
a.
Prepare the general
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry:
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Accounting rules for Journal entries:
- To record increase balance of account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record decrease balance of account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Prepare the general journal entry of Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Event | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| 1. | Sales tax payable | $290 | |
| Cash | $290 | ||
| (To record sales taxes payable) | |||
| 2. | Employee income tax payable | $500 | |
| FICA social security tax payable | $600 | ||
| FICA Medicare tax payable | $150 | ||
| $630 | |||
| Cash | $1,880 | ||
| (To record payment made for payroll liabilities) | |||
| 3. | Building | $125,000 | |
| Land | $25,000 | ||
| Cash | $50,000 | ||
| Notes payable | $100,000 | ||
| (To record purchase of land and building) | |||
| 4. | Cash | $49,000 | |
| Discount on bonds payable | $1,000 | ||
| Bonds payable | $50,000 | ||
| (To record issuance of bonds payable at discount) | |||
| 5. | Supplies | $660 | |
| Accounts payable | $660 | ||
| (To record purchase of supplies) | |||
| 6. | Merchandise inventory | $51,000 | |
| Cash | $51,000 | ||
| (To record purchase of 170 alarm systems) | |||
| 7. | Allowance for doubtful accounts | $2,450 | |
| | $2,450 | ||
| (To record write off uncollectible accounts receivable) | |||
| 8a. | Accounts receivable | $97,440 | |
| Alarm sales revenue | $92,800 | ||
| Sales tax payable | $4,640 | ||
| (To record sales of alarm systems) | |||
| 8b. | Cost of goods sold | $47,620 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $47,620 | ||
| (To record the adjustment from cost to market value for inventory write-downs) | |||
| 9. | Accounts receivable - credit card | $34,560 | |
| Accounts receivable | $84,000 | ||
| Credit card expense | $120,000 | ||
| Monitoring service revenue | |||
| (To record service rendered to monitoring services) | |||
| 10. | Maintenance expense | $65 | |
| Office supplies expense | $24 | ||
| Cash | $89 | ||
| (To record replenishment of petty cash fund) | |||
| 11. | Cash | $34,560 | |
| Accounts receivable - credit card | $34,560 | ||
| (To record cash received from credit card company) | |||
| 12. | Sales tax payable | $4,250 | |
| Cash | $4,250 | ||
| (To record sales tax paid to alarm services) | |||
| 13. | Cash | $167,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | $167,000 | ||
| (To record cash received from accounts receivable) | |||
| 14. | Salaries expense | $82,000 | |
| Employee income tax payable | $9,600 | ||
| FICA Tax - social security tax payable | $4,920 | ||
| FICA tax - Medicare tax payable | $1,230 | ||
| Cash | $66,250 | ||
| (To record payroll expenses) | |||
| 15. | Warranty payable | $1,250 | |
| Cash | $1,250 | ||
| (To record warranty expense) | |||
| 16. | Notes payable | $12,000 | |
| Interest Payable | $320 | ||
| Interest expense | $640 | ||
| Cash | $12,960 | ||
| (To record notes payable to Bank S) | |||
| 17. | Advertising expense | $18,000 | |
| Cash | $18,000 | ||
| (To record payment of advertising expense) | |||
| 18. | Utilities expense | $5,600 | |
| Cash | $5,600 | ||
| (To record payment of utilities expense) | |||
| 19. | Payroll income tax expense | $5,625 | |
| Employee income tax payable | $8,600 | ||
| FICA - Social security tax payable | $4,500 | ||
