
Concept explainers
 ICA 10-5
ICA 10-5
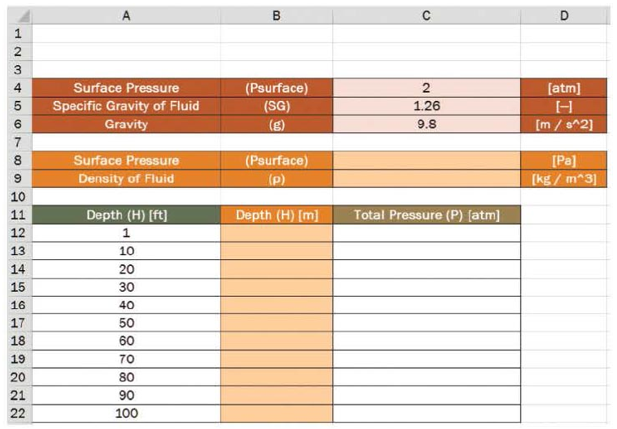
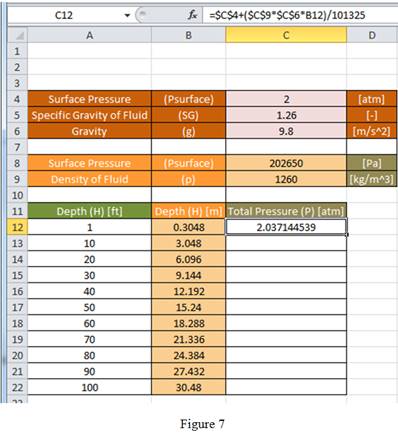
The worksheet shown here was designed to calculate the total pressure felt by an object submerged in a fluid as a function of the depth to which the object is submerged. The user will enter the surface pressure (in units of atmospheres), specific gravity of the fluid, and the gravity of the planet (in units of meters per second squared). All user input is shown in red. The worksheet will calculate the surface pressure in units of pascals, the density of the fluid in kilograms per cubic meter, and depth in units of feet. All conversions are shown in orange. Finally, the worksheet will calculate the total pressure in units of atmospheres.
- a. What formula should be typed in cell C8 to convert the surface pressure in cell C4 from atmospheres to pascals?
- b. What formula should be typed in cell C9 to determine the density in units of kilograms per cubic meter?
- c. What formula should be typed into cell B12 that can then be copied clown column B to convert the depth from units of feet to units of meters?
- d. What formula should be typed into cell C12 that can then be copied down column C to calculate the total pressure in units of atmospheres?
a.
Write the formula to be entered in cell C8 to convert the atmospheres surface pressure entered in cell C4 to Pascal.
Answer to Problem 1ICA
The formula to be entered in cell C8 to convert the atmospheres surface pressure entered in cell C4 to Pascal is “
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The worksheet is given as follows.
Calculation:
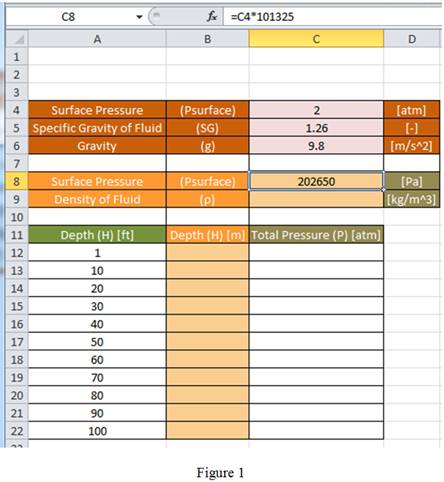
Consider the conversion factor for atmospheres to Pascal.
Step 1:
Using equation (1), enter the formula “
Conclusion:
Hence, the formula to be entered in cell C8 to convert the atmospheres surface pressure entered in cell C4 to Pascal is “
b.
Write the formula to be entered in cell C9 to determine the density in units of kilograms per cubic meter.
Answer to Problem 1ICA
The formula to be entered in cell C9 to determine the density in units of kilograms per cubic meter is “
Explanation of Solution
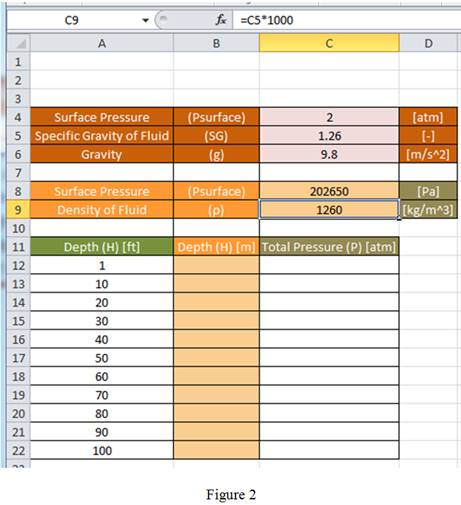
Calculation:
Write the expression for density.
