
Activity-Based Costing of Customers
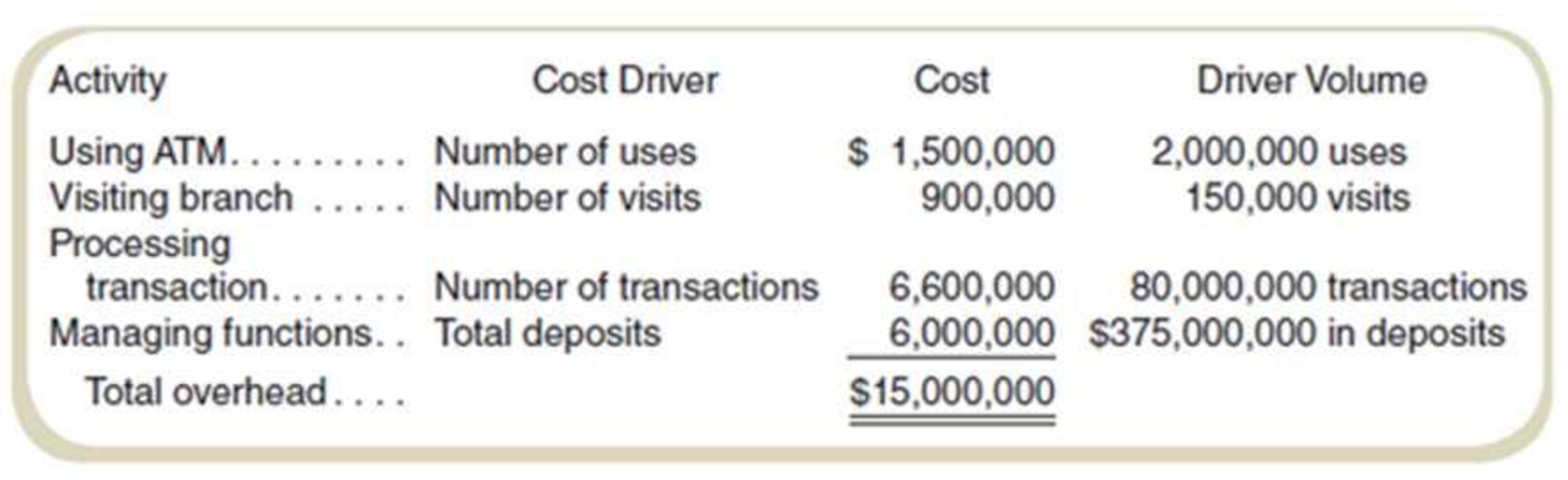
Rock Solid Bank and Trust (RSB&T) oilers only checking accounts. Customers can write checks and use a network of automated teller machines. RSB&T earns revenue by investing the money deposited; currently, it averages 5.2 percent annually on its investments of those deposits. To compete with larger banks. RSB&T pays depositors 0.5 percent on all deposits. A recent study classified the bank’s annual operating costs into four activities:
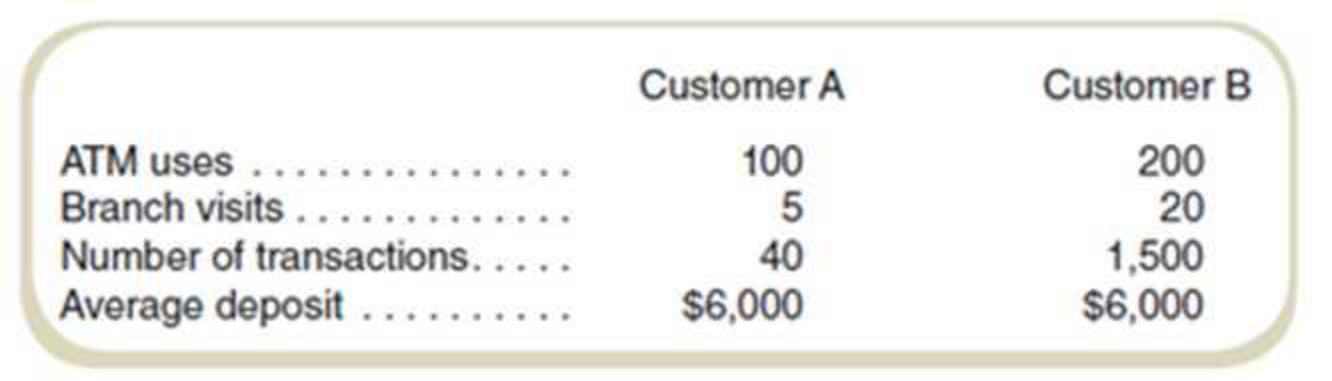
Data on two representative customers follow:
Required
- a. Compute RSB&T’s operating profits.
