
a)
To determine: The probability of earning more than 10 percent on long-term corporate bonds.
Introduction:
The
Standard deviation refers to the variation in the actual observations from the average.
Z-Score helps to know how many numbers of standard deviations is the raw score or outcome away from the average or mean.
a)
Answer to Problem 28QP
The probability of earning more than 10 percent on long-term corporate bonds is 33.41 percent.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Assume that the returns of long-term corporate bonds have a normal distribution. The average return or mean of long-term corporate bonds is 6.4 percent, and the standard deviation is 8.4 percent (Refer to Figure 10.10 in the text).
Determine the probability of having a return greater than 10 percent on long-term government bonds:
Follow the common steps from Step 1 to Step 3 given below. Then, proceed with the Step 4.
The common steps to be followed to use the “NORM.DIST” function in Excel:
Step 1:
Open an Excel worksheet.
Step 2:
Place the cursor in cell A1.
Step 3:
Select the “Formulas” tab, and go to “More functions” in the ribbon. Under “More functions”, select “Statistical”. Under the drop-down menu of “Statistical”, select “NORM.DIST” function.
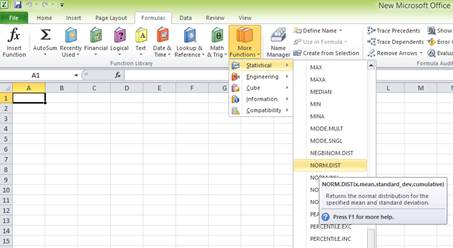
After clicking the “NORM.DIST” function, a popup window named “Function arguments” appears.
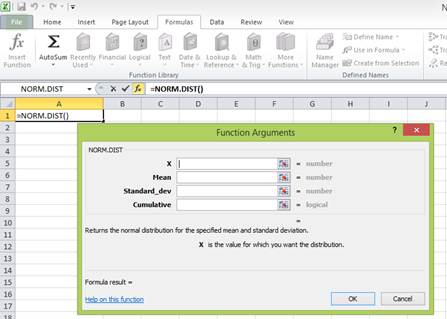
Step 4:
Enter the values. “X” represents the raw score or outcome. Here, it is necessary to test the probability of having more than 10 percent returns. Hence, “X” equals 10 percent. The mean or average return is 6.4 percent. The standard deviation is 8.4 percent. The cumulative distribution function provides the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, enter “TRUE” in the “Cumulative” column.
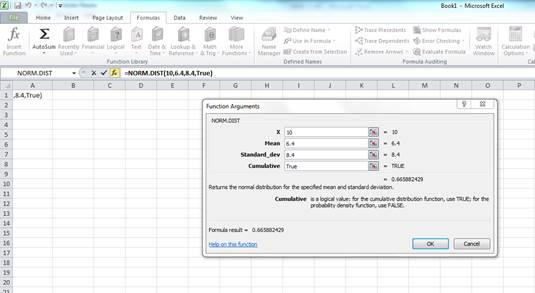
Press “OK” after providing the inputs. The probability of the area to the left of Z is as follows:
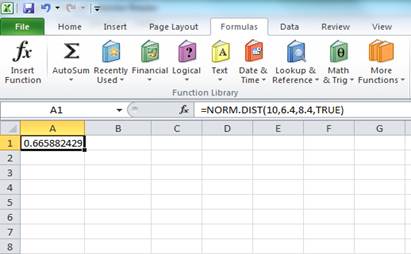
The probability of 0.665882 represents the area to the left of Z. The area to the left of Z is the probability of getting less than 10 percent return. The area to the right of Z is the probability of getting a return of 10 percent or more.
The total area represented by the normal distribution curve has a probability of “1”. The area to the left of Z has a probability of 0.665882. Hence, the probability of the area to the right of Z is “1” minus the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, the probability of getting 10 percent return or more is 0.334118 or 33.4118 percent
To determine: The probability of earning less than 0 percent on long-term corporate bonds
Answer to Problem 28QP
The probability of earning less than 0 percent on long-term corporate bonds is 0.223058 or 0.223058 percent
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Assume that the returns of long-term corporate bonds have a normal distribution. The average return or mean of long-term corporate bonds is 6.4 percent, and the standard deviation is 8.4 percent (Refer to Figure 10.10 in the text).