| FICA - Medicare tax payable | $1,125 | ||
| Cash | $19,850 | ||
| (To record payroll liabilities) | |||
| 20. | Accounts payable | $660 | |
| Cash | $660 | ||
| (To record cash paid for accounts payable) | |||
| 21. | Interest expense | $3,200 | |
| Discount on bonds payable | $200 | ||
| Cash | $3,000 | ||
| (To record payment of interest expenses made) | |||
| 22. | Interest expense | $7,000 | |
| Notes Payable | $7,238 | ||
| Cash | $14,238 | ||
| (To record payment of amortized note) | |||
| 23. | Dividends | $10,000 | |
| Cash | $10,000 | ||
| (To record payment of cash dividend) | |||
| 24. | Supplies expense | $615 | |
| Supplies | $615 | ||
| (To record | |||
| 25. | Rent expense | $3,000 | |
| Prepaid rent | $3,000 | ||
| (To record adjustment for rent expense) | |||
| 26. | Uncollectible accounts expense | $2,722 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | $2,722 | ||
| (To record adjustment for uncollectible accounts expense) | |||
| 27. | $5,025 | ||
| | $5,025 | ||
| (To record adjustment entry for depreciation expense) | |||
| 28. | Warranty expense | $1,856 | |
| Warranty payable | $1,856 | ||
| (To record adjustment entry for warranty expense) | |||
| 29. | Payroll tax expense | $945 | |
| Unemployment tax payable | $945 | ||
| (To record adjustment entry for unemployment tax expense) | |||
| 30. | Payroll tax expense | $525 | |
| FICA - Social security tax payable | $420 | ||
| FICA - Medicare tax payable | $105 | ||
| (To record adjustment entry for payroll expense) |
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Unit (A) |
Cost per unit ($) (B) | Total |
| 38 | 290 | $11,020 |
| 122 | 300 | $36,600 |
| Total | $47,620 | |
Table (2) (1)
Calculate sales tax payable:
Calculate FICA – Social security tax payable:
Calculate FICA – Medicare tax payable:
Calculate FICA – Social security tax payable:
Calculate FICA – Social security tax payable:
Calculate FICA – Medicare tax payable:
Calculate discount on bonds payable:
Calculate interest expense:
Calculate Cash paid:
Calculate the value of supplies expense
Calculate rent expense:
Calculate uncollectible accounts expense:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Alarm sales on account | $97,440 |
| Add: Monitoring service revenue | $84,000 |
| Total credit sales (A) | $181,440 |
| Estimated uncollectible percent (B) | 1.5% |
| Uncollectible Account expense (A÷B) | $2,722 |
Table (3) (13)
Calculate the depreciation expense for equipment using straight line method:
Calculation depreciation expense of van using double declining method:
Note: Depreciation expense for Van limited to $750. (15)
Calculate depreciation expense of building using straight line method:
Calculation of total depreciation expense:
Calculate merchandise inventory on 1/15.
Calculate merchandise inventory on 8/1.
Calculate merchandise inventory on 9/5.
Calculate total cost of goods sold.
| Particulars | Units (A) | Per unit (B) | Amount (A×B) |
| Beginning inventory | 9 | $240 | $2,160 |
| Add: Inventory purchased (1/15) | 20 | $250 | $5,000 |
| Inventory purchased (8/1) | 25 | $260 | $6,500 |
| Inventory purchased | 6 | $265 | $1,590 |
| Total cost of goods sold | 60 | $15,250 |
Table (4)
…… (21)
Calculate supplies expense.

…… (22)
Calculate rent expense.
Calculate Expired van lease payment.
Calculate expired office rent payment for year 4 and year 5.
Calculate unearned revenue.
Calculate warranty expenses:
Note: Sale of Company p ($92,800) =
Calculate Payroll tax Expense:
b.
Post the transactions of T-Accounts for Incorporation PSS.
b.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal
The components of the T-account are as follows:
a) The title of the account
b) The left or debit side
c) The right or credit side
Post the transactions of T-Accounts for Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Cash | |||||||||
| Bal. | 122,475 | 1. | 290 | ||||||
| 4. | 49,000 | 2. | 1,880 | ||||||
| 11. | 34,560 | 3. | 50,000 | ||||||
| 13. | 167,000 | 6. | 51,000 | ||||||
| 10. | 89 | ||||||||
| 12. | 4,250 | ||||||||
| 14. | 66,250 | ||||||||
| 15. | 1,250 | ||||||||
| 16. | 12,960 | ||||||||
| 17. | 18,000 | ||||||||
| 18. | 5,600 | ||||||||
| 19. | 19,850 | ||||||||
| 20. | 660 | ||||||||
| 21. | 3,000 | ||||||||
| 22. | 14,238 | ||||||||
| 23. | 10,000 | ||||||||
| Bal. | 113,718 | ||||||||
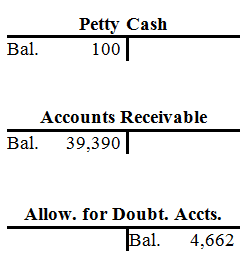
| Petty Cash | |||||||||
| Bal. | 100 | ||||||||
| Accounts Receivable | |||||||||
| Bal. | 27,400 | ||||||||
| 8a. | 97,440 | 7. | 2,450 | ||||||
| 9 | 84,000 | 13. | 167,000 | ||||||
| Bal. | 39,390 | ||||||||
| Accounts Rec. Credit Cards | |||||||||
| 9. | 34,560 | 11. | 34,560 | ||||||
| Bal. | -0- | ||||||||
| Allow. for Doubt. Accounts | |||||||||
| 7. | 2,450 | Bal. | 4,390 | ||||||
| 26. | 2,722 | ||||||||
| Bal. | 4,662 | ||||||||
| Supplies | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 165 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5. | 660 | 24. | 615 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 210 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prepaid Rent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 3,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25. | 3,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | -0- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merchandise Inventory | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 11,020 | 8b. | 47,620 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6. | 51,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 14,400 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 9,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
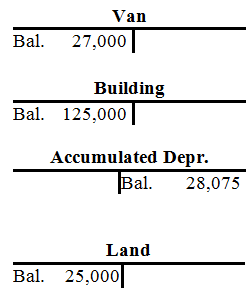
| Van | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 27,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated Depreciation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 23,050 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27. | 5,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 28,075 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Building | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | 125,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 125,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | 25,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 25,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20. | 660 | 5. | 660 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | -0- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
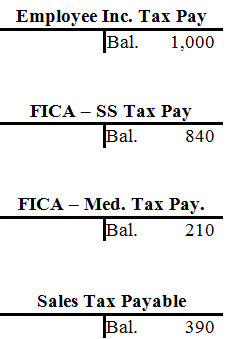
| Employee Inc. Tax Pay. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | 500 | 14. | 9,600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. | 8,600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 1,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FICA - S. S. Tax Pay | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | 600 | 14. | 4,920 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. | 4,500 | 30. | 420 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 840 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FICA - Med. Tax. Pay | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 150 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | 150 | 14. | 1,230 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. | 1,125 | 30. | 105 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 210 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales Tax Payable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 290 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. | 290 | 8a. | 4,640 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12. | 4,250 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 390 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
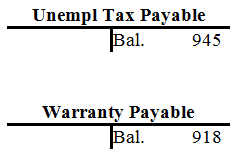
| Warranty Payable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 312 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15. | 1,250 | 28. | 1,856 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 918 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unemployment Tax Pay. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 630 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | 630 | 29. | 945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Payable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 320 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16. | 320 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | -0- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
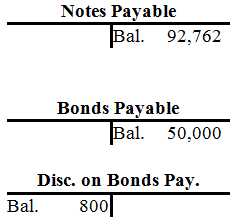
| Notes Payable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 12,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16. | 12,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | -0- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notes Payable - Bldg. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22. | 7,238 | 3. | 100,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 92,762 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds Payable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | 50,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 50,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount on Bonds Pay. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4. | 1,000 | 21. | 200 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 800 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
