
Linear Algebra and Its Applications (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321982384
Author: David C. Lay, Steven R. Lay, Judi J. McDonald
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.2, Problem 20E
Consider the mouse in the following maze, which includes “one-way” doors.
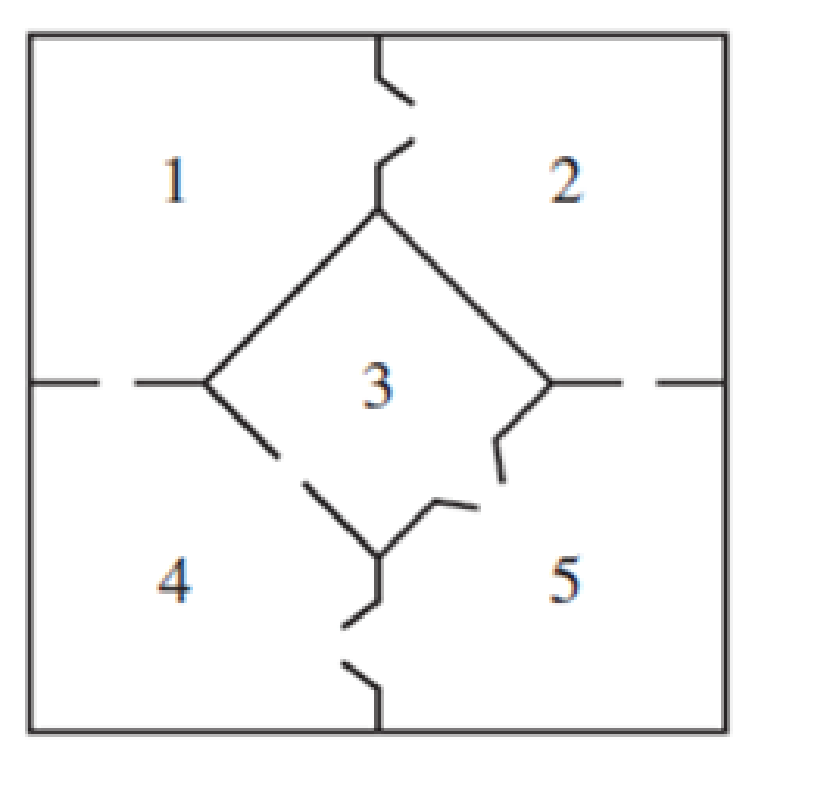
What fraction of the time does the mouse spend in each of the rooms in the maze?
In Exercises 19 and 20, suppose a mouse wanders through the given maze, some of whose doors are “one-way”: they are just large enough for the mouse to squeeze through in only one direction. The mouse still must move into a different room at each time step if possible. When faced with accessible openings into two or more rooms, the mouse chooses them with equal probability.
20. The mouse is placed in room 1 of the maze shown below.
- a. Construct a transition matrix and an initial probability
vector for the mouse’s travels. - b. What are the probabilities that the mouse will be in each of the rooms after 3 moves?
