
1 to 7.
Prepare payroll register for Company A from the information given.
1 to 7.
Explanation of Solution
Payroll: The total payment that a company is required to pay to its employee for the services received is called as payroll.
Payroll withholding deduction: The amounts which the employer withheld from employees’ gross pay to deduct taxes such as federal income tax, state income tax, social security tax, and Medicare tax are called payroll withholding deduction.
Payroll register: A schedule which is maintained by the company to record the earnings, earnings withholdings, and net pay of each employee is referred to as payroll register.
The purpose of payroll register is used to record the following:
- Earnings of each employee.
- Taxes (Social security tax, Medicare tax, and federal income tax) and other withholdings (health insurance, and other) of each employee.
- Net pay of each employee.
Prepare payroll register for Company A as below:
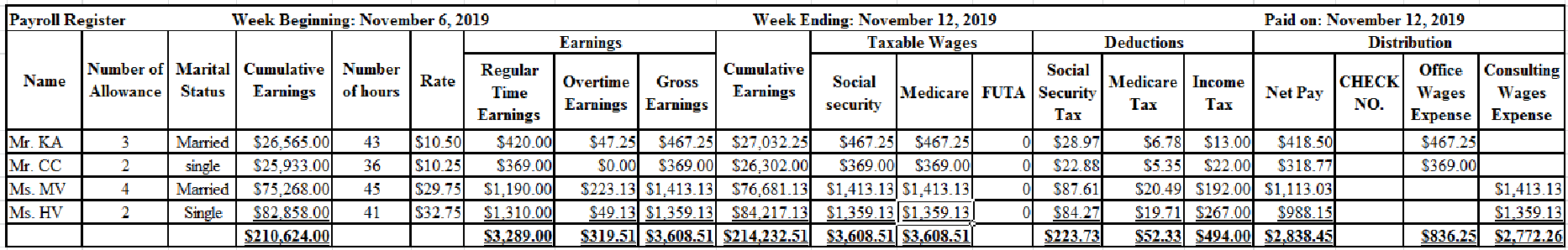
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculate regular time earnings for Mr. KA.
Calculate regular time earnings for Mr. CC.
Calculate regular time earnings for Ms. MV.
Calculate regular time earnings for Ms. HV.
Calculate overtime earnings for Mr. KA.
Calculate overtime earnings for Ms. MV.
Calculate overtime earnings for Ms. HV.
Calculate social security tax for Mr. KA.
Calculate social security tax for Mr. CC.
Calculate social security tax for Ms. MV.
Calculate social security tax for Ms. HV.
Calculate Medicare tax for Mr. KA.
Calculate Medicare tax for Mr. CC.
Calculate Medicare tax for Ms. MV.
Calculate Medicare tax for Ms. HV.
Calculate the amount of Federal income tax for Mr. KA.
Mr. KA is married, claims three withholding allowances, and earned weekly salary of $467.25. Hence, by using withholding table (Refer figure 10.2B) his Federal income tax amount would be $13.
Calculate the amount of Federal income tax for Mr. CC.
Mr. CC is single, claims two withholding allowances, and earned weekly salary of $369.00. Hence, by using withholding table (Refer figure 10.2A) his Federal income tax amount would be $22.
Notes:
- Gross earnings are calculated by using the following formula:
- Net pay is calculated by using the following formula:
8.
Journalize the entry to record the payroll on November 12, 2019.
8.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare general journal entry to record the payroll on November 12, 2019.
| General Journal | Page 32 | |||||||
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||
| 2019 | Office Wages Expense | 836.25 | ||||||
| November | 12 | Consulting Wages Expense | 2,772.26 | |||||
| Social Security Taxes Payable | 223.73 | |||||||
| Medicare Taxes Payable | 52.33 | |||||||
| Employees Income Taxes Payable | 494.00 | |||||||
| Wages Payable | 2,838.45 | |||||||
| (To record wages expense and payroll withholdings) | ||||||||
Table (2)
- Office Wages expense is an expense and it decreases equity value. So, debit it by $836.25.
- Consulting Wages expense is an expense and it decreases equity value. So, debit it by $2,772.26.
- Social security taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $223.73.
- Medicare taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $52.33.
- Employee income taxes payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $494.00.
- Wages payable is a liability and it is increased. So, credit it by $2,838.45.
9.
Journalize the entry to record the payment of weekly payroll on November 12, 2019.
9.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare general journal entry to record payment of weekly payroll on November 12, 2019.
| General Journal | Page 32 | ||||||
| Date | Accounts and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |||
| 2019 | Wages Payable | 2,838.45 | |||||
| November | 12 | Cash | 2,838.45 | ||||
| (To record the payment of weekly payroll) | |||||||
Table (3)
- Wages payable is a liability and it is decreased. So, debit it by $2,838.45.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased. So, credit it by $2,838.45.
Analyze: The total deductions taken from the employee paychecks on November 12, 2019 is $770.06
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
COLLEGE ACCOUNTING (LL)W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- General Accounting Question Solve Now plsarrow_forwardThe balance in the dividends account is closed to:A. CashB. RevenueC. Retained EarningsD. Common Stock needarrow_forwardWhat is the effect of writing off an uncollectible account under the allowance method?A. Increases net incomeB. No effect on total assetsC. Decreases revenueD. Increases expensescorrectarrow_forward
- What is the effect of writing off an uncollectible account under the allowance method?A. Increases net incomeB. No effect on total assetsC. Decreases revenueD. Increases expenses needarrow_forwardWhat is the normal balance of Accounts Payable?A. DebitB. CreditC. ZeroD. Variespls coarrow_forwardWhat is the normal balance of Accounts Payable?A. DebitB. CreditC. ZeroD. Variescorrectarrow_forward

 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