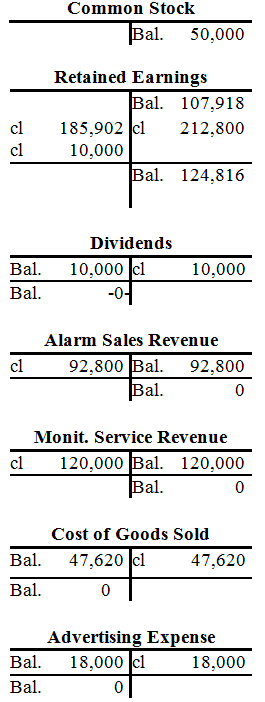
| Common Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 50,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 107,918 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23. | 10,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 10,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alarm Sales Revenue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8a. | 92,800 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 92,800 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monitoring Service Rev. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9. | 120,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 120,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8b. | 47,620 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 47,620 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Advertising Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17. | 18,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 18,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
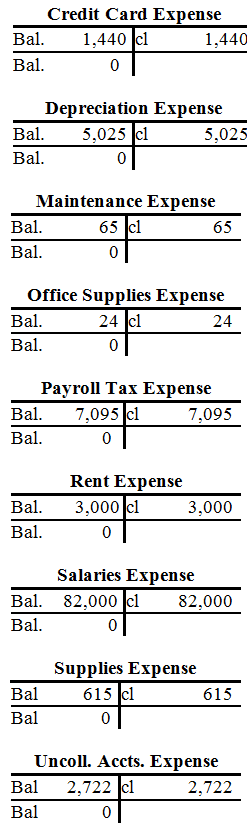
| Credit Card Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9. | 1,440 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 1,440 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27. | 5,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 5,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maintenance Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10. | 65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Payroll Tax Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. | 5,625 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29. | 945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30. | 525 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 7,095 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Office Supplies Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10. | 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rent Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25. | 3,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 3,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salaries Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14. | 82,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 82,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Supplies Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24. | 615 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 615 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uncollectible Accts. Exp. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26. | 2,722 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 2,722 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Utilities Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18. | 5,600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 5,600 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Warranty Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28. | 1,856 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 1,856 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interest Expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16. | 640 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21. | 3,200 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22. | 7,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bal. | 10,840 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
c.
Prepare trail balance of Incorporation PSS.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
A trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts. The trial balance is prepared to check the total balance of the debit column with the total of the balance of the credit column, which must be equal. The trial balance is usually prepared to check accuracy of ledger accounts balances before the preparation of financial statements.
Prepare trail balance of Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Trail Balance | ||
| December 31, Year 10 | ||
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $113,718 | |
| Petty Cash | $100 | |
| Accounts receivable | $39,390 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | $4,662 | |
| Supplies | $210 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $14,400 | |
| Equipment | $9,000 | |
| Van | $27,000 | |
| Building | $125,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | $28,075 | |
| Land | $25,000 | |
| Sales tax payable | $390 | |
| Employee Income tax payable | $1,000 | |
| FICA - Social security tax payable | $840 | |
| FICA - Medicare tax payable | $210 | |
| Warranty payable | $918 | |
| Unemployment tax payable | $945 | |
| Notes payable | $92,762 | |
| Bonds payable | $50,000 | |
| Discount on bonds payable | $800 | |
| Common stock | $50,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $107,918 | |
| Dividend | $10,000 | |
| Alarms Sales Revenue | 92,800 | |
| Monitoring Service Revenue | 120,000 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 47,620 | |
| Advertising Expense | 18,000 | |
| Credit Card Expense | 1,440 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 5,025 | |
| Maintenance Expense | 65 | |
| Payroll Tax Expense | 7,095 | |
| Office Supplies Expense | 24 | |
| Rent Expense | 3,000 | |
| Salaries Expense | 82,000 | |
| Supplies Expense | 615 | |
| Uncollectible Accounts Expense | 2,722 | |
| Utilities Expense | 5,600 | |
| Warranty Expense | 1,856 | |
| Interest Expense | 10,840 | |
| Total | $550,520 | $550,520 |
Table (5)
d.
