
A spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and F of the linkage shown. Neglecting the weight of the spring and linkage, determine the force in the spring and the vertical motion of point G when a vertical downward 120-N force is applied (a) at point C, (b) at points C and H.
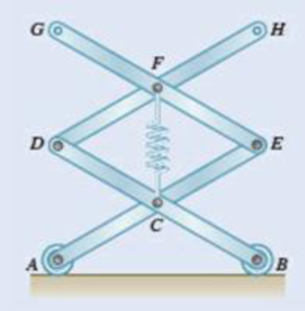
Fig. P10.5 and P10.6
(a)
Find the force in the spring and the vertical motion of point G when a vertical load of
Answer to Problem 10.5P
The force in the spring is
The vertical motion of point G is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The spring constant is
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the spring assembly as in Figure 1.
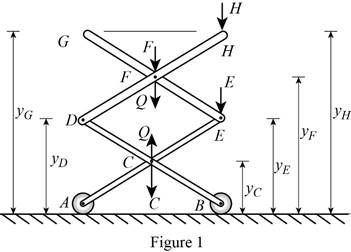
Write the relation of the deflections at point G, H, F, E, D with C as follows;
The deflection
Assume the spring force Q is in tension.
Find the force in the spring Q using the relation.
Here, the spring constant is k.
Substitute
Use the virtual work principle:
Here,
Substitute 120 N for C,
The spring force Q is in compression. The assumption is incorrect.
Therefore, the force in the spring is
Substitute –60 N for Q in Equation (1).
Find the vertical motion
Substitute –2 mm for
Therefore, the vertical motion of point G is
(b)
Find the force in the spring and the vertical motion of point G when a vertical load of
Answer to Problem 10.5P
The force in the spring is
The vertical motion of point G is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The spring constant is
Calculation:
Use the virtual work principle:
Here,
Substitute 120 N for C,
The spring force Q is in compression. The assumption is incorrect.
Therefore, the force in the spring is
Substitute –300 N for Q in Equation (1).
Find the vertical motion
Substitute –10 mm for
Therefore, the vertical motion of point G is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
VECTOR MECH....F/ENGNRS-STATICS -CONNECT
- For the shown frame and loads P=972 KN and Q=1944 KN, 3 m 3 m→ B 1.5 m A 1 m 8 m 6 m magnitude of y-component of reaction at B (KN) a. 216 b. 270 c. 324 d. 337.5 е. 378 magnitude of x-component of reaction at B (KN) a. 5616 b. 2808 c. 7020 d. 8424 e. 9828 magnitude of x-component of reaction at C (KN) magnitude of y-component of reaction at C (KN) magnitude of y-component of reaction at A (KN)arrow_forwardA baseball attachment that helps people with mobility impairments play T-ball and baseball is powered by a spring that is unstretched at position 2. The spring is attached to a cord that is fastened to point B on the 75-mm radius pulley. The pulley is fixed at point O , rotates backwards to the cocked position at 0 , and the rope wraps around the pulley and stretches the spring with a stiffness of k = 2000 N/m. The combined mass moment of inertia of all the rotating components about point O is 0.40 kg·m2. The swing is timed perfectly to strike a 145-gram baseball travelling with a speed of V0 = 10 m/s at a distance of h = 0.7 m away from point O. Knowing that the coefficient of restitution between the bat and ball is 0.59, determine the velocity of the baseball immediately after the impact. Assume that the ball is travelling primarily in the horizontal plane and that its spin is negligible.arrow_forward3. (a) A 15 kg rod AB of length 2.5 m and a uniform cross section, is held in equilibrium as shown in the following figure, with one end against a vertical wall and the other attached to a cord AC. Knowing that the coefficient of friction between the rod and the wall are ug = 0.37 and Hg = 0.23, determine the range of values of the length L of the cord for which equilibrium is maintained. 1.5 m B -2.5 m-arrow_forward
- Please solve this question in handwriting step by step .arrow_forwardThe control rod CE passes through a horizontal hole in the body of the toggle system shown. Knowing that link BD is 250 mm long, determine the force Q required to hold the system in equilibrium when β= 20°.arrow_forwardKnowing that the radius of each pulley is 200 mm and neglecting friction, determine the internal forces at point J of the frame shown.arrow_forward
- Referring to Prob. 10.43 and using the value found for the force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder CD , determine the change in the length of CD required to raise the 10-kN load by 15 mm.Reference to Problem 10.43:arrow_forwardPlease answer this NEATLY, COMPLETELY, and CORRECTLY for an UPVOTE. A pulley assembly is designed to measure the weight of block F using a counterweight. Springs G and H (k = 960 N/m) are compressed by 0.2 meters. Knowing that the system is in equilibrium, determine the mass of block F. Also, determine the tension carried by cable AI and the forces from bar A and bar C. Notes!There's a single cable from point J to point B. This cable is not attached to the cable from C to F. This cable is also not attached to the horizontal bar at C. There's also a single cable running from A to block M. This cable is not attached to the horizontal bar at A. L is also a block with mass 41 kg.arrow_forwardmodified book exercise: Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics (8th Edition) chapter 4 and exercise 12 Four boxes are placed on a 17,7 kg uniform wooden plank that rests on two trestles. Knowing that the masses of boxes B and D are 2.5 kg and 32 kg, determine, respectively, the range of values for the mass of box A so that the plate remains in equilibrium when box C is removed. answer 1 2 kg found ≤ma ≤ 196.4kg( I don't know if this is correct)arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