Determine the probability of having a return less than 0 percent on long-term government bonds:
Follow the common steps from Step 1 to Step 3 given below. Then, proceed with the Step 4.
The common steps to be followed to use the “NORM.DIST” function in Excel:
Step 1:
Open an Excel worksheet.
Step 2:
Place the cursor in cell A1.
Step 3:
Select the “Formulas” tab, and go to “More functions” in the ribbon. Under “More functions”, select “Statistical”. Under the drop-down menu of “Statistical”, select “NORM.DIST” function.
After clicking the “NORM.DIST” function, a popup window named “Function arguments” appears.
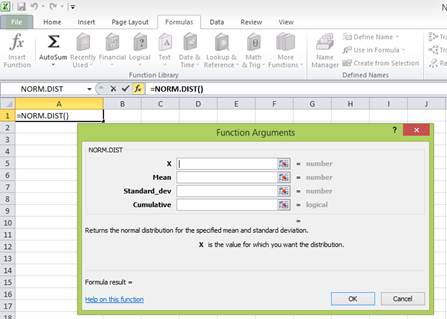
Step 4:
Enter the values. “X” represents the raw score or outcome. Here, it is necessary to test the probability of having (0 percent) return or less. Hence, “X” equals (0 percent). The mean or average return is 6.4 percent. The standard deviation is 8.4 percent. The cumulative distribution function provides the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, enter “TRUE” in the “Cumulative” column.
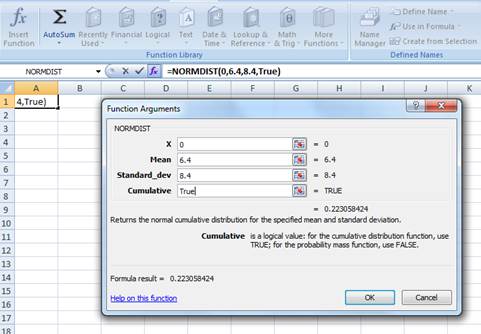
Press “OK” after providing the inputs. The probability of the area to the left of Z is as follows:
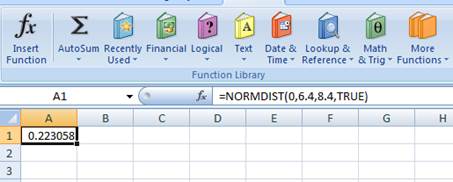
The probability of 0.223058 represents the area to the left of Z. The area to the left of Z refers to the probability of getting (0 percent) return or less because the left-hand side of the normal distribution curve indicates negative returns. Hence, the probability of earning less than 0 percent is 0.223058 or 0.223058 percent.
b)
To determine: The probability of earning more than 10 percent on Treasury bills
b)
Answer to Problem 28QP
The probability of earning more than 10 percent on Treasury bills is 0.018006785 or 1.80 percent.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Assume that the returns of Treasury bills have a normal distribution. The average return or mean of Treasury bills is 3.5 percent, and the standard deviation is 3.1 percent (Refer to Figure 10.10 in the textbook).
Determine the probability of having a return greater than 10 percent on Treasury bills:
Follow the common steps from Step 1 to Step 3 given below. Then, proceed with the Step 4.
The common steps to be followed to use the “NORM.DIST” function in Excel:
Step 1:
Open an Excel worksheet.
Step 2:
Place the cursor in cell A1.

Step 3:
Select the “Formulas” tab, and go to “More functions” in the ribbon. Under “More functions”, select “Statistical”. Under the drop-down menu of “Statistical”, select “NORM.DIST” function.
After clicking the “NORM.DIST” function, a popup window named “Function arguments” appears.
Step 4:
Enter the values. “X” represents the raw score or outcome. Here, it is necessary to test the probability of having more than 10 percent returns. Hence, “X” equals 10 percent. The mean or average return is 3.5 percent. The standard deviation is 3.1 percent. The cumulative distribution function provides the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, enter “TRUE” in the “Cumulative” column.
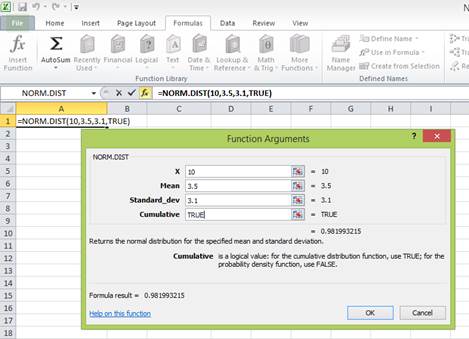
Press “OK” after providing the inputs. The probability of the area to the left of Z is as follows:
The probability of 0.981993215 represents the area to the left of Z. The area to the left of Z is the probability of getting less than 10 percent return. The area to the right of Z is the probability of getting a return of 10 percent or more.
The total area represented by the normal distribution curve has a probability of “1”. The area to the left of Z has a probability of 0.981993215. Hence, the probability of the area to the right of Z is “1” minus the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, the probability of getting 10 percent return or more is 0.018006785 or 1.80 percent
To determine: The probability of earning less than 0 percent on Treasury bills.
Answer to Problem 28QP
The probability of earning less than 0 percent on Treasury bills is 0.129442113 or 12.94 percent.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Assume that the returns of Treasury bills have a normal distribution. The average return or mean of Treasury bills is 3.5 percent, and the standard deviation is 3.1 percent (Refer to Figure 10.10 in the text).
Determine the probability of having a return less than 0 percent on Treasury bills:
Follow the common steps from Step 1 to Step 3 given below. Then, proceed with the Step 4.
The common steps to be followed to use the “NORM.DIST” function in Excel:
Step 1:
Open an Excel worksheet.
Step 2:
Place the cursor in cell A1.
Step 3:
Select the “Formulas” tab, and go to “More functions” in the ribbon. Under “More functions”, select “Statistical”. Under the drop-down menu of “Statistical”, select “NORM.DIST” function.

After clicking the “NORM.DIST” function, a popup window named “Function arguments” appears.
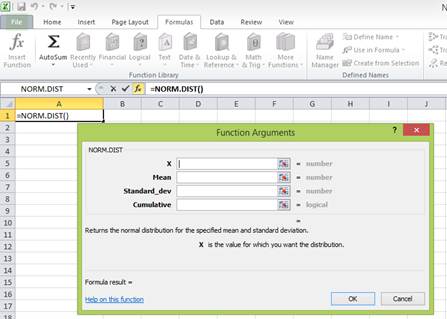
Step 4:
Enter the values. “X” represents the raw score or outcome. Here, it is necessary to test the probability of having (0 percent) return or less. Hence, “X” equals (0 percent). The mean or average return is 3.5 percent. The standard deviation is 3.1 percent. The cumulative distribution function provides the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, enter “TRUE” in the “Cumulative” column.
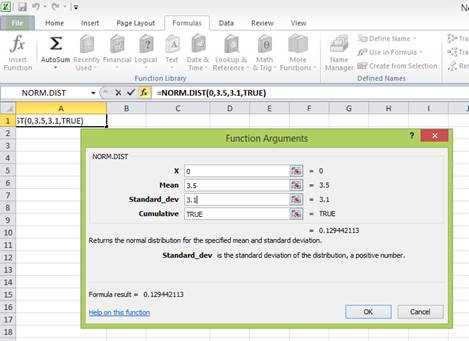
Press “OK” after providing the inputs. The probability of the area to the left of Z is as follows:
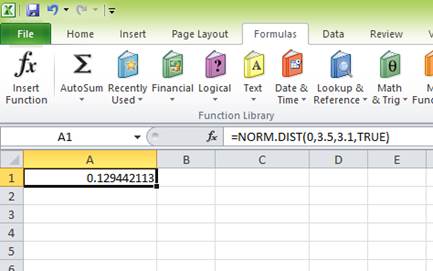
The probability of 0.129442113 represents the area to the left of Z. The area to the left of Z refers to the probability of getting (0 percent) return or less because the left-hand side of the normal distribution curve indicates negative returns. Hence, the probability of earning less than 0 percent is 0.129442113 or 12.94 percent.
c)
To determine: The probability of earning (4.18 percent) on long-term corporate bonds.
c)
Answer to Problem 28QP
The probability of earning (4.18 percent) on long-term corporate bonds is 0.1039 or 10.39 percent.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Assume that the returns of long-term corporate bonds have a normal distribution. The average return or mean of long-term corporate bonds is 6.4 percent, and the standard deviation is 8.4 percent (Refer to Figure 10.10 in the textbook).
