Problem 1RQ: What are intermolecular forces? How do they differ from intramolecular forces? What are... Problem 2RQ: Define the following terms and describe how each depends on the strength of the intermolecular... Problem 3RQ: Compare and contrast solids, liquids, and gases. Problem 4RQ Problem 5RQ: What is a lattice? What is a unit cell? Describe a simple cubic unit cell. How many net atoms are... Problem 6RQ: What is closest packing? What is the difference between hexagonal closest packing and cubic closest... Problem 8RQ: Describe, in general, the structures of ionic solids. Compare and contrast the structure of sodium... Problem 9RQ Problem 10RQ Problem 11RQ: Compare and contrast the phase diagrams of water and carbon dioxide. Why doesn t CO2 have a normal... Problem 1ALQ: It is possible to balance a paper clip on the surface of water in a beaker. lf you add a bit of soap... Problem 2ALQ: Consider a sealed container half-filled with water. Which statement best describes what occurs in... Problem 3ALQ: Explain the following: You add 100 mL water to a 500-mL round-bottom flask and heat the water until... Problem 4ALQ Problem 5ALQ Problem 6ALQ: Why do liquids have a vapor pressure? Do all liquids have vapor pressures? Explain. Do solids... Problem 7ALQ Problem 8ALQ: What is the vapor pressure of water at 100C? How do you know? Problem 9ALQ Problem 10ALQ Problem 11ALQ Problem 12ALQ: Why is N2 a gas at room temperature? Explain why lowering the temperature allows for liquid N2 to... Problem 13ALQ Problem 15Q: In the diagram below, which lines represent the hydrogen bonding? a. the dotted lines between the... Problem 16Q Problem 17Q Problem 18Q: The conductivity of silicon is enhanced by doping. What is doping? Problem 19Q: Atoms are assumed to touch in closest packed structures, yet every closest packed unit cell contains... Problem 20Q: Define critical temperature and critical pressure. In terms of the kinetic molecular theory, why is... Problem 21Q Problem 22Q: Describe what is meant by a dynamic equilibrium in terms of the vapor pressure of a liquid. Problem 23Q Problem 24Q Problem 25Q Problem 26Q Problem 27Q: When wet laundry is hung on a clothesline on a cold winter day, it will freeze but eventually dry.... Problem 29Q: You have three covalent compounds with three very different boiling points. All of the compounds... Problem 30Q Problem 31Q: Compare and contrast the structures of the following solids. a. CO2(s) versus H2O(s) b. NaCl(s)... Problem 32Q: Silicon carbide (SiC) is an extremely hard substance that acts as an electrical insulator. Propose a... Problem 34Q: A common prank on college campuses is to switch the salt and sugar on dining hall tables, which is... Problem 35Q: A plot of In (Pvap) versus 1/T (K) is linear with a negative slope. Why is this the case? Problem 36Q Problem 37E: Identify the most important types of interparticle forces present in the solids of each of the... Problem 38E Problem 39E: Predict which substance in each of the following pairs would have the greater intermolecular forces.... Problem 40E: Consider the compounds CI2, HCI. F2, NaF, and HF. Which compound has a boiling point closest to that... Problem 41E Problem 42E: Consider the following electrostatic potential diagrams: Rank the compounds from lowest to highest... Problem 43E: In each of the following groups of substances, pick the one that has the given property. Justify... Problem 44E Problem 45E: The shape of the meniscus of water in a glass tube is different from that of mercury in a glass... Problem 46E Problem 47E: Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a syrupy liquid with a relatively low vapor pressure and a normal... Problem 48E: Carbon diselenide (CSe2) is a liquid at room temperature. The normal boiling point is l25C, and the... Problem 49E: X rays from a copper X-ray tube ( = 154 pm) were diffracted at an angle of 14.22 degrees by a... Problem 50E: The second-order diffraction (n = 2) for a gold crystal is at an angle of22.20 for X rays of 154 pm.... Problem 51E: A topaz crystal has an interplanar spacing (d) of 1.36 (1 = 1 1010 m). Calculate the wavelength... Problem 52E: X rays of wavelength 2.63 were used to analyze a crystal. The angle of first-order diffraction (n =... Problem 53E: Calcium has a cubic closest packed structure as a solid. Assuming that calcium has an atomic radius... Problem 54E: Nickel has a face-centered cubic unit cell. The density of nickel is 6.84 g/cm3. Calculate a value... Problem 55E: A certain form of lead has a cubic closest packed structure with an edge length of 492 pm. Calculate... Problem 56E: The density of polonium metal is 9.2 g/cm3. If the extended lattice of polonium exhibits a simple... Problem 57E: You are given a small bar of an unknown metal X. You find the density of the metal to be 10.5 g/cm3.... Problem 58E: A metallic solid with atoms in a face-centered cubic unit cell with an edge length of 392 pm has a... Problem 59E: Titanium metal has a body-centered cubic unit cell. The density of titanium is 4.50 g/cm3. Calculate... Problem 60E: Barium has a body-centered cubic structure. If the atomic radius of barium is 222 pm, calculate the... Problem 61E: The radius of gold is 144 pm, and the density is 19.32 g/cm3. Does elemental gold have a... Problem 62E: The radius of tungsten is 137 pm and the density is 19.3 g/cm3. Does elemental tungsten have a... Problem 63E: What fraction of the total volume of a cubic closest packed structure is occupied by atoms? (Hint:... Problem 64E: Iron has a density of 7.86 g/cm3 and crystallizes in a body-centered cubic lattice. Show that only... Problem 65E Problem 66E Problem 67E: Selenium is a semiconductor used in photocopying machines. What type of semiconductor would be... Problem 68E Problem 69E Problem 70E Problem 71E: The structures of some common crystalline substances are shown below. Show that the net composition... Problem 72E: The unit cell for nickel arsenide is shown below. What is the formula of this compound? Problem 73E: Cobalt fluoride crystallizes in a closest packed array of fluoride ions with the cobalt ions filling... Problem 74E: The compounds Na2O, CdS, and ZrI4. all can be described as cubic closest packed anions with the... Problem 75E: What is the formula for the compound that crystallizes with a cubic closest packed array of sulfur... Problem 76E Problem 77E: A certain metal fluoride crystallizes in such a way that the fluoride ions occupy simple cubic... Problem 78E: The structure of manganese fluoride can be described as a simple cubic array of manganese ions with... Problem 79E: The unit cell of MgO is shown below l Does MgO have a structure like that of NaCl or ZnS? If the... Problem 80E: In solid KCl the smallest distance between the centers of a. potassium ion and a chloride ion is 314... Problem 81E: The CsCl structure is a simple cubic array of chloride ions with a cesium ion at the center of each... Problem 82E: MnO has either the NaCI type structure or the CsCI type structure (see Exercise 69). The edge length... Problem 83E: What type of solid will each of the following substances form? a. CO2 b. SiO2 c. Si d. CH4 e. Ru f.... Problem 84E: What type of solid will each of the following substances form? a. diamond b. PH3 c. H2 d. Mg e. KCl... Problem 85E: The memory metal, nitinol, is an alloy of nickel and titanium. It is called a memory metal because... Problem 86E: Superalloys have been made of nickel and aluminum. The alloy owes its strength to the formation of... Problem 87E: Perovskite is a mineral containing calcium, titanium, and oxygen. Two different representations of... Problem 88E: A mineral crystallizes in a cubic closest packed array of oxygen ions with aluminum ions in some of... Problem 89E: Materials containing the elements Y, Ba, Cu, and O that are superconductors (electrical resistance... Problem 90E: The structures of another class of ceramic, high-temperature superconductors are shown in figures... Problem 91E: Plot the following data and determine Hvap for magnesium and lithium. In which metal is the bonding... Problem 92E: From the following data for liquid nitric acid, deter mine its heat of vaporization and normal... Problem 93E: In Breckenridge, Colorado, the typical atmospheric pressure is 520. torr. What is the boiling point... Problem 94E: The temperature inside a pressure cooker is 115C. Calculate the vapor pressure of water inside the... Problem 95E: Diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) was one of the first chemicals used as an anesthetic. At 34.6C,... Problem 96E: Mercury is the only metal that is a liquid at room temperature. When mercury vapor is inhaled, it is... Problem 97E: A substance, X, has the following properties: Specific Heat Capacities Hvap 20.kj/mol C(s) 3.0j/gC... Problem 98E: Use the heating-cooling curve below to answer the following questions. a. What is the freezing point... Problem 99E: The molar heat of fusion of sodium metal is 2.60 kJ/mol, whereas its heat of vaporization is 97.0... Problem 100E Problem 101E: What quantity of energy does it take to convert 0.500 kg ice at 20.C to steam at 250.C? Specific... Problem 103E: An ice cube tray contains enough water at 22.0C to make 18 ice cubes that each has a mass of 30.0 g.... Problem 104E: A 0.250-g chunk of sodium metal is cautiously dropped into a mixture of 50.0 g water and 50.0 g ice,... Problem 105E Problem 106E Problem 107E Problem 108E Problem 109E Problem 110E: Consider the following data for xenon: Triple point: 121C, 280 torr Normal melting point: 112C... Problem 111AE Problem 112AE: Consider the following formulas for n-pentane and neopentane: CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 -Pentane Both... Problem 113AE: Some of the physical properties of H2O and D2O are as follows: Property H2O D2O Density at 20C... Problem 114AE: Rationalize the following boiling points: Problem 115AE: Consider the following vapor pressure versus temperature plot for three different substances: A, B,... Problem 116AE: Consider the following enthalpy changes:... Problem 117AE: Consider the following data for an unknown substance X: Hvap = 20.00 kJ/mol Hfus = 5.00 kJ/mol... Problem 118AE: Consider the data for substance X given in Exercise 117. When the temperature of 1.000 mole of X(g)... Problem 119AE Problem 120AE: Boron nitride (BN) exists in two forms. The first is a slippery solid formed from the reaction of... Problem 121AE Problem 122AE: Argon has a cubic closest packed structure as a solid. Assuming that argon has a radius of 190. pm,... Problem 123AE Problem 124AE: A 20.0-g sample of ice at 10.0C is mixed with 100.0 g water at 80.0C. Calculate the final... Problem 125AE Problem 126AE: Carbon tetrachloride. CCl4, has a vapor pressure of 213 torr at 40.C and 836 torr at 80.C. What is... Problem 127AE: A special vessel (see Fig. 10.45) contains ice and supercooled water (both at 10C) connected by... Problem 128AE Problem 129AE: In regions with dry climates, evaporative coolers are used to cool air. A typical electric air... Problem 131CWP: Which of the following compound(s) exhibit only London dispersion intermolecular forces? Which... Problem 132CWP: Which of the following statements about intermolecular forces is( are) true? a. London dispersion... Problem 133CWP Problem 134CWP: Aluminum has an atomic radius of 143 pm and forms a solid with a cubic closest packed structure.... Problem 135CWP: Pyrolusite is a mineral containing manganese ions and oxide ions. Its structure can best be... Problem 136CWP: The structure of the compound K2O is best described as a cubic closest packed array of ox.ide ions... Problem 137CWP Problem 138CWP: Some ice cubes at 0c with a total mass of 403 g are placed in a microwave oven and subjected to 750.... Problem 139CWP: The enthalpy of vaporization for acetone is 32.0 kJ/mol. The normal boiling point for acetone is... Problem 140CWP Problem 141CP: When I mole of benzene is vaporized at a constant pressure of 1.00 atm and at its boiling point of... Problem 142CP: You and a friend each synthesize a compound with the formula XeCI2F2. Your compound is a liquid and... Problem 143CP Problem 144CP Problem 145CP: Consider two different organic compounds, each with the formula C2H6O. One of these compounds is a... Problem 146CP: Rationalize the differences in physical properties in terms of intermolecular forces for the... Problem 147CP Problem 148CP: Some ionic compounds contain a mixture of different charged cations. For example, wstite is an oxide... Problem 149CP: Some ionic compounds contain a mixture of different charged cations. For example, some titanium... Problem 150CP: Spinel is a mineral that contains 37.9% aluminum, 17.1% magnesium, and 45.0% oxygen, by mass, and... Problem 151CP: Mn crystallizes in the same type of cubic unit cell as Cu. Assuming that the radius of Mn is 5.6%... Problem 152CP: You are asked to help set up a historical display in the park by stacking some cannonballs next to a... Problem 153CP: Some water is placed in a sealed glass container connected to a vacuum pump (a device used to pump... Problem 154CP: The molar enthalpy of vaporization of water at 373 K and 1.00 atm is 40.7 kJ/mol. What fraction of... Problem 155CP Problem 156CP: Rubidium chloride has the sodium chloride structure at normal pressures but assumes the cesium... Problem 157IP Problem 158IP: A metal burns in air at 600c under high pressure to form an oxide with formula MO2. This compound is... Problem 159IP Problem 160MP: General Zod has sold Lex Luthor what Zod claims to be a new copper-colored form of kryptonite, the... format_list_bulleted

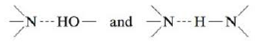

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div