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows of Incorporation PSS.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues and vice versa.
Prepare the income statement of Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| December 31, Year 10 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Revenue: | ||
| Monitoring service revenue | $120,000 | |
| Alarm sales revenue | $92,800 | |
| Total revenue | $212,800 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | $47,620 | |
| Gross margin | $165,180 | |
| Less: Expenses: | ||
| Advertising expense | $18,000 | |
| Credit card expense | $1,440 | |
| Depreciation expense | $5,025 | |
| Maintenance expense | $65 | |
| Office supplies expense | $24 | |
| Payroll tax expense | $7,095 | |
| Rent expense | $3,000 | |
| Salaries expense | $82,000 | |
| Supplies expense | $615 | |
| Uncollectible accounts expense | $2,722 | |
| Utilities expense | $5,600 | |
| Warranty expense | $1,856 | |
| Total Operating expenses | $127,442 | |
| Net operating income | $37,738 | |
| Less: Non -operating expense | ||
| Interest expense | $10,840 | |
| Net income | $26,898 | |
Table (6)
Statement of changes in Stockholder’s equity:
This statement reports the beginning stockholders’ equity and all the changes, which led to ending stockholders’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and drawings are deducted from beginning stockholders’ equity to arrive at the result, ending stockholders’ equity.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity of Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Statement of Changes in Stockholders' Equity | ||
| December 31, Year 10 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Opening common stock | $50,000 | |
| Add: Common stock issued | $0 | |
| Ending Common stock | $50,000 | |
| Opening retained earnings | $107,918 | |
| Add: Net income | $26,898 | |
| Less: Dividends | $10,000 | |
| Ending Retained earnings | $124,816 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | $174,816 | |
Table (7)
Balance Sheet:
Balance Sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the Balance sheet of Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| December 31, Year 10 | ||
| Amount | Amount | |
| Assets: | ||
| Cash | $113,718 | |
| Petty cash | $100 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $39,390 | |
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | $4,662 | $34,728 |
| Supplies | $210 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $14,400 | |
| Equipment | $9,000 | |
| Van | $27,000 | |
| Building | $125,000 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | $28,075 | $96,925 |
| Land | $25,000 | |
| Total Assets | $321,081 | |
| Liabilities: | ||
| Employee income tax payable | $1,000 | |
| FICA social security tax payable | $840 | |
| FICA - Medicare tax payable | $210 | |
| Sales Tax payable | $390 | |
| Warranty payable | $918 | |
| Unemployment tax payable | $945 | |
| Notes payable | $92,762 | |
| Bonds payable | $50,000 | |
| Less: Discount on bonds payable | $800 | $49,200 |
| Total liabilities | $146,265 | |
| Stockholders' equity | ||
| Common stock | $50,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $124,816 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | $174,816 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $321,081 | |
Table (8)
Statement of cash flows:
Statement of cash flows reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Prepare the statement of cash flows for Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| December 31, Year 10 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash flows from Operating Activities: | ||
| Cash receipts from customers | $201,560 | |
| Cash payment for expenses | ($164,579) | |
| Cash payment for sales tax payable | ($4,540) | |
| Cash payment for interest | ($10,960) | |
| Net cash flow from Operating Activities | $21,481 | |
| Cash flow from Investing Activities: | ||
| Cash payment for building and land | ($50,000) | |
| Net cash flow from Investing Activities | ($50,000) | |
| Cash flow from Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash inflow from bonds | $49,000 | |
| Cash payment on Notes payable | ($19,238) | |
| Cash payment for dividends | ($10,000) | |
| Net cash flow from Financing Activities | $19,762 | |
| Net decrease in cash | ($8,757) | |
| Add: Opening cash balance | $122,475 | |
| Ending cash balance | $113,718 | |
Table (9)
Working notes:
Calculate total cash from customers.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Collection of Accounts Receivable | $167,000 |
| Add: Collection of credit cards | $34,560 |
| Total cash from customers | $201,560 |
Table (10)
…… (11)
Calculate total cash payment for expenses.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Payment of compensation and related taxes | $87,980 |
| Payment of inventory | $51,000 |
| Payment of accounts payable | $660 |
| Payment of advertising | $18,000 |
| Payment for Utilities expense | $5,600 |
| Payment for warranty expense | $1,250 |
| Payment for Expense from petty cash | $89 |
| Total cash payment for expenses | $164,579 |
Table (11)
…… (12)
e.
