
Concept explainers
Check your understanding of the flow of genetic information through a cell by filling in the blanks.
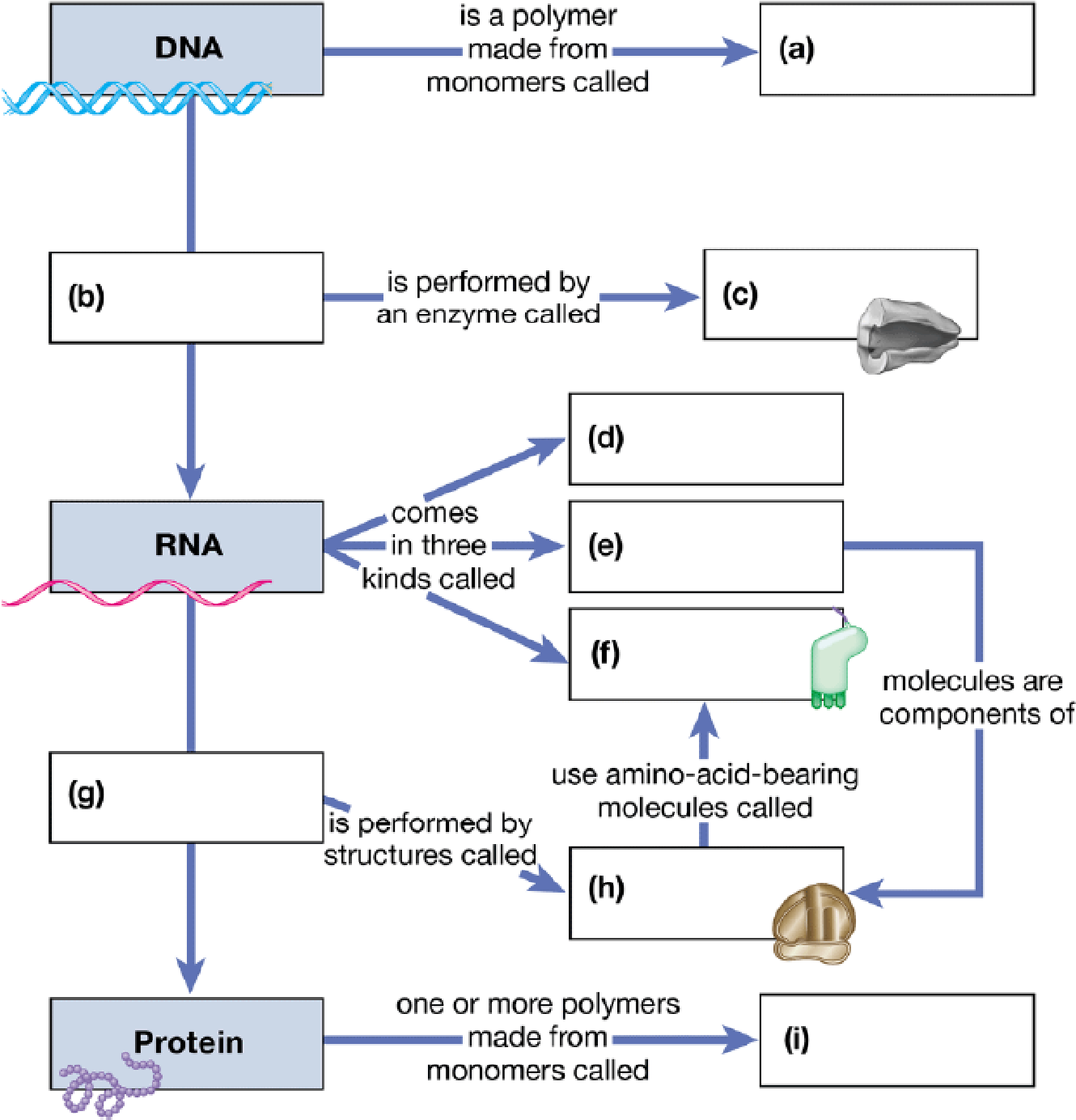
To complete: The given map showing the flow of genetic information through a cell.
Introduction: DNA is the blueprint of life. The genetic information of DNA is based in the nucleotide base sequences. These sequences are transcribed into mRNA triplets. These triplets of nucleotides are known as codons and they form the genetic code. They code for specific amino acids for the synthesis of proteins is known as functional gene products. This is known as gene expression.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: Fig. 1 shows the completed map of flow of genetic information through a cell.
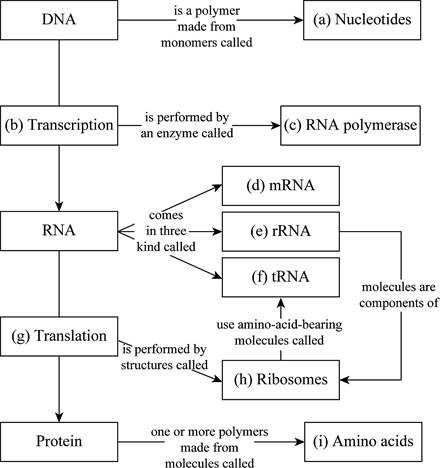
Fig.1 Flow of genetic information through a cell
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Nucleotides.
Explanation: The nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). DNA is a polymer made up of nucleotide monomers (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) and also known as polynucleotide. Hence, the correct answer is nucleotides.
(b)
Correct answer: Transcription.
Explanation: DNA consists of genetic instructions in the form of nucleotide sequences. It acts as a template and directs the messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis in the cell. The process of formation of mRNA is known as transcription. Hence, the correct answer is transcription.
(c)
Correct answer: RNA polymerase.
Explanation: RNA polymerase enzymes are of three types out of which, RNA pol II transcribes mRNA. RNA pol II enzyme first binds to the transcription factors and then forms a complex with promoter at start codon for the beginning of transcription process. Hence, the correct answer is RNA polymerase.
(d)
Correct answer: mRNA.
Explanation: Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes consist of three types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. mRNA forms 5% of the total RNA in a cell. mRNA consists of the genetic code in the form of triplets of nucleotides known as codons. Hence, the correct answer is mRNA.
(e)
Correct answer: rRNA
Explanation: rRNA forms 80% of the total RNA and is found in ribosomes. rRNAs along with proteins form ribosomes, which act as a site for protein synthesis. Hence, the correct answer is rRNA.
(f)
Correct answer: tRNA
Explanation: tRNAs are smallest among the three types of RNA. The mRNA sequence is read by transfer RNAs (tRNAs) to form polypeptide or a chain of amino acids in a process known as translation. The tRNA molecule with an attached amino acid binds to its specific mRNA codon. This mRNA codon codes for that specific amino acid. Hence, the correct answer is tRNA.
(g)
Correct answer: Translation.
Explanation: The mRNA acts as a template for the synthesis of polypeptide chain. Each letter in the gene sequence is copied which codes for a particular amino acid. The polypeptide chain is synthesized on the basis of amino acid sequences in the reading frame. This process is known as translation. Hence, the correct answer is translation.
(h)
Correct answer: Ribosomes.
Explanation: rRNAs along with proteins form ribosomes. Ribosomes act as a site of protein synthesis, that is, translation. Hence, the correct answer is ribosomes.
(i)
Correct answer: Amino acids.
Explanation: Amino acids are the monomer units of proteins. Amino acids are linked through peptide bonds to form a long polypeptide chain. Hence, the correct answer is amino acids.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- Describe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
- Describe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardPlease help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forwardA 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forward
- please fill in missing parts , thank youarrow_forwardplease draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





