of the entire path of failure from root cause to the top event (i.e., the swing’s detachment) and to identify interactions between misuse, material decay and inspection errors.arrow_forwardhi can you please help me in finding the stress intensity factor using a k-calcluator for the scenario attathced in the images.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical Design (Machine Design) Clutches, Brakes and Flywheels Intro (S20 ME470 Class 15); Author: Professor Ted Diehl;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eMvbePrsT34;License: Standard Youtube License