
Viking Corporation (a U.S.-based company) has a subsidiary in Japan that imports finished products from unrelated suppliers in China and sells all of its purchases to customers in Japan. Cost of goods sold represents 75 percent of total costs. Budgets in Japanese yen (JPY) and U.S. dollars (USD) using the beginning of period exchange rate of USD 0.010 per JPY 1.00 are as follows:
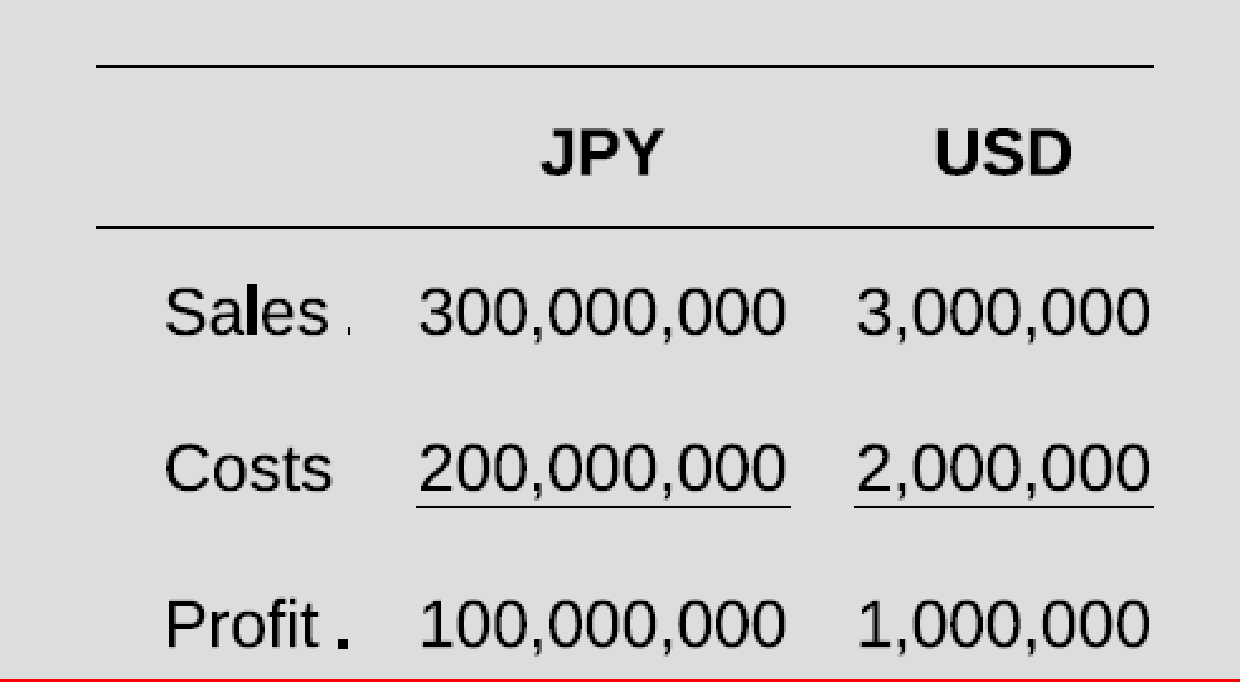
During the budget period, the JPY decreased in value by 20 percent against world currencies, such that the end-of-period exchange rate was USD 0.008 per JPY 1.00. As a result of the increased cost of imports, the manager of the Japanese subsidiary switched to purchasing some of the goods it sells from Japanese manufacturers. Assuming that Viking uses the end-of-period exchange rate to track actual performance, actual results in JPY and USD are as follows:
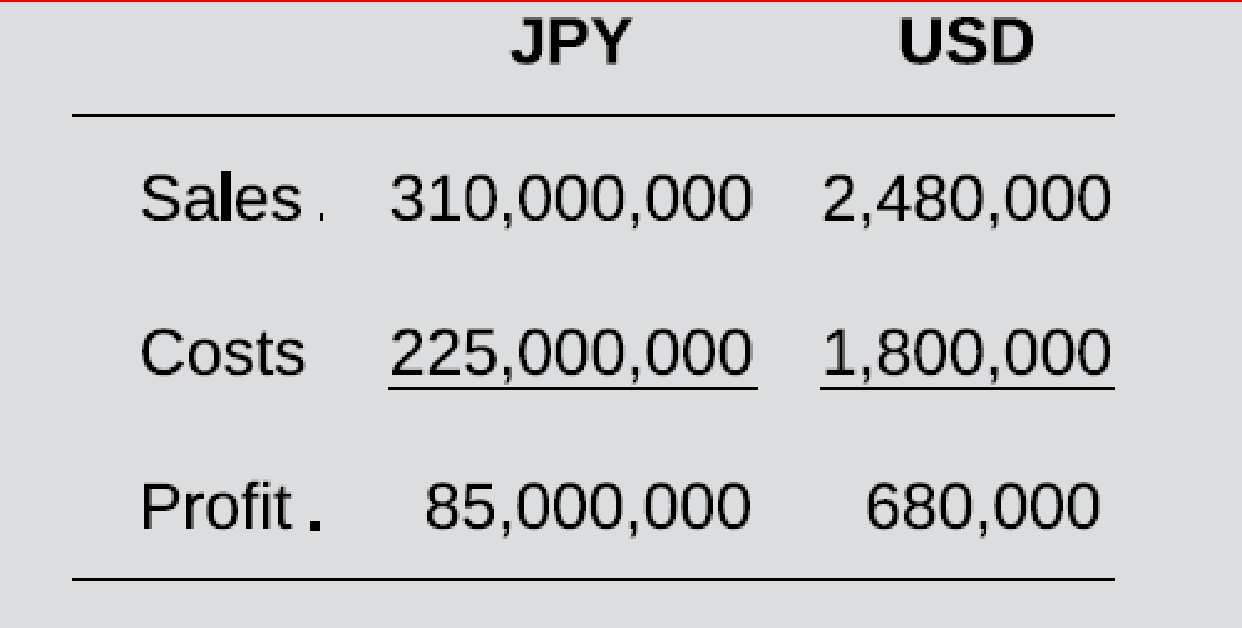
As a result, there is an unfavorable total
Required:
- a. Determine the amount of the USD 320,000 unfavorable total budget variance caused by the change in the USD/JPY exchange rate.
- b. Taking economic exposure to foreign exchange risk into consideration, estimate what profit would have been (in both JPY and USD) if the Japanese subsidiary’s manager had not taken advantage of the decrease in value of the JPY.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL ACCOUNTING>CUSTOM<
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