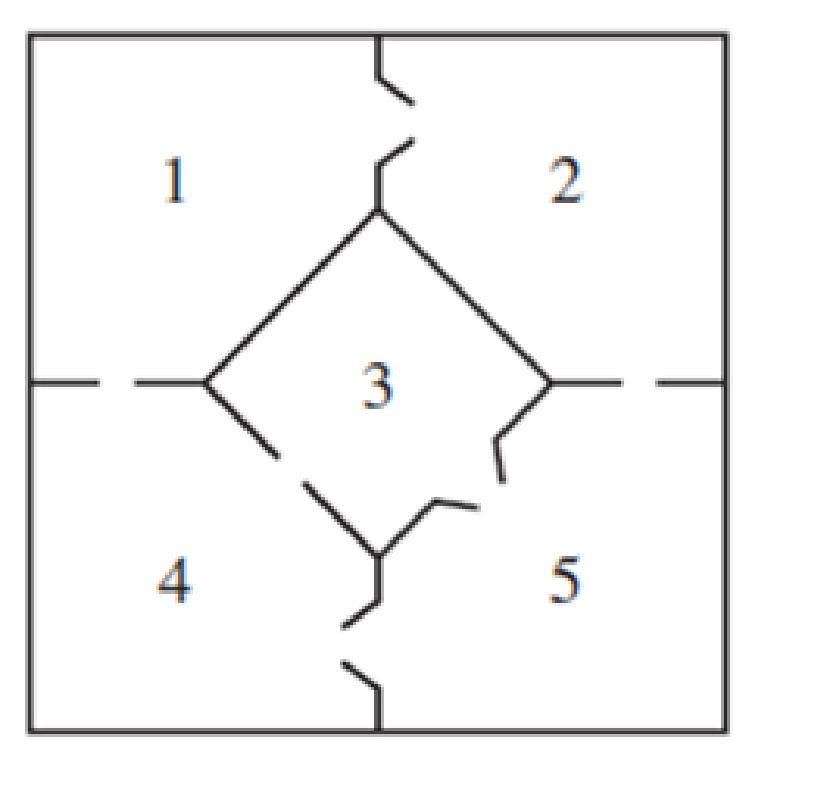
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Pls help.
Pls help.
Pls help.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Linear Algebra and Its Applications (5th Edition)
Ch. 10.1 - Fill in the missing entries in the stochastic...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 2PPCh. 10.1 - In Exercises 1 and 2, determine whether P is a...Ch. 10.1 - In Exercises 1 and 2, determine whether P is a...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.1 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.1 - In Exercises 5 and 6, the transition matrix P for...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.1 - In Exercises 7 and 8, the transition matrix P for...Ch. 10.1 - In Exercises 7 and 8, the transition matrix P for...
Ch. 10.1 - Consider a pair of Ehrenfest urns labeled A and B....Ch. 10.1 - Consider a pair of Ehrenfest urns labeled A and B....Ch. 10.1 - Consider an unbiased random walk on the set...Ch. 10.1 - Consider a biased random walk on the set {1,2,3,4}...Ch. 10.1 - In Exercises 13 and 14, find the transition matrix...Ch. 10.1 - In Exercises 13 and 14, find the transition matrix...Ch. 10.1 - In Exercises 15 and 16, find the transition matrix...Ch. 10.1 - In Exercises 15 and 16, find the transition matrix...Ch. 10.1 - The mouse is placed in room 2 of the maze shown...Ch. 10.1 - The mouse is placed in room 3 of the maze shown...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 19ECh. 10.1 - In Exercises 19 and 20, suppose a mouse wanders...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 10.1 - In Exercises 21 and 22, mark each statement True...Ch. 10.1 - The weather in Charlotte, North Carolina, can be...Ch. 10.1 - Suppose that whether it rains in Charlotte...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 25ECh. 10.1 - Consider a set of five webpages hyperlinked by the...Ch. 10.1 - Consider a model for signal transmission in which...Ch. 10.1 - Consider a model for signal transmission in which...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 29ECh. 10.1 - Another model for diffusion is called the...Ch. 10.1 - To win a game in tennis, one player must score...Ch. 10.1 - Volleyball uses two different scoring systems in...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 33ECh. 10.2 - Consider the Markov chain on {1, 2, 3} with...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 1 and 2, consider a Markov chain on...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.2 - In Exercises 3 and 4, consider a Markov chain on...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.2 - In Exercises 5 and 6, find the matrix to which Pn...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 7 and 8, determine whether the given...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.2 - Consider a pair of Ehrenfest urns with a total of...Ch. 10.2 - Consider a pair of Ehrenfest urns with a total of...Ch. 10.2 - Consider an unbiased random walk with reflecting...Ch. 10.2 - Consider a biased random walk with reflecting...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 13ECh. 10.2 - In Exercises 13 and 14, consider a simple random...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 15 and 16, consider a simple random...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 15 and 16, consider a simple random...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 17ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 18ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 19ECh. 10.2 - Consider the mouse in the following maze, which...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 21 and 22, mark each statement True...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 21 and 22, mark each statement True...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 23ECh. 10.2 - Suppose that the weather in Charlotte is modeled...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 25 and 26, consider a set of webpages...Ch. 10.2 - In Exercises 25 and 26, consider a set of webpages...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 27ECh. 10.2 - Consider beginning with an individual of known...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 29ECh. 10.2 - Consider the Bernoulli-Laplace diffusion model...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 31ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 32ECh. 10.2 - Prob. 33ECh. 10.2 - Let 0 p, q 1, and define P = [p1q1pq] a. Show...Ch. 10.2 - Let 0 p, q 1, and define P = [pq1pqq1pqp1pqpq]...Ch. 10.2 - Let A be an m m stochastic matrix, let x be in m...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 37ECh. 10.2 - Consider a simple random walk on a finite...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 39ECh. 10.3 - Consider the Markov chain on {1, 2, 3, 4} with...