Prepare to close the temporary accounts to retained earnings of Incorporation PSS.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are recorded in order to close the temporary accounts such as incomes and expenses by transferring them to the permanent accounts. It is passed at the end of the accounting period, to transfer the final balance.
Prepare to close the temporary accounts to retained earnings of Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31 | Alarm sales revenue | $92,800 | |
| Monitoring service revenue | $120,000 | ||
| Retained earnings | $212,800 | ||
| (To close all revenue accounts) | |||
| December 31 | Retained earnings | $185,902 | |
| Cost of goods sold | $47,620 | ||
| Advertising expense | $18,000 | ||
| Credit card expense | $1,440 | ||
| Depreciation expense | $5,025 | ||
| Maintenance expense | $65 | ||
| Office supplies expense | $24 | ||
| Payroll tax expense | $7,095 | ||
| Rent expense | $3,000 | ||
| Salaries expense | $82,000 | ||
| Supplies expense | $615 | ||
| Uncollectible accounts expense | $2,722 | ||
| Utilities expense | $5,600 | ||
| Warranty expense | $1,856 | ||
| Interest Expense | $10,840 | ||
| (To close all expenses accounts) | |||
| December 31 | Retained earnings | $10,000 | |
| Dividends | $10,000 | ||
| (To record dividend account) |
Table (12)
f.
Post the closing entries to the T-Accounts and prepare an after closing trail balance of Incorporation PSS.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Post-Closing Trial Balance:
After passing all the journal entries and the closing entries of the permanent accounts and then further posting them to each of the respective accounts, a post-closing trial balance is prepared which consists of a list of all the permanent accounts. A post-closing trial balance serves as an evidence to prove that the balance of the permanent accounts is equal.
Post the closing entries to the T- Accounts of Incorporation PSS as follows:
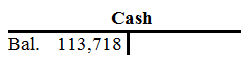

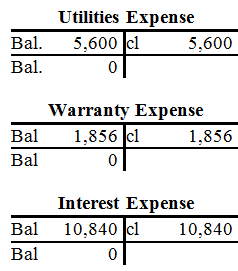
Prepare post -closing trail balance of Incorporation PSS as follows:
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Trail Balance | ||
| December 31, Year 10 | ||
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $113,718 | |
| Petty Cash | $100 | |
| Accounts receivable | $39,390 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | $4,662 | |
| Supplies | $210 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $14,400 | |
| Equipment | $9,000 | |
| Van | $27,000 | |
| Building | $125,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | $28,075 | |
| Land | $25,000 | |
| Sales tax payable | $390 | |
| Employee Income tax payable | $1,000 | |
| FICA - Social security tax payable | $840 | |
| FICA - Medicare tax payable | $210 | |
| Warranty payable | $918 | |
| Unemployment tax payable | $945 | |
| Notes payable | $92,762 | |
| Bonds payable | $50,000 | |
| Discount on bonds payable | $800 | |
| Common stock | $50,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $124,816 | |
| Total | $354,618 | $354,618 |
Table (13)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts
- The GNR Manufacturing Co. recorded overhead costs of $21,500 at an activity level of 5,000 machine hours and $8,000 at 2,500 machine hours. The records also indicated that overhead of $10,000 was incurred at 4,200 machine hours. Using the high-low method to estimate the cost equation, determine the variable cost per machine hour.arrow_forwardNeed help this question solution pleasearrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





