
Concept explainers
The following transactions were completed by Yang Restaurant Equipment during January, the first month of this fiscal year. Terms of sale are 2/10, n/30. The balances of the accounts as of January 1 have been recorded in the general ledger in your Working Papers or in CengageNow. Yang Restaurant Equipment does not track cash sales by customer. If you are using the form-based approach with QuickBooks or general ledger, select “Cash Sales” as the customer for all cash sales transactions.


Required
- 1. Record the transactions for January using a general journal, page 1. Assume the periodic inventory method is used.*
* If using QuickBooks, record transactions using either the
The chart of accounts is as follows:
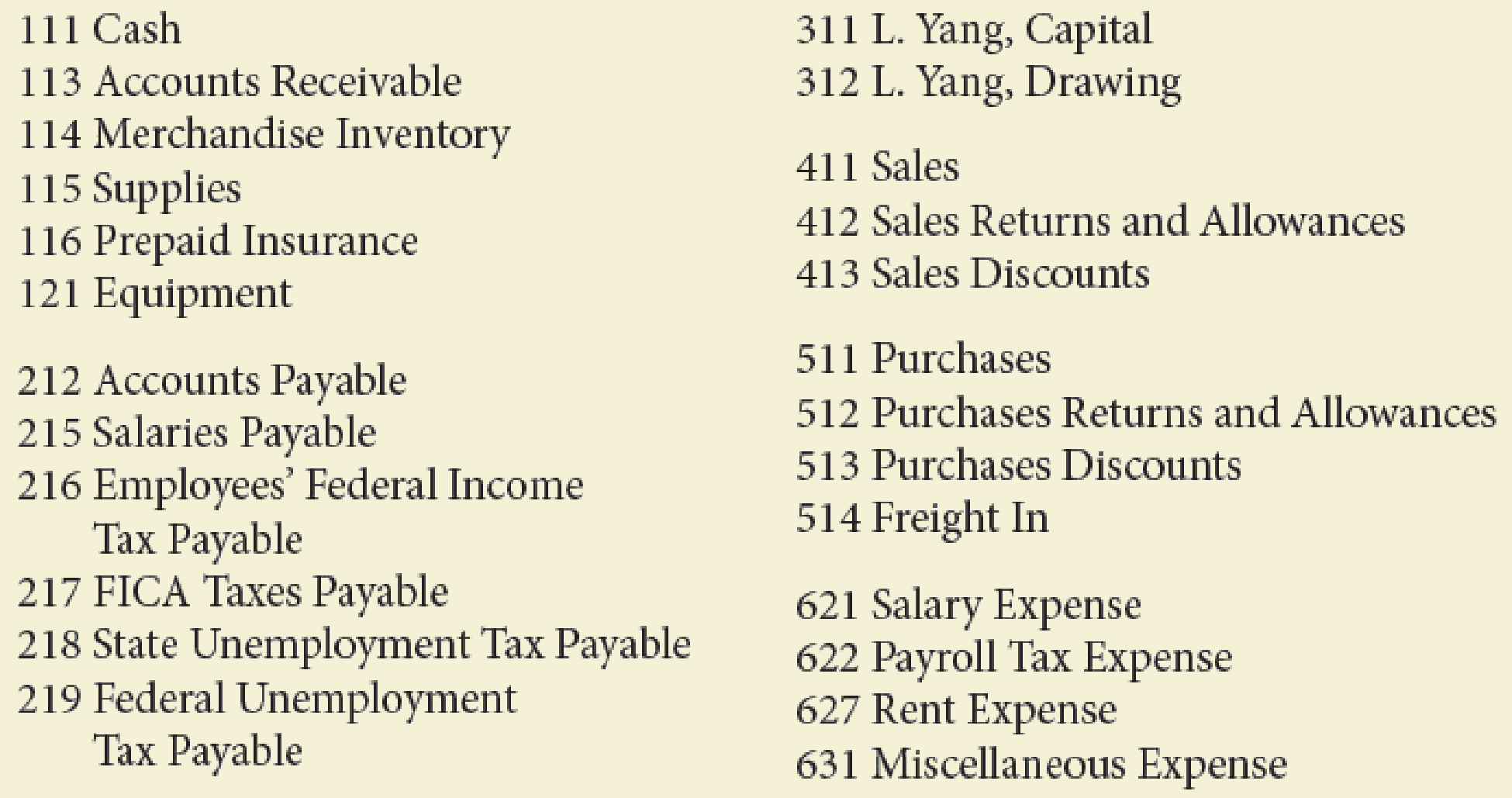
- 2.