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.3 - In Exercises 16, consider a Markov chain with...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.3 - Consider the mouse in the following maze from...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.3 - Consider an unbiased random walk with absorbing...Ch. 10.3 - In Exercises 13 and 14, consider a simple random...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.3 - In Exercises 15 and 16, consider a simple random...Ch. 10.3 - In Exercises 15 and 16, consider a simple random...Ch. 10.3 - Consider the mouse in the following maze from...Ch. 10.3 - Consider the mouse in the following maze from...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 19ECh. 10.3 - In Exercises 19 and 20, consider the mouse in the...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 21ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 22ECh. 10.3 - Suppose that the weather in Charlotte is modeled...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 24ECh. 10.3 - The following set of webpages hyperlinked by the...Ch. 10.3 - The following set of webpages hyperlinked by the...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 27ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 28ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 29ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 30ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 31ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 32ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 33ECh. 10.3 - In Exercises 33 and 34, consider the Markov chain...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 35ECh. 10.3 - Prob. 36ECh. 10.4 - Consider the Markov chain on {1, 2, 3, 4} with...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 1-6, consider a Markov chain with...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 1-6, consider a Markov chain with...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 1-6, consider a Markov chain with...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 1-6, consider a Markov chain with...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 1-6, consider a Markov chain with...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 1-6, consider a Markov chain with...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 7-10, consider a simple random walk...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 7-10, consider a simple random walk...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 7-10, consider a simple random walk...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 7-10: consider a simple random walk...Ch. 10.4 - Reorder the states in the Markov chain in Exercise...Ch. 10.4 - Reorder the states in the Markov chain in Exercise...Ch. 10.4 - Reorder the states in the Markov chain in Exercise...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.4 - Prob. 15ECh. 10.4 - Prob. 16ECh. 10.4 - Find the transition matrix for the Markov chain in...Ch. 10.4 - Find the transition matrix for the Markov chain in...Ch. 10.4 - Consider the mouse in the following maze from...Ch. 10.4 - Consider the mouse in the following maze from...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 21-22, mark each statement True or...Ch. 10.4 - In Exercises 21-22, mark each statement True or...Ch. 10.4 - Confirm Theorem 5 for the Markov chain in Exercise...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 24ECh. 10.4 - Consider the Markov chain on {1, 2, 3} with...Ch. 10.4 - Follow the plan of Exercise 25 to confirm Theorem...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 27ECh. 10.4 - Prob. 28ECh. 10.4 - Prob. 29ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 1PPCh. 10.5 - Consider a Markov chain on {1, 2, 3, 4} with...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.5 - In Exercises 13, find the fundamental matrix of...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 7ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.5 - Consider a simple random walk on the following...Ch. 10.5 - Consider a simple random walk on the following...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 15ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 16ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 17ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 18ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 19ECh. 10.5 - Consider the mouse in the following maze from...Ch. 10.5 - In Exercises 21 and 22, mark each statement True...