
Concept explainers
Suppose that at time zero the can attached to the spring such as shown in Figure 10.8 is released from rest at position
Figure 10.8 Dynamics of
(a)
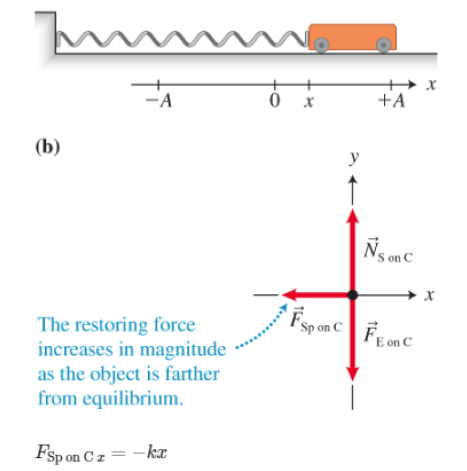
The spring is the only object that exerts a force with a nonzero x-component on the cart. Thus the x-component form of Newton's second
We now understand why the acceleration-versus-time graph in Figure 10.4c is the same shape as the position-versus-time graph in Figure 10.4a with the sign of a being opposite me sign of x at all times the restoring force exerted can the vibrating object is proportional to the displacement of the object from equilibrium but opposite in direction. Whenever this relation holds for a system, that system's motion can be described mathematically as simple harmonic motion.
Stop for a moment and think how unusual Eq. (10.6) is. When we studied linear motion at constant acceleration (Chapter 2 ). the acceleration of a moving object was the same at any location and did not depend on the position When we studied constant speed circular motion (Chapter 5). the direction of acceleration charged with changing positon along the circle. but the magnitude remained the same. In SHM the acceleration of an object changes in time in both magnitude and direction but is synchronized with the displacement of the object Thus the sum of the forces exerted on an object moving in a circle at constant speed is constant in magnitude and only changes direction (it always ports toward the center of the circle). The sum of the forces exerted on an object undergoing SHM not only changes direction during the motion but a so changes magnitude.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
College Physics: Explore And Apply, Volume 2 (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
- Make a plot of the acceleration of a ball that is thrown upward at 20 m/s subject to gravitation alone (no drag). Assume upward is the +y direction (and downward negative y).arrow_forwardLab Assignment #3 Vectors 2. Determine the magnitude and sense of the forces in cables A and B. 30° 30° 300KN 3. Determine the forces in members A and B of the following structure. 30° B 200kN Name: TA: 4. Determine the resultant of the three coplanar forces using vectors. F₁ =500N, F₂-800N, F, 900N, 0,-30°, 62-50° 30° 50° F₁ = 500N = 900N F₂ = 800Narrow_forwardLab Assignment #3 Vectors Name: TA: 1. With the equipment provided in the lab, determine the magnitude of vector A so the system is in static equilibrium. Perform the experiment as per the figure below and compare the calculated values with the numbers from the spring scale that corresponds to vector A. A Case 1: Vector B 40g Vector C 20g 0 = 30° Vector A = ? Case 2: Vector B 50g Vector C = 40g 0 = 53° Vector A ? Case 3: Vector B 50g Vector C 30g 0 = 37° Vector A = ?arrow_forward
- Three point-like charges are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 20.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between q1 and q2 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (A). Let q1=-1.30 µC, q2=-4.20µC, and q3= +4.30 µC. __________________ N/Carrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forward
- The position of a coffee cup on a table as referenced by the corner of the room in which it sits is r=0.5mi +1.5mj +2.0mk . How far is the cup from the corner? What is the unit vector pointing from the corner to the cup?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardFind the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. HF 5.0 µF 3.5 µF №8.0 μLE 1.5 µF Ι 0.75 μF 15 μFarrow_forward
- the answer is not 0.39 or 0.386arrow_forwardFind the total capacitance in micro farads of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure below. 2.01 0.30 µF 2.5 µF 10 μF × HFarrow_forwardI do not understand the process to answer the second part of question b. Please help me understand how to get there!arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