Determine the probability of having (4.18 percent) on long-term government bonds:
Follow the common steps from Step 1 to Step 3 given below. Then, proceed with the Step 4.
The common steps to be followed to use the “NORM.DIST” function in Excel:
Step 1:
Open an Excel worksheet.
Step 2:
Place the cursor in cell A1.
Step 3:
Select the “Formulas” tab, and go to “More functions” in the ribbon. Under “More functions”, select “Statistical”. Under the drop-down menu of “Statistical”, select “NORM.DIST” function.

After clicking the “NORM.DIST” function, a popup window named “Function arguments” appears.

Step 4:
Enter the values. “X” represents the raw score or outcome. Here, it is necessary to test the probability of having (4.18 percent) return or less. Hence, “X” equals (4.18 percent). The mean or average return is 6.4 percent. The standard deviation is 8.4 percent. The cumulative distribution function provides the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, enter “TRUE” in the “Cumulative” column.
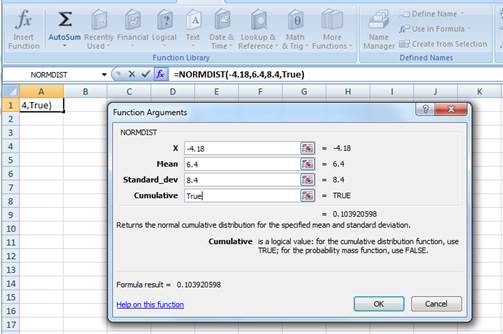
Press “OK” after providing the inputs. The probability of the area to the left of Z is as follows:
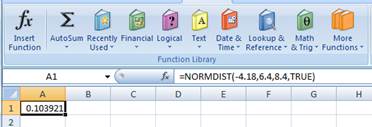
The probability of 0.103921 represents the area to the left of Z. The area to the left of Z refers to the probability of getting (4.18 percent) return or less because the left-hand side of the normal distribution curve indicates negative returns. Hence, the probability of earning (4.18 percent) is 0.1039 or 10.39 percent.
To determine: The probability of earning 10.56 percent on Treasury bills.
Answer to Problem 28QP
The probability of earning 10.56 percent on Treasury bills is 0.011380598 or 1.14 percent
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Assume that the returns of Treasury bills have a normal distribution. The average return or mean of Treasury bills is 3.5 percent, and the standard deviation is 3.1 percent (Refer to Figure 10.10 in the text).
Determine the probability of having a return of 10.56 percent on Treasury bills:
Follow the common steps from Step 1 to Step 3 given below. Then, proceed with the Step 4.
The common steps to be followed to use the “NORM.DIST” function in Excel:
Step 1:
Open an Excel worksheet.
Step 2:
Place the cursor in cell A1.
Step 3:
Select the “Formulas” tab, and go to “More functions” in the ribbon. Under “More functions”, select “Statistical”. Under the drop-down menu of “Statistical”, select “NORM.DIST” function.

After clicking the “NORM.DIST” function, a popup window named “Function arguments” appears.
Step 4:
Enter the values. “X” represents the raw score or outcome. Here, it is necessary to test the probability of having 10.56 percent returns. Hence, “X” equals 10.56 percent. The mean or average return is 3.5 percent. The standard deviation is 3.1 percent. The cumulative distribution function provides the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, enter “TRUE” in the “Cumulative” column.
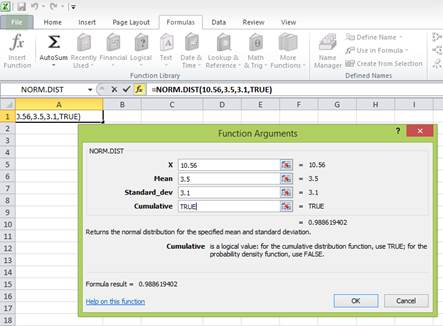
Press “OK” after providing the inputs. The probability of the area to the left of Z is as follows:
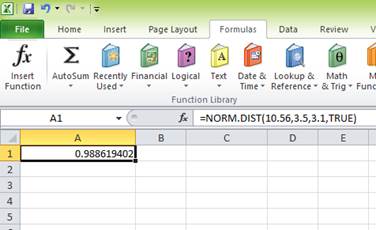
The probability of 0.988619402 represents the area to the left of Z. The area to the left of Z is the probability of getting less than 10.56 percent return. The area to the right of Z is the probability of getting a return of 10.56 percent or more.