Post daily all entries involving customer accounts to theaccounts receivable ledger.* - 3. Post daily all entries involving creditor accounts to the accounts payable ledger.*
- 4. Post daily the general journal entries to the general ledger. Write the owner’s name in the Capital and Drawing accounts.*
- 5. Prepare a
trial balance . - 6. Prepare a schedule of accounts receivable (A/R Aging Detail report in QuickBooks) and a schedule of accounts payable (A/P Aging Detail report in QuickBooks). Do the totals equal the balances of the related controlling accounts?
*If using QuickBooks or general ledger, ignore Steps 2, 3, and 4.
1.
Journalize the transaction in the general journal using periodic inventory method.
Explanation of Solution
General journal is a record of financial transaction. The transactions are recorded in the journal prior to posting them to the accounts in the general ledger.
Periodic inventory system: The method or system of recording the transactions related to inventory occasionally or periodically are referred to as periodic inventory system.
Journalize the transaction in general journal:
| General journal | Page:1 | ||||
| Date | Description | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |
| 20___ | |||||
| Jan. | 2 | Rent expense | 627 | 850 | |
| Cash | 111 | 850 | |||
| (Record rent paid by cash, Ck.no.6981) | |||||
| 2 | Cash | 111 | 4,500 | ||
| Mr. L capital | 311 | 4,500 | |||
| (Record additional capital invested | |||||
| by owner) | |||||
| 4 | Purchases | 212 | 376 | ||
| Accounts payable, V company | 512 | 376 | |||
| (Record purchase of merchandise from | |||||
| V company, invoice no: A694) | |||||
| 4 | Cash | 111 | 980 | ||
| Sales discounts | 413 | 20 | |||
| Accounts receivable, V company | 113 | 1,000 | |||
| (Record received check from V company | |||||
| for $980 in payment of invoice) | |||||
| 4 | Accounts receivable, L company | 113 | 755 | ||
| Sales | 411 | 755 | |||
| (Record merchandise sold on account | |||||
| to L company) | |||||
| 6 | Cash | 111 | 637 | ||
| Sales discount | 413 | 13 | |||
| Accounts receivable, P company | 113 | 650 | |||
| (Record received check from P company | |||||
| for $637 in payment of invoice) | |||||
| 7 | Accounts payable, F and S | 212 | 600 | ||
| Purchase discounts | 513 | 12 | |||
| Cash | 111 | 588 | |||
| (Record issued check to F and S in | |||||
| payment of invoice no: C127) | |||||
| 7 | Supplies | 625 | 93.54 | ||
| Accounts payable, D company | 212 | 93.54 | |||
| (Record purchase of supplies on account | |||||
| from D company) | |||||
| 7 | Accounts receivable, E and C | 113 | 1,115 | ||
| Sales | 411 | 1,115 | |||
| (Record merchandise sold to E and C) | |||||
Table (1)
| General journal | Page:2 | ||||
| Date | Description | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |
| 20___ | 9 | Sales returns and allowances | 412 | 47 | |
| Jan. | Accounts receivable | 113 | 47 | ||
| (Record issued credit memo to E and C for return of merchandise) | |||||
| 11 | Cash | 111 | 4,454.87 | ||
| Sales | 411 | 4,454.87 | |||
| (record cash sales) | |||||
| 11 | Accounts payable, V company | 212 | 2,830 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 2,773.40 | |||
| Purchase discounts | 513 | 56.6 | |||
| (Record issued check to V company for$2,773.40 in payment of invoice) | |||||
| 14 | Accounts receivable, V company | 113 | 2,100 | ||
| Sales | 411 | 2,100 | |||
| (Record merchandise sold to V company) | |||||
| 14 | Cash | 11 | 693.84 | ||
| Sales discount | 413 | 14.16 | |||
| Accounts receivable, L company | 113 | 708 | |||
| (Record received check from L company for $980 in payment of invoice) | |||||
| 19 | Purchases | 511 | 3,700 | ||
| Freight in | 514 | 142 | |||
| Accounts payable, C company | 212 | 3,842 | |||
| (Record purchase of merchandise on account from C company) | |||||
| 21 | Miscellaneous expense | 631 | 245 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 245 | |||
| (Record issued check to A.B company for | |||||
| $245 in payment of invoice) | |||||
| 21 | Cash | 111 | 3,689 | ||
| Sales | 411 | 3,689 | |||
| (Record cash sales) | |||||
| 23 | Accounts payable | 212 | 87 | ||
| Purchase returns and allowances | 512 | 87 | |||
| (Record received credit memo from C company) | |||||
Table (2)
| General journal | Page:3 | ||||
| Date | Description | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |
| 20___ | |||||
| Jan. | 29 | Accounts receivable, B company | 113 | 1,697.2 | |
| Sales | 411 | 1,697.2 | |||
| (Record sale of merchandise to B company) | |||||
| 29 | Freight in | 514 | 64 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 64 | |||
| (Record freight in charges) | |||||
| 31 | Cash | 111 | 3,862 | ||
| Sales | 411 | 3,862 | |||
| (Record cash sales) | |||||
| 31 | Miscellaneous expense | 631 | 65 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 65 | |||
| (Record payment of miscellaneous expense to M company) | |||||
| 31 | Salary expense | 621 | 5,900 | ||
| Employees Federal Income Tax payable | 216 | 795 | |||
| FICA Tax payable | 217 | 451.35 | |||
| Salaries payable | 215 | 4,653.65 | |||
| (Record salaries paid) | |||||
| 31 | Payroll tax expense | 622 | 764.05 | ||
| FICA Tax payable | 217 | 451.35 | |||
| State Unemployment Tax payable | 218 | 265.50 | |||
| Federal Unemployment Tax payable | 219 | 47.20 | |||
| (Record payment of payroll tax expense) | |||||
| 31 | Salaries payable | 215 | 4,653.65 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 4,653.65 | |||
| (Record payment of salaries) | |||||
| 31 | Mr. L , drawing | 312 | 1,000 | ||
| Cash | 111 | 1,000 | |||
| (Record Mr. L withdraw cash for personal use) | |||||
Table (3)
2.
Record the entries from customer accounts to the accounts receivable ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Account receivable: The amount of money to be received by a company for the sale of goods and services to the customers is referred to as account receivable.
Entries from customer accounts to the accounts receivable ledger:
| Accounts receivable ledger | ||||||
| Name: B company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 29 | 3 | 1,697.2 | 1,697.2 | ||
| Name: E and C company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 7 | 1 | 1,115 | 1,115 | ||
| Name: L company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 4 | 1 | 755 | 755 | ||
| 9 | 2 | 47 | 708 | |||
| 14 | 2 | 708 | 0 | |||
| Name: P company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 650 | |||
| 6 | 1 | 650 | 0 | |||
| Name: V company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 1,000 | |||
| 4 | 1 | 1,000 | 0 | |||
| 14 | 2 | 2,100 | 2,100 | |||
Table (4)
3.
Record the entries from creditor accounts to the accounts payable ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Account payable: The amount of money to be paid by a company for the purchase of goods and services from the seller is referred to as account payable.
Entries from creditor accounts to the accounts payable ledger:
| Accounts payable ledger | ||||||
| Name: C company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 19 | 2 | 3,842 | 3,842 | ||
| 23 | 2 | 87 | 3,755 | |||
| Name: D company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 7 | 1 | 93.5 | 93.5 | ||
| Name: F and sons | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 600 | |||
| 7 | 1 | 600 | 0 | |||
| Name: V company | ||||||
| Address: | ||||||
| Date | Items | Post ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| 20___ | ||||||
| Jan | 4 | 1 | 2,830 | 2,830 | ||
| 11 | 2 | 2,830 | 0 | |||
Table (5)
4.
Post the prepared general journal entries to the general ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Posting of transaction: The process of transferring the journalized transactions into the accounts of the ledger is known as posting of transaction.
Posting the transaction from general journal entries to general ledger:
| General ledger | |||||||||||||||||
| Account: Cash | Account No:111 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 8,740 | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | 1 | 850 | 7,890.00 | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | 1 | 4,500 | 12,390.00 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 980 | 13,370 | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | 1 | 637 | 14,007 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 1 | 588 | 13,419 | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | 2 | 4,454.87 | 17,873.87 | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | 2 | 2,773.40 | 15,100.47 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | 2 | 693.84 | 15,794.31 | ||||||||||||||
| 21 | 2 | 245 | 15,549.31 | ||||||||||||||
| 21 | 2 | 3,689 | 19,238.31 | ||||||||||||||
| 29 | 3 | 64 | 19,174.31 | ||||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 3,862 | 23,036.31 | ||||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 65 | 22,971.31 | ||||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 4,653.65 | 18,317.66 | ||||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 1,000 | 17,317.66 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Accounts receivable | Account No:113 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 1650 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 1000 | 650 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 755 | 1,405 | ||||||||||||||
| 6 | 1 | 650 | 755 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 1 | 1,115 | 1,870 | ||||||||||||||
| 9 | 2 | 47 | 1,823 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | 2 | 2,100 | 3,923 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | 2 | 708 | 3,215 | ||||||||||||||
| 29 | 3 | 1,697.20 | 4,912.20 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Merchandise inventory | Account No:114 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 20,584 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Suppliers | Account No:115 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 592 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 1 | 93.54 | 685.54 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Prepaid insurance | Account No:116 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 390 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Equipment | Account No:121 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 3,644 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Accounts payable | Account No:212 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 600 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 2,830 | 3,430 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 1 | 600 | 2,830 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 1 | 93.54 | 2,923.54 | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | 2 | 2,830 | 93.54 | ||||||||||||||
| 19 | 2 | 3,842 | 3,935.54 | ||||||||||||||
| 23 | 2 | 87 | 3,848.54 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Salaries payable | Account No:215 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 4,653.65 | 4,653.65 | |||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 4,653.65 | 0 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Employees federal income tax payable | Account No:216 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 795 | 795 | |||||||||||||
| Account: FICA tax payable | Account No:217 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 451.35 | 451.35 | |||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 451.35 | 902.7 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: State unemployment tax payable | Account No:218 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 265.5 | 265.5 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Federal unemployment tax payable | Account No:219 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 47.2 | 47.2 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Mr. Y capital | Account No:311 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 1 | Balance | 35,000 | ||||||||||||||
| 2 | 1 | 4,500 | 39,500 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Mr. Y Drawing | Account No:312 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 1,000 | 1,000 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Sales | Account No:411 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 4 | 1 | 755 | 755 | |||||||||||||
| 7 | 1 | 1,115 | 1,870 | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | 2 | 4,454.87 | 6,324.87 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | 2 | 2,100 | 8,424.87 | ||||||||||||||
| 21 | 2 | 3,689 | 12,113.87 | ||||||||||||||
| 29 | 3 | 1,697.20 | 13,811.07 | ||||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 3,862 | 17,673.07 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Sales return and allowance | Account No:412 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 9 | 2 | 47 | 47 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Sales discounts | Account No:413 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 4 | 1 | 20 | 20 | |||||||||||||
| 6 | 1 | 13 | 33 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | 2 | 14.16 | 47.16 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Purchases | Account No:511 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 4 | 1 | 2,830 | 2,830 | |||||||||||||
| 19 | 2 | 3,700 | 6,530 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Purchases returns and allowances | Account No:512 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 23 | 2 | 87 | 87 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Purchase discounts | Account No:513 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 7 | 1 | 12 | 12.0 | |||||||||||||
| 11 | 2 | 56.6 | 68.6 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Freight in | Account No:514 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 19 | 2 | 142 | 142 | |||||||||||||
| 29 | 3 | 64 | 206 | ||||||||||||||
| Account: Salary expense | Account No:621 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 5,900 | 5,900 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Payroll tax expense | Account No:622 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 31 | 3 | 764.05 | 764.05 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Rent expense | Account No:627 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 2 | 1 | 850 | 850 | |||||||||||||
| Account: Miscellaneous expense | Account No:631 | ||||||||||||||||
| Date | Item | Post ref | Debit | Credit | Balance | ||||||||||||
| 20___ | ($) | ($) | Debit ($) | Credit($) | |||||||||||||
| Jan | 21 | 2 | 245 | 245 | |||||||||||||
| 31 | 3 | 65 | 310 | ||||||||||||||
Table (6)
5.
Prepare a trail balance for Y Restaurant.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance: Trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts balances presented in a tabular form with two column, debit and credit. It checks the mathematical accuracy of the ledger postings and helps preparing the final accounts.
Preparing the trial balance for Y Company:
| Y Restaurant | ||
| Trail balance | ||
| January 31, 20__ | ||
| Account name | Debit ($) | Credit($) |
| Cash | 17,317.6 | |
| Accounts receivable | 4,912.2 | |
| Merchandise inventory | 20,584 | |
| Supplies | 685.5 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 390 | |
| Equipment | 3,644 | |
| Accounts payable | 3,848.5 | |
| Employee's federal income tax payable | 795 | |
| FICA tax payable | 902.7 | |
| State unemployment tax payable | 265.5 | |
| Federal unemployment tax payable | 47.2 | |
| Mr. L capital | 39,500 | |
| Mr. L drawings | 1,000 | |
| Sales | 17,673.07 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | 47 | |
| Sales discounts | 47.16 | |
| Purchases | 6,530 | |
| Purchases returns and allowances | 87 | |
| Purchases discounts | 68.6 | |
| Freight in | 206 | |
| Salary expense | 5,900 | |
| Payroll tax expense | 764.05 | |
| Rent expense | 850 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 310 | |
| Total | 63,187.61 | 63,187.61 |
Table (7)
6.
Prepare a schedule for accounts receivable and accounts payable.
Explanation of Solution
Schedule for the accounts receivable:
| Y Restaurant | |
| Schedule of accounts receivable | |
| January 31, 20__ | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| B company | 1,697.2 |
| E and C company | 1,115 |
| V company | 2,100 |
| Total accounts receivable | $4,912.2 |
Table (8)
Schedule for the accounts payable:
| Y Restaurant | |
| Schedule of accounts payable | |
| January 31, 20__ | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| C company | 3,755 |
| D company | 93.5 |
| Total accounts payable | $3,848.5 |
Table (9)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
- Helparrow_forwardNet income?arrow_forwardGarrison Polymers produces synthetic materials used in the manufacturing of electronic components. In 2015, its first year of operations, Garrison produced 5,000 tons of synthetic material and sold 3,200 tons. In 2016, the company produced the same amount and sales were 6,000 tons (i.e., the company sold all of its inventory). In each year, the selling price per ton was $2,500, variable manufacturing costs per ton were $500, and variable selling expenses were $700 per ton. Fixed manufacturing costs were $5,000,000, and fixed administrative expenses were $600,000. What is the net income under variable costing in year 2015?arrow_forward
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





