
Concept explainers
Shumaker Company manufactures a line of high-top basketball shoes. At the beginning of the year, the following plans for production and costs were revealed:

During the year, a total of 50,000 units were produced and sold. The following actual costs were incurred:
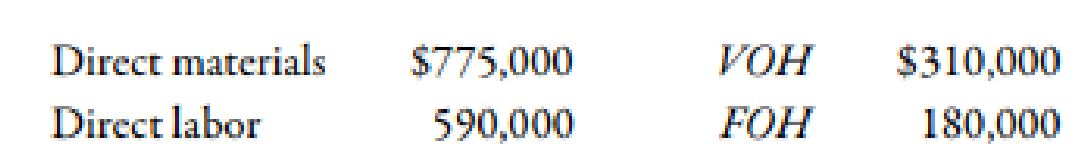
There were no beginning or ending inventories of raw materials. In producing the 50,000 units 63,000 hours were worked, 5% more hours than the standard allowed for the actual output.
Required:
- 1. Using a flexible budget, prepare a performance report comparing expected costs for the actual production with actual costs.
- 2. Determine the following: (a) Fixed overhead spending and volume variances and (b) Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.
1.
Construct the performance report by comparing the expected costs for the actual production with actual costs with the help of flexible budget.
Explanation of Solution
Flexible Budgets:
Flexible budgets are prepared for various levels of activities or outputs. This enables the entity to know the result for the selected level of activity.
Performance report of the variances:
| Budgeted variance | |||
| Overhead cost item |
Actual cost (A) ($) |
Actual Costs (B) ($) |
Spending variance ($) |
| Direct material | 775,000 | 750,0001 | 25,000 (U) |
| Direct labor | 590,000 | 600,0002 | 10,000 (F) |
| Variable overhead | 310,000 | 300,0003 | 10,000 (U) |
| Fixed overhead | 180,000 | 165,0004 | 15,000 (U) |
| Total | 1,855,000 | 1,815,000 | 40,000 (U) |
Table (1)
Working Note:
1. Calculation of actual cost of direct material:
2. Calculation of actual cost of direct labor:
3. Calculation of actual cost of variable overhead:
4. Calculation of actual cost of fixed overhead:
2.
Calculate the value of fixed overhead spending and volume variance. Also, calculate the value of variable overhead spending and efficiency variance.
Explanation of Solution
(a).
Use the following formula to calculate fixed overhead spending variance:
Substitute $180,000 for actual fixed overhead and $165,000 for budgeted fixed overhead in the above formula.
Therefore, the fixed overhead spending variance is $15,000 (U).
Use the following formula to calculate volume variance:
Substitute $165,000 for budgeted fixed overhead, $2.50 for fixed overhead rate and $60,000 for standard hours in the above formula.
Therefore, the volume variance is $15,000 (U).
(b).
Use the following formula to calculate variable overhead spending variance:
Substitute $310,000 for actual overhead, $5.00 for standard variable overhead and 63,000 hours for actual hours in the above formula.
Therefore, the variable overhead spending variance is $5,000 (F).
Use the following formula to calculate variable efficiency variance:
Substitute 63,000 hours for actual hours, 60,000 hours for standard hours and $5.00 for applied variable overhead in the above formula.
Therefore, the efficiency variance is $15,000 (U).
Working Note:
1. Calculation of standard hours:
2. Calculation of fixed overhead rate:
First, hours allowed computed so as calculating the fixed overhead rate:
3. Calculation of variable overhead rate
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making, Loose-Leaf Version, 7th + CengageNOWv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub