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 22ECh. 10.5 - Suppose that the weather in Charlotte is modeled...Ch. 10.5 - Suppose that the weather in Charlotte is modeled...Ch. 10.5 - Consider a set of webpages hyperlinked by the...Ch. 10.5 - Consider a set of webpages hyperlinked by the...Ch. 10.5 - Exercises 27-30 concern the Markov chain model for...Ch. 10.5 - Exercises 27-30 concern the Markov chain model for...Ch. 10.5 - Exercises 27-30 concern the Markov chain model for...Ch. 10.5 - Exercises 27-30 concern the Markov chain model for...Ch. 10.5 - Exercises 31-36 concern the two Markov chain...Ch. 10.5 - Exercises 31-36 concern the two Markov chain...Ch. 10.5 - Exercises 31-36 concern the two Markov chain...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 34ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 35ECh. 10.5 - Prob. 36ECh. 10.5 - Consider a Markov chain on {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} with...Ch. 10.5 - Consider a Markov chain on {1,2,3,4,5,6} with...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 39ECh. 10.6 - Let A be the matrix just before Example 1. Explain...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 2PPCh. 10.6 - Prob. 1ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 2ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 3ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 4ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 5ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 6ECh. 10.6 - Major League batting statistics for the 2006...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 8ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 9ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 10ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 11ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 12ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 14ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 15ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 16ECh. 10.6 - Prob. 17ECh. 10.6 - In the previous exercise, let p be the probability...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pls help.arrow_forwardSolve the system of equation for y using Cramer's rule. Hint: The determinant of the coefficient matrix is -23. - 5x + y − z = −7 2x-y-2z = 6 3x+2z-7arrow_forwarderic pez Xte in z= Therefore, we have (x, y, z)=(3.0000, 83.6.1 Exercise Gauss-Seidel iteration with Start with (x, y, z) = (0, 0, 0). Use the convergent Jacobi i Tol=10 to solve the following systems: 1. 5x-y+z = 10 2x-8y-z=11 -x+y+4z=3 iteration (x Assi 2 Assi 3. 4. x-5y-z=-8 4x-y- z=13 2x - y-6z=-2 4x y + z = 7 4x-8y + z = -21 -2x+ y +5z = 15 4x + y - z=13 2x - y-6z=-2 x-5y- z=-8 realme Shot on realme C30 2025.01.31 22:35 farrow_forward
- Use Pascal's triangle to expand the binomial (6m+2)^2arrow_forwardListen A falling object travels a distance given by the formula d = 6t + 9t2 where d is in feet and t is the time in seconds. How many seconds will it take for the object to travel 112 feet? Round answer to 2 decimal places. (Write the number, not the units). Your Answer:arrow_forwardSolve by the quadratic formula or completing the square to obtain exact solutions. 2 e 104 OA) -16±3√6 B) 8±√10 O c) -8±√10 OD) 8±3√√6 Uarrow_forward
- Question 14 (1 point) Listen The frame on a picture is 18 in by 22 in outside and is of uniform width. Using algebraic methods, what is the width of the frame if the inner area of the picture shown is 250 in²2? Write answer to 2 decimal places. (Write the number with no units). 18 in Your Answer: 22 inarrow_forward◄ Listen A vacant lot is being converted into a community garden. The garden and a walkway around its perimeter have an area of 560 square feet. Find the width of the walkway (x) if the garden measures 15 feet wide by 19 feet long. Write answer to 2 decimal places. (Write the number without units). X 15 feet Your Answer: 19 feet Xarrow_forwardListen A stuntman jumps from a roof 440 feet from the ground. How long will it take him to reach the ground? Use the formula, distance, d = 16t2, (where t is in seconds). Write answer to 1 decimal place. (Write the number, not the units). Your Answer:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305657960
Author:Joseph Gallian
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:9780135163078
Author:Michael Sullivan
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:9780980232776
Author:Gilbert Strang
Publisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:9780077836344
Author:Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Finite Math: Markov Chain Example - The Gambler's Ruin; Author: Brandon Foltz;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=afIhgiHVnj0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Introduction: MARKOV PROCESS And MARKOV CHAINS // Short Lecture // Linear Algebra; Author: AfterMath;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qK-PUTuUSpw;License: Standard Youtube License
Stochastic process and Markov Chain Model | Transition Probability Matrix (TPM); Author: Dr. Harish Garg;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sb4jo4P4ZLI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY