
(a)
Find the
(a)
Answer to Problem 16CAP
The mean difference for the difference scores is –0.8.
The standard deviation for the difference scores is 2.8.
The standard error for the difference scores is 1.3.
Explanation of Solution
Calculations:
From the Question 15, the difference scores are –4, 1, –2, –2, and 3.
The formula for sample mean difference score is,
The formula for sample standard deviation difference score is,
The formula for sample standard error of difference score is,
Mean for the difference:
Substitute, the values for difference scores, –4, 1, –2, –2, 3 and
Thus, the mean for the difference scores is –0.8.
Standard deviation for the difference scores:
Substitute, the values for difference scores, –4, 1, –2, –2, 3,
Thus, the standard deviation for the difference scores is 2.8.
Standard error for the difference scores:
Substitute,
Thus, the standard error for the difference scores is 1.3.
(b)
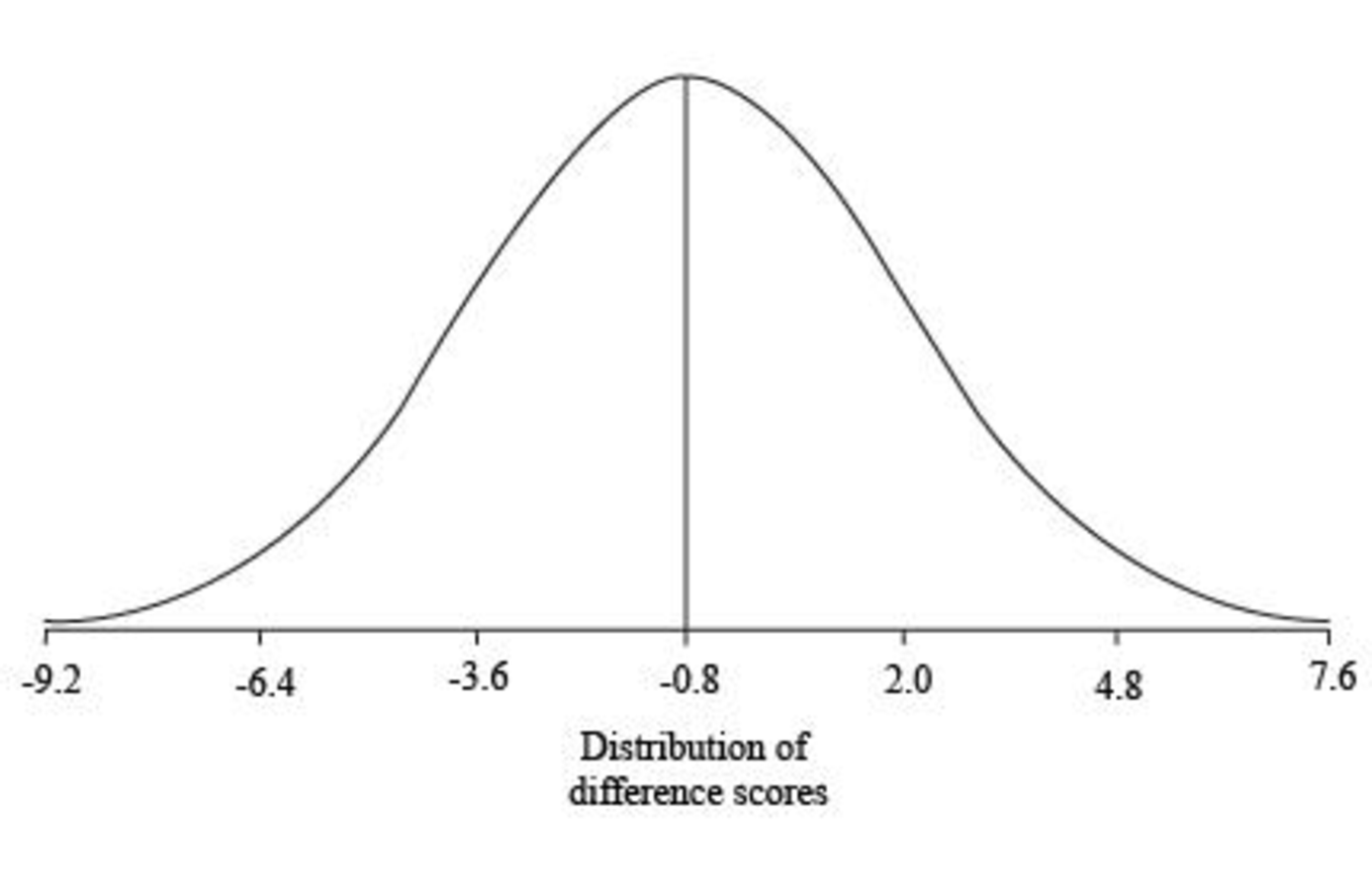
Sketch the shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
(b)
Answer to Problem 16CAP
The shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The value of
For 1 standard deviation:
For two standard deviation:
For three standard deviation:
Thus, the standard deviation limits for the distribution are
Sketch of Graph:
Step by step procedure for sketching the graph:
- The mean of the distribution is taken in the centre of the graph.
- The one standard deviation limits are taken on either side of the mean.
- The two standard deviations limits are taken on either side of one standard deviation limits.
- The three standard deviations limits are taken on either side of two standard deviations limits.
(c)
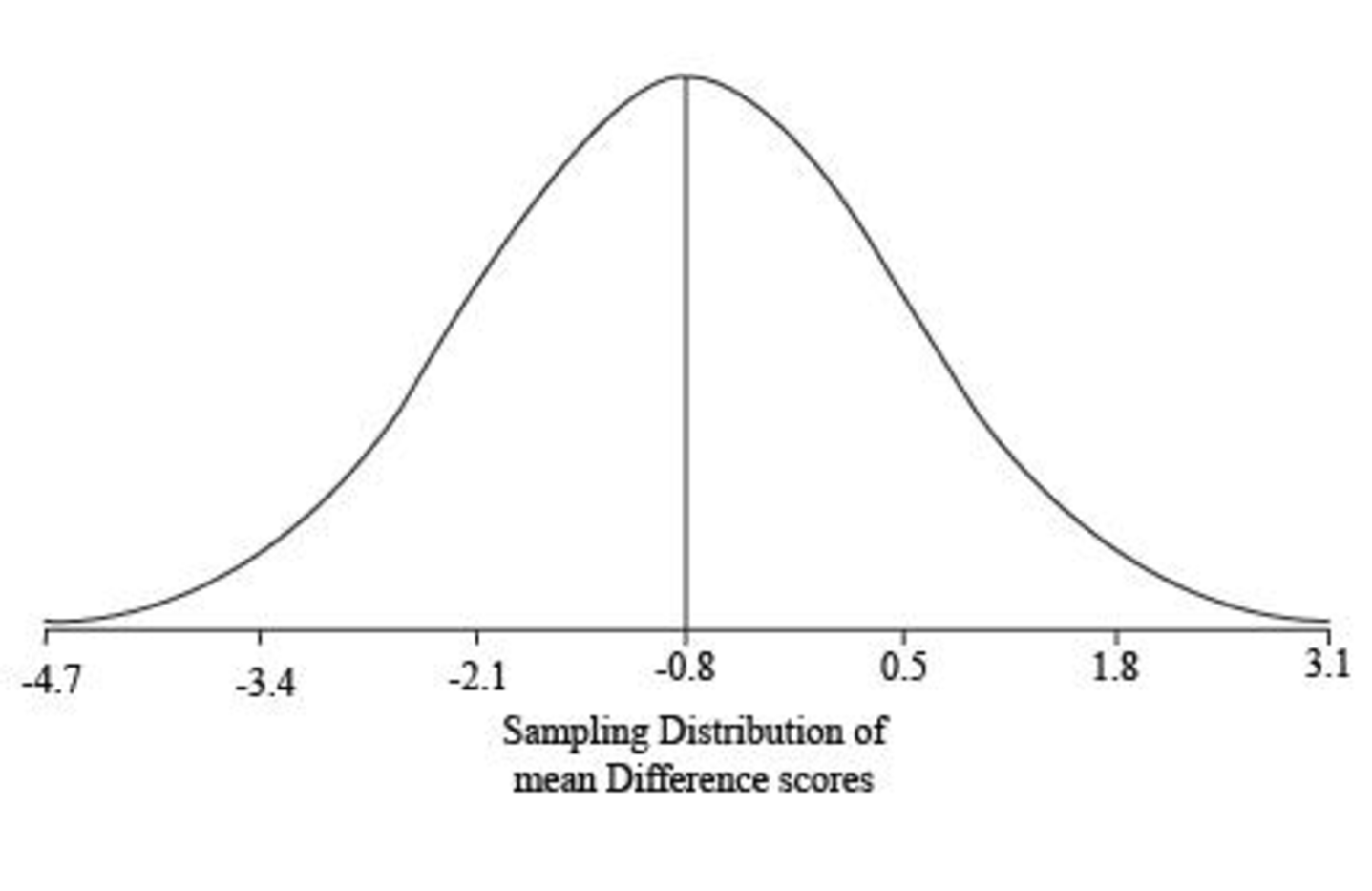
Sketch the shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
(c)
Answer to Problem 16CAP
The shape of the distribution of mean difference scores
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The value of
For 1 standard deviation:
For two standard deviation:
For three standard deviation:
Thus, the standard deviation limits for the distribution are
Sketch of Graph:
Step by step procedure for sketching the graph:
- The mean of the distribution is taken in the centre of the graph.
- The one standard deviation limits are taken on either side of the mean.
- The two standard deviations limits are taken on either side of one standard deviation limits.
- The three standard deviations limits are taken on either side of two standard deviations limits.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
- Please help me answer the following questions from this problem.arrow_forwardPlease help me find the sample variance for this question.arrow_forwardCrumbs Cookies was interested in seeing if there was an association between cookie flavor and whether or not there was frosting. Given are the results of the last week's orders. Frosting No Frosting Total Sugar Cookie 50 Red Velvet 66 136 Chocolate Chip 58 Total 220 400 Which category has the greatest joint frequency? Chocolate chip cookies with frosting Sugar cookies with no frosting Chocolate chip cookies Cookies with frostingarrow_forward
- The table given shows the length, in feet, of dolphins at an aquarium. 7 15 10 18 18 15 9 22 Are there any outliers in the data? There is an outlier at 22 feet. There is an outlier at 7 feet. There are outliers at 7 and 22 feet. There are no outliers.arrow_forwardStart by summarizing the key events in a clear and persuasive manner on the article Endrikat, J., Guenther, T. W., & Titus, R. (2020). Consequences of Strategic Performance Measurement Systems: A Meta-Analytic Review. Journal of Management Accounting Research?arrow_forwardThe table below was compiled for a middle school from the 2003 English/Language Arts PACT exam. Grade 6 7 8 Below Basic 60 62 76 Basic 87 134 140 Proficient 87 102 100 Advanced 42 24 21 Partition the likelihood ratio test statistic into 6 independent 1 df components. What conclusions can you draw from these components?arrow_forward
- What is the value of the maximum likelihood estimate, θ, of θ based on these data? Justify your answer. What does the value of θ suggest about the value of θ for this biased die compared with the value of θ associated with a fair, unbiased, die?arrow_forwardShow that L′(θ) = Cθ394(1 −2θ)604(395 −2000θ).arrow_forwarda) Let X and Y be independent random variables both with the same mean µ=0. Define a new random variable W = aX +bY, where a and b are constants. (i) Obtain an expression for E(W).arrow_forward
- The table below shows the estimated effects for a logistic regression model with squamous cell esophageal cancer (Y = 1, yes; Y = 0, no) as the response. Smoking status (S) equals 1 for at least one pack per day and 0 otherwise, alcohol consumption (A) equals the average number of alcohoic drinks consumed per day, and race (R) equals 1 for blacks and 0 for whites. Variable Effect (β) P-value Intercept -7.00 <0.01 Alcohol use 0.10 0.03 Smoking 1.20 <0.01 Race 0.30 0.02 Race × smoking 0.20 0.04 Write-out the prediction equation (i.e., the logistic regression model) when R = 0 and again when R = 1. Find the fitted Y S conditional odds ratio in each case. Next, write-out the logistic regression model when S = 0 and again when S = 1. Find the fitted Y R conditional odds ratio in each case.arrow_forwardThe chi-squared goodness-of-fit test can be used to test if data comes from a specific continuous distribution by binning the data to make it categorical. Using the OpenIntro Statistics county_complete dataset, test the hypothesis that the persons_per_household 2019 values come from a normal distribution with mean and standard deviation equal to that variable's mean and standard deviation. Use signficance level a = 0.01. In your solution you should 1. Formulate the hypotheses 2. Fill in this table Range (-⁰⁰, 2.34] (2.34, 2.81] (2.81, 3.27] (3.27,00) Observed 802 Expected 854.2 The first row has been filled in. That should give you a hint for how to calculate the expected frequencies. Remember that the expected frequencies are calculated under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. FYI, the bounderies for each range were obtained using JASP's drag-and-drop cut function with 8 levels. Then some of the groups were merged. 3. Check any conditions required by the chi-squared…arrow_forwardSuppose that you want to estimate the mean monthly gross income of all households in your local community. You decide to estimate this population parameter by calling 150 randomly selected residents and asking each individual to report the household’s monthly income. Assume that you use the local phone directory as the frame in selecting the households to be included in your sample. What are some possible sources of error that might arise in your effort to estimate the population mean?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning

