
Concept explainers
A tiny solid ball
![Chapter 10, Problem 55SP, 10.55 [II] A tiny solid ball rolls without slipping on the inside surface of a hemisphere as shown](https://content.bartleby.com/tbms-images/9781259587399/Chapter-10/images/87399-10-55sp-question-digital_image54.png)
Fig. 10-12
(a)
The speed of the ball as it passes through the point B as shown in Fig. 10-12.
Answer to Problem 55SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The moment of inertia of the solid ball is
The ball is released at point A. Therefore, the value of the initial velocity at that point is zero.
The movement of ball is as shown in Fig. 10-12;itfollows a circular path of radius
Formula used:
Write the expression for calculating thepotential energy of an object:
Here,
Write the expression for the total kinetic energy of a rolling object:
Here,
Write the expression for total energy of system:
Here,
Write the expression for conservation of energy:
Here,
Write the expression for linear velocity in terms of angular velocity:
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the arrangement of the system shown in Fig 1:
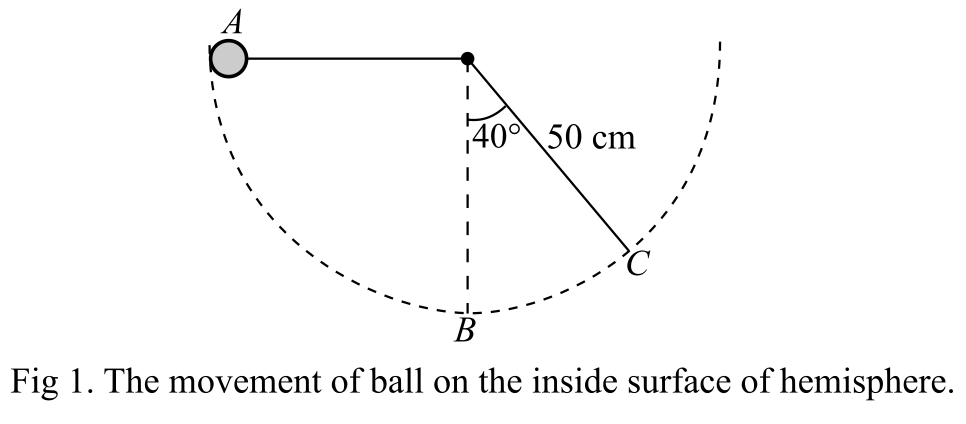
Consider the point B be the reference point, that is, the height of the ball is measured with respect to this point.
The expression forpotential energy of the ball at point A is
Here,
For point A, substitute
The expression forpotential energy of ball at point B is
Here,
For point B, substitute
The expression for the total kinetic energy of theball at point A is
Here,
Since the ball is released from rest at point A, its initial velocity is zero.
For point A, substitute
The expression for linear velocity in terms of angular velocity at point B is
Here,
At point B, substitute
Solve for
The expression for the total kinetic energy of ball at point B is
Here,
For point B, substitute
The expression for total energy of the system at point A is
Here,
At point A, substitute
The expression for the total energy of the system at point B is
Here,
At point B, substitute
The expression for conservation of energy for the point of observation A and point B is
Substitute
Solve for
Take square root both sides:
Conclusion:
The speed of the ball as it passes through the point B is
(b)
The speed of the ball as it passes through the point Cas shown in Fig. 10-12.
Answer to Problem 55SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The moment of inertia of the solid ball is
The ball is released at point A that is the velocity of the ball at this point is zero.
The movement of ball is shown in Fig. 10-12;it follows a circular path of radius
Formula used:
Write the expression for calculating the potential energy of an object:
Here,
Write the expression for total kinetic energy of a rolling object:
Here,
Write the expression for total energy of a system:
Here,
Write the expression for conservation of energy:
Here,
Write the expression for linear velocity in terms of angular velocity:
Here,
Explanation:
Let point B be the reference point, that is, the height of the ball is measured with respect to this point.
Recall the total energy at point A from subpart (a):
The expression forpotential energy of ball at point C is
Here,
The expression for height of point C is
Here,
Substitute
For point C, substitute
The expression for total kinetic energy of a rolling object at point C is
Here,
The expression for linear velocity in terms of angular velocity is
Here,
At point C, substitute
Solve for
For point C, substitute
The expression for total energy of the system at point C is
Here,
At point C, substitute
The expression for conservation of energy for the point of observation A and C is
Substitute
Solve for
Further, solve for
Conclusion:
The speed of the ball as it passes through the point C is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forward3arrow_forward13. After a gust of wind, an orb weaver spider with a mass of 35 g, hanging on a strand of web of length L = .420 m, undergoes simple harmonic motion (SHO) with an amplitude A and period T. If the spider climbs 12.0 cm up the web without perturbing the oscillation otherwise, what is the period of oscillation, in Hz to three significant figures?arrow_forward
- 15. An object of mass m = 8.10 kg is attached to an ideal spring and allowed to hang in the earth's gravitational field. The spring stretches 23.10 cm before it reaches its equilibrium position. The mass then undergoes simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 10.5 cm. Calculate the velocity of the mass in m/s at a time t= 1.00s to three significant figures.arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly. Thank you!!arrow_forward18arrow_forward
- 1. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .14 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forward16arrow_forward11. A small charged plastic ball is vertically above another charged small ball in a frictionless test tube as shown in the figure. The balls are in equilibrium at a distance d= 2.0 cm apart. If the charge on one ball is tripled, find the new equilibrium distance between the balls in cm and report it to the proper number of significant figures.arrow_forward
- 12. The electric field at a point 1.3 cm from a small object points toward the object with a strength of 180,000 N/C. Find the object's charge q, in nC to the proper number of significant figures. k = 1/4πε0 = 8.99 × 10^9 N ∙ m^2/C^2arrow_forward14. When the potential difference between the plates of an ideal air-filled parallel plate capacitor is 35 V, the electric field between the plates has a strength of 670 V/m. If the plate area is 4.0 × 10^-2 m^2, what is the capacitance of this capacitor in pF? (ε0 = 8.85 × 10^-12 C^2/N ∙ m^2)arrow_forward10. A small styrofoam ball of mass 0.500 g is placed in an electric field of 1140 N/C pointing downward. What excess charge must be placed on the ball for it to remain suspended in the field? Report your answer in micro-Coulombs to three significant figures.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





