
To identify:
The parts of the human respiratory system.
Introduction:
Human respiratory system is an organ system that is related to life supporting breathing process that is taking in oxygen and exhaling out carbon dioxide. It consists of several parts like the bronchi, alveoli, lungs, nostrils and many more. Every organ performs different functions.
Pictorial representation:
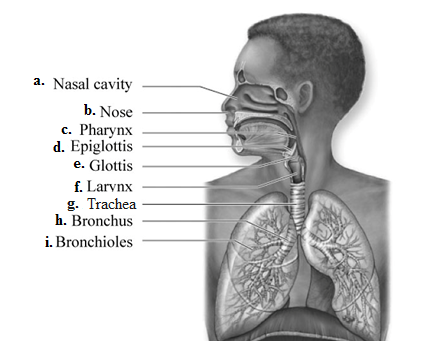
Fig.1: The parts of human respiratory system.
Explanation of Solution
(a) Nasal cavity: It is the empty space from where the oxygen enters the respiratory tract and carbon dioxide leaves the respiratory tract. It is also the first part and the opening of the respiratory tract.
(b) Nose: It is also called nares. It has hairs and there is also the lining of mucosal epithelial cells. There function is to trap dust, germs and small insects that enter through the air in our body.
(c) Pharynx: It is the cavity that is covered by membrane. It is found behind the nose and the mouth. It connects the esophagus with the nose and the mouth.
(d) Epiglottis: It is a flap-like structure that guards the opening and the closing of the wind pipe and thereby it protects humans from the entry of food in the windpipe.
(e) Glottis: It is a part of larynx that has vocal cords and it has a slit-like opening between the vocal cords. Glottis affects the pitch of the voice by its contraction and relaxation.
(f) Larynx: It is a hollow organ that is made up of muscle cells. It forms an air passage for the air to pass to the lungs. It also holds the Adam’s apple.
(g) Trachea: It is a C shaped structure that is made up of cartilage. It is also called the windpipe. It connects larynx and the esophagus.
(h) Bronchus: Bronchus is the structure that originates from trachea. They further branch into lobular structures called the bronchioles.
(i) Bronchioles: These are the minute branches that originate from bronchi. They are a connecting link between alveoli and bronchi. They do not contain any cartilage.
Several organs of the respiratory system are the trachea, bronchi, alveoli, and so on.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
HUMAN BIOLOGY (LOOSELEAF)-W/CONNECT
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
- What are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardDescribe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardPlease help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forward
- A 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forwardStandard Concentration (caffeine) mg/L Absorbance Reading 10 0.322 20 0.697 40 1.535 60 2.520 80 3.100arrow_forwardPlease draw in the missing answer, thank youarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