Step 1:
Using equation (2), enter the formula “
Conclusion:
Hence, the formula to be entered in cell C9 to determine the density in units of kilograms per cubic meter is “
c.
Write the formula to be entered in cell B12 that can be then be copied down column B to convert the depth in feet to meters.
Answer to Problem 1ICA
The formula to be entered in cell B12 that can be then be copied down column B to convert the depth in feet to meters is “
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Write the conversion factor for feet to meter.
Step 1:
Using equation (3), enter the formula “
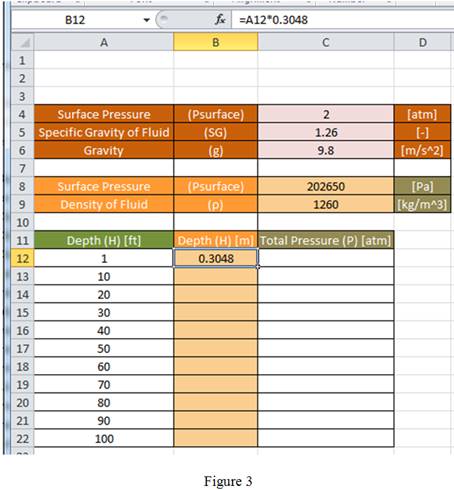
Drag the same formula for remaining cells in the column to obtain the value of depth in terms of m as shown in Figure 4.
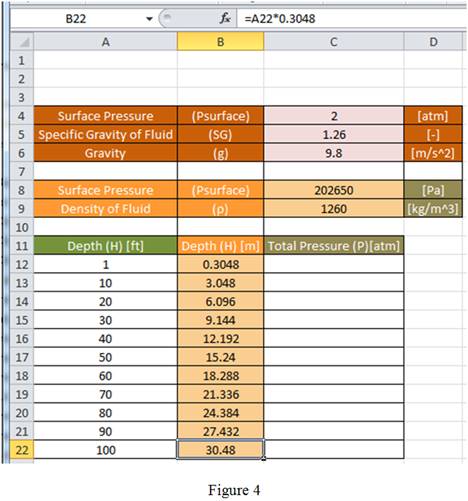
Conclusion:
Hence, the formula to be entered in cell B12 that can be then be copied down column B to convert the depth in feet to meters is “
d.
Write the formula to be entered in cell C12 that can be then be copied down column C to calculate the total pressure in atmospheres.
Answer to Problem 1ICA
The formula to be entered in cell C12 that can be then be copied down column C to calculate the total pressure in atmospheres is “
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Write the expression for total pressure.
Re-arrange equation (1) as follows.
Step 1:
Since, the content of cell C8 is in Pascal, the result obtained for total pressure using cell C8, C9, C6 and B12 is divided by 101,325 to convert the result from Pascal to atmosphere.
Using equation (4) and (5), enter the formula “
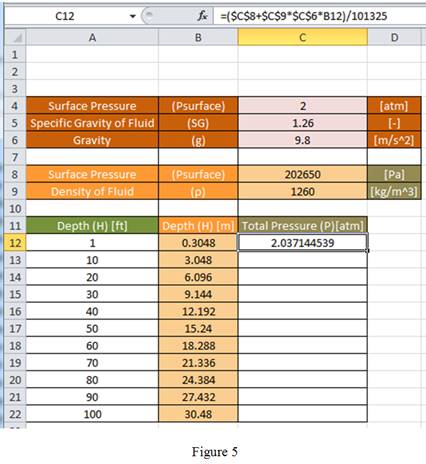
Drag the same formula for remaining cells in the column to obtain the total pressure value as shown in Figure 6.
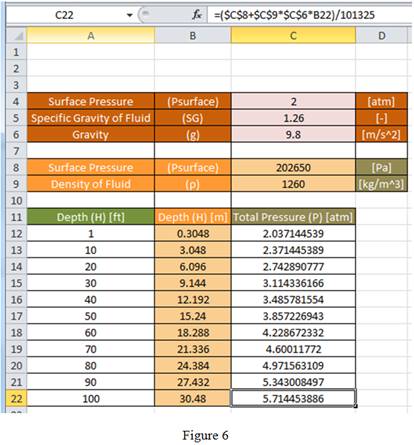
Since, the content of cell C4 is in atmosphere, the result obtained for
Using equation (4) and (5), enter the formula “
Drag the same formula for remaining cells in the column to obtain the total pressure value as shown in Figure 8.
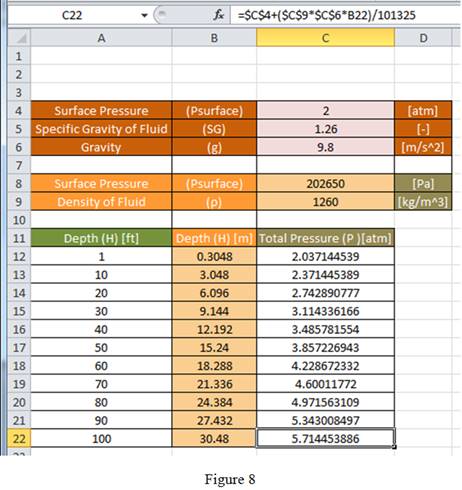
Compare Figure 5 with Figure 7 and Figure 6 with Figure 8, the result obtained for total pressure using formula
Conclusion:
Hence, the formula to be entered in cell C12 that can be then be copied down column C to calculate the total pressure in atmospheres is “
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Thinking Like an Engineer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Q4 The two solid shafts are connected by gears as shown and are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing stress is 7000 psi. Knowing the diameters of the two shafts are, respectively, dBC determine the largest torque Tc that can be applied at C. 4 and dEF dBC=Last 1 student ID+3 inch dEF=Last 1 student ID+1 inch 7 R=Last 1 Student ID+5 inch 9 R B Tc 2.5 in. E TF Harrow_forwardExperiment تكنولوجيا السيارات - Internal Forced convenction Heat transfer Air Flow through Rectangular Duct. objective: Study the convection heat transfer of air flow through rectangular duct. Valve Th Top Dead Centre Exhaust Valve Class CP. N; ~ RIVavg Ti K 2.11 Te To 18.8 21.3 45.8 Nath Ne Pre Calculations:. Q = m cp (Te-Ti) m: Varg Ac Acca*b Q=hexp As (Ts-Tm) 2 2.61 18.5 20.846.3 Tm = Te-Ti = 25 AS-PL = (a+b)*2*L Nu exp= Re-Vavy D heep Dh k 2ab a+b Nu Dh the- (TS-Tm) Ts. Tmy Name / Nu exp Naxe بب ارتدان العشريarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findarrow_forward
- Procedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thearrow_forwardProcedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2D3D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D ∑Fx=0 ∑Fy=0 ∑Fz=0 ∑Mx=0 ∑My=0 ΣMz=0 2D ΣFx=0 ΣFy=0 ΣMz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of thearrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2D3D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D∑Fx=0∑Fy=0∑Fz=0∑Mx=0∑My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thearrow_forward
- Procedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the sectionarrow_forwardProcedure: 1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D, type of support 2- Free body diagram 3 - Find the support reactions 4- If you find a negative number then flip the force 5- Find the internal force 3D \sum Fx=0 \sum Fy=0 \sum Fz=0 \sum Mx=0 \sum My=0 \Sigma Mz=0 2D \Sigma Fx=0 \Sigma Fy=0 \Sigma Mz=0 5- Use method of section and cut the element where you want to find the internal force and keep either side of the sectionarrow_forwardFor each system below with transfer function G(s), plot the pole(s) on the s-plane. and indicate whether the system is: (a) "stable" (i.e., a bounded input will always result in a bounded output), (b) "marginally stable," or (c) "unstable" Sketch a rough graph of the time response to a step input. 8 a) G(s) = 5-5 8 b) G(s) = c) G(s) = = s+5 3s + 8 s² - 2s +2 3s +8 d) G(s): = s²+2s+2 3s+8 e) G(s): = s² +9 f) G(s): 8 00 == Sarrow_forward
- Please answer the following question. Include all work and plase explain. Graphs are provided below. "Consider the Mg (Magnesium) - Ni (Nickel) phase diagram shown below. This phase diagram contains two eutectic reactions and two intermediate phases (Mg2Ni and MgNi2). At a temperature of 505oC, determine what the composition of an alloy would need to be to contain a mass fraction of 0.20 Mg and 0.80 Mg2Ni."arrow_forwardThe triangular plate, having a 90∘∘ angle at AA, supports the load PP = 370 lblb as shown in (Figure 1).arrow_forwardDesign a 4-bar linkage to carry the body in Figure 1 through the two positions P1 and P2 at the angles shown in the figure. Use analytical synthesis with the free choice values z = 1.075, q= 210°, ß2 = −27° for left side and s = 1.24, y= 74°, ½ = − 40° for right side. φ 1.236 P2 147.5° 210° 2.138 P1 Figure 1 Xarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





