
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure with the lowest formal charges of
Concept introduction:
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Formula to calculate the formal charge of the atom is as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.5BFP
Lewis structure with lowest formal charges for
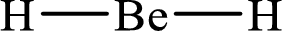
The formal charge on
The formal charge on each
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons of
Substitute 3 for the total number of
The Lewis structure of
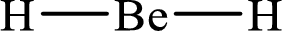
Substitute 2 for the number of valence electrons, 0 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 1 for the number of valence electrons, 0 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each hydrogen atom.
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure with the lowest formal charges of
Concept introduction:
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Formula to calculate the formal charge of the atom is as follows:
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.5BFP
The Lewis structure of
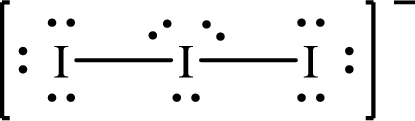
The formal charge on central
The formal charge on the terminal
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons of
Substitute 3 for the total number of
The Lewis structure of
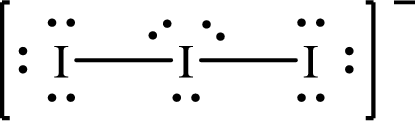
Substitute 7 for the number of valence electrons, 6 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on the central
Substitute 7 for the number of valence electrons, 6 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each terminal
Only one Lewis structure is possible for
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure with the lowest formal charges of
Concept introduction:
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Formula to calculate the formal charge of the atom is as follows:
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.5BFP
Lewis structure of
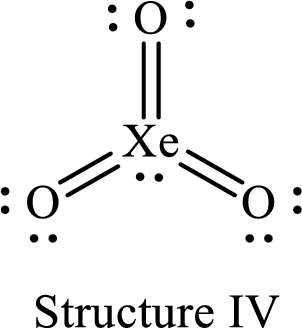
The formal charge on
The formal charge on each
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structures of
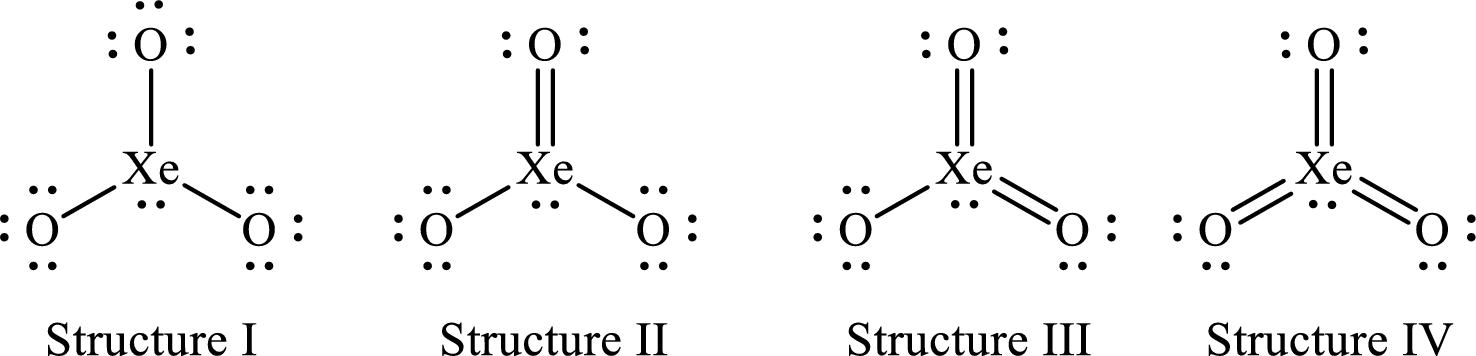
For structure I:
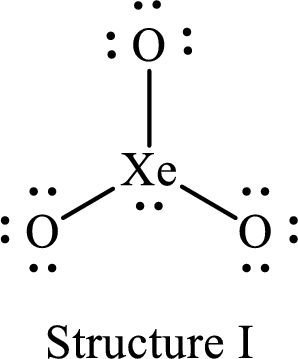
Substitute 8 for the number of valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 6 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for the number of valence electrons, 6 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each single bonded oxygen atom.
For structure II:
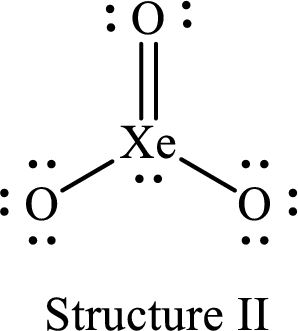
Substitute 8 for the number of valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 8 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for the number of valence electrons, 6 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each single bonded oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for the number of valence electrons, 4 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on the double bonded oxygen atom.
For structure III:
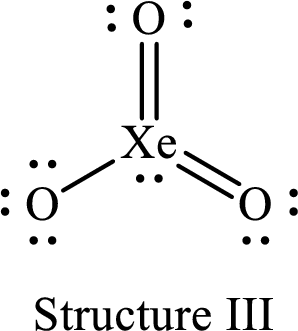
Substitute 8 for the number of valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 10 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for the number of valence electrons, 6 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on the single bonded oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for the number of valence electrons, 4 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each double bonded oxygen atom.
For structure IV:
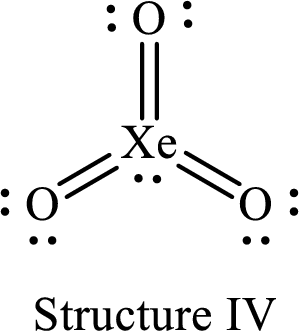
Substitute 8 for the number of valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 12 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for the number of valence electrons, 4 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each double bonded oxygen atom.
Four Lewis structures are possible for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
CHEM 212:STUDENT SOLUTION MANUAL
- Can you help me understand the CBC method on metal bridging by looking at this problem?arrow_forwardA partir de Aluminio y Co(NO3)2ꞏ6H2O, indicar las reacciones a realizar para obtener Azul de Thenard (Al2CoO4).arrow_forwardTo obtain Thenard Blue (Al2CoO4), the following reaction is correct (performed in an oven):Al(OH)3 + Co(OH)2 → Al2CoO4 + 4 H2Oarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