- b. Compute the profit from Customer A and Customer B, assuming that customer costs are based only on deposits. Interest costs = 0.5 percent of deposits; operating costs are 4 percent (= $15,000,000/$375,000,000) of deposits.
- c. Compute the profit from Customer A and Customer B, assuming that customer costs are computed using the information in the activity-based costing analysis.
a.
Compute the operating profit.
Explanation of Solution
Operating profit:
Operating profit is the amount retained by subtracting the total costs of operations occurred from the sales revenues earned.
Compute the operating profit:
| Particulars | Amount |
|
Sales revenue | $19,500,000 |
| Costs: | |
|
Interest on deposits | $1,875,000 |
| Operating costs | $15,000,000 |
|
Total costs | $16,875,000 |
|
Operating profit | $2,625,000 |
Table: (1)
b.
Compute the profit from customer A and customer B according to the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Profit:
Profit is the amount retained by subtracting the total costs from the sales revenues earned.
Compute the customer profit of both the customers:
| Particulars | Customer A | Customer B |
|
Sales revenue | $312 | $312 |
|
Interest on deposits | $30 | $30 |
|
Operating costs | $240 | $240 |
|
Customer profit | $42 | $42 |
Table: (2)
Measures that are used for computation:
| Particulars | Details |
| Deposit of customer A | $6,000 |
| Deposit of customer B | $6,000 |
| Interest earned | 5.20% |
| Interests charged | 0.50% |
| Operating cost | 4.00% |
Table: (3)
c.
Compute the profit from customer A and customer B according to the information given in the question.
Explanation of Solution
Cost driver:
Cost driver refers to the factor that causes changes in the determination of the cost of the activity.
Compute the rates required for the computation of the customer profit:
| Activity | Cost driver |
Cost |
Driver volume |
Rate |
| Use ATM | Number of uses | $1,500,000 | 2,000,000 | 0.75 |
| Visit Branch | Number of visits | $900,000 | 150,000 | 6.00 |
| Process transaction | Number of transactions | $6,600,000 | 80,000,000 | 0.0825 |
| General bank overhead | Total deposits | $6,000,000 | 375,000,000 | 1.60% |
Table: (4)
| Customer A | Customer B | |
| Activity | Amount | Amount |
|
Sales revenue | $312 | $312 |
|
Interest on deposit | $30 | $30 |
| Account margin | $282 | $282 |
| Operating costs: | ||
|
Use ATM | $75 | $150 |
|
Add: Visit branch | $30 | $120 |
|
Add: Process transaction | $3 | $124 |
|
Add: General bank overhead | $96 | $69 |
| Total operating cost | $204 | $490 |
|
Customer profit | $78 | ($208) |
Table: (5)
| Particulars | Details |
| Deposit of customer A | $6,000 |
| Deposit of customer B | $6,000 |
| Interest earned | 5.20% |
| Interests charged | 0.50% |
Table: (6)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING IA
- Provide answer accounting question with calculationarrow_forwardThe following data were taken from the records of Skysong Company for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2025. Raw Materials Inventory 7/1/24 $51,600 Accounts Receivable $35,400 Raw Materials Inventory 6/30/25 45,500 Factory Insurance 5,200 Finished Goods Inventory 7/1/24 Finished Goods Inventory 6/30/25 99,100 Factory Machinery Depreciation 17,900 22,300 Factory Utilities 31,100 Work in Process Inventory 7/1/24 29,600 Office Utilities Expense 9.450 Work in Process Inventory 6/30/25 28,100 Sales Revenue 557,100 Direct Labor 145,750 Sales Discounts 5,000 Indirect Labor 26,660 Factory Manager's Salary 65,300 Factory Property Taxes 9.710 Factory Repairs 2,200 Raw Materials Purchases 99,000 Cash 39.400arrow_forwardchois best answerarrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