The total area represented by the normal distribution curve has a probability of “1”. The area to the left of Z has a probability of 0.988619402. Hence, the probability of the area to the right of Z is “1” minus the probability of the area to the left of Z. Hence, the probability of getting 10.56 percent return or more is 0.011380598 or 1.14 percent
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Essentials of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- Use the binomial method to determine the value of an American Put option at time t = 0. The option expires at time t = T = 1/2 and has exercise price E = 55. The current value of the underlying is S(0) = 50 with the underlying paying continuous dividends at the rate D = 0.05. The interest rate is r = 0.3. Use a time step of St = 1/6. Consider the case of p = 1/2 and suppose the volatility is σ = 0.3. Perform all calculations using a minimum of 4 decimal places of accuracy. =arrow_forwardConsider a European chooser option with exercise price E₁ and expiry date T₁ where the relevant put and call options, which depend on the value of the same underlying asset S, have the same exercise price E2 and expiry date T₂. Determine, in terms of other elementary options, the value of the chooser option for the special case when T₁ = T2. Clearly define all notation that you use.arrow_forwardThe continuous conditional probability density function pc(S, t; S', t') for a risk neutral lognormal random walk is given by Pc(S, t; S', t') = 1 σS'√2π(t' - t) - (log(S/S) (ro²)(t − t)] exp 202 (t't) In the binomial method, the value of the underlying is Sm at time step môt and the value of the underlying at time step (m + 1)St is Sm+1. For this case evaluate Ec[(Sm+1)k|Sm] = [°° (S')*pc(S™, mdt; S', (m + 1)8t)dS' showing all steps, where k is a positive integer with k ≥ 1. You may assume that 1 e (x-n)2 2s2dx = 1 for all real numbers n and s with s > 0.arrow_forward
- John and Jane Doe, a married couple filing jointly, have provided you with their financial information for the year, including details of federal income tax withheld. They need assistance in preparing their tax return. W-2 Income: John earns $150,000 with $35,000 withheld for federal income tax. Jane earns $85,000 with $15,500 withheld for federal income tax. Interest Income: They received $2500 in interest from a savings account, with no tax withheld. Child Tax Credit: They have two children under the age of 17. Mortgage Interest: Paid $28,000 in mortgage interest on their primary residence. Property Taxes: Paid $4,800 in property taxes on their primary residence. Charitable Donations: Donated $22,000 to qualifying charitable organizations. Other Deductions: They have no other deductions to claim. You will gather the appropriate information and complete the forms provided in Blackboard (1040, Schedule A, and Schedule B in preparation of their tax file.arrow_forwardOn the issue date, you bought a 20-year maturity, 5.85% semi-annual coupon bond. The bond then sold at YTM of 6.25%. Now, 5 years later, the similar bond sells at YTM of 5.25%. If you hold the bond now, what is your realized rate of return for the 5-year holding period?arrow_forwardBond Valuation with Semiannual Payments Renfro Rentals has issued bonds that have an 11% coupon rate, payable semiannually. The bonds mature in 17 years, have a face value of $1,000, and a yield to maturity of 9.5%. What is the price of the bonds? Round your answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forward
- analyze at least three financial banking products from both the liability side (like time deposits, fixed income, stocks, structure products, etc). You will need to examine aspects such as liquidity, risk, and profitability from a company and an individual point of view.arrow_forwardHow a does researcher ensure that consulting recommendations are data-driven? What does make it effective, and sustainable? Please help explain and give the example How does DMAC help researchers to improve their business processes? How to establish feedback loops for ongoing refinement. Please give the examplesarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Explain what the business model of payday lenders, title pawn lenders, and “credit approved” used car dealers.arrow_forwardThe current NPV of a $30 million bond with 9% interest, 8% coupon rate, and discounted at $95arrow_forwardCould you please help to explain the DMAIC phases and how a researcher would use them to conduct a consulting project? What is a measure process performance and how to analyze the process? What is an improve process performance and how the control improves process and future process performance?arrow_forward
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning



