
(a)
Bonds
Bonds are a kind of interest bearing notes payable, usually issued by companies, universities and governmental organizations. It is a debt instrument used for the purpose of raising fund of the corporations or governmental agencies. If selling price of the bond is equal to its face value, it is called as par on bond. If selling price of the bond is lesser than the face value, it is known as discount on bond. If selling price of the bond is greater than the face value, it is known as premium on bond.
To Prepare: The
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.8AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of bonds of Corporation F on January 1, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1, 2017 | Cash (1) | $2,040,000 | |
| Premium on bonds payable (2) | $40,000 | ||
| Bonds payable | $2,000,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of bonds payable at premium value for Corporation F ) |
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculate Cash received from issuance of bonds payable of Corporation F as shown below:
Calculate premium on bonds payable of Corporation F as shown below:
Explanation of Solution
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash account for $2,040,000.
- Premium on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit premium on bonds payable for $40,000.
- Bonds payable is a long-term liability, and increased. Therefore, credit bonds payable account for $2,000,000.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the accrued interest expense, and premium on amortize bond for Corporation F on December 31, 2017.
Answer to Problem 10.8AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the accrued interest expense and premium on amortize bond for Corporation F on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2017 | Interest expense (3) | $132,000 | |
| Premium on bonds payable (1) | $8,000 | ||
| Interest payable (2) | $140,000 | ||
| (To record the accrued interest expense and premium on amortize bond for Corporation F) |
Table (2)
Working notes:
Calculate premium of bonds payable for Corporation F as shown below:
Calculate interest payable amount of Corporation F as shown below:
Calculate interest expense of Corporation F as shown below:
Explanation of Solution
- Interest expense is a component of
stockholders’ equity , and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $132,000. - Premium on bonds payable is a contra liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit premium on bonds payable for $8,000.
- Interest payable is a
- current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $140,000.
(b)
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the issuance of bonds of Corporation F on January 1, 2017.
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.8AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of bonds of Corporation F on January 1, 2017as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1, 2017 | Cash (1) | $1,940,000 | |
| Discount on bonds payable (2) | $60,000 | ||
| Bonds payable | $2,000,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of bonds payable at discount value for Corporation F ) |
Table (3)
Working notes:
Calculate Cash received from issuance of bonds payable of Corporation F as shown below:
Calculate discount on bonds payable of Corporation F as shown below:
Explanation of Solution
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash account for $1,940,000.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit discount on bonds payable for $60,000.
- Bonds payable is a long-term liability, and increased. Therefore, credit bonds payable account for $2,000,000.
To Prepare: The journal entry to record the accrued interest expense and premium on amortize bond for Company O on December 31, 2017.
Answer to Problem 10.8AP
Prepare the journal entry to record the accrued interest expense and premium on amortize bond for Company O on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| December 31, 2017 | Interest expense (3) | $152,000 | |
| Discount on bonds payable (1) | $12,000 | ||
| Interest payable (2) | $140,000 | ||
| (To record the accrued interest expense and discount on amortize bond for Corporation F) |
Table (4)
Working notes:
Calculate discount of bonds payable for Company O as shown below:
Calculate interest payable amount of Company O as shown below:
Calculate interest expense of Company O as shown below:
Explanation of Solution
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $152,000.
- Discount on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit discount on bonds payable for $12,000.
- Interest payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit interest payable account for $152,000.
(c-1)
To Prepare: The balance sheet presentation for issuance of bonds at December 31, 2017 using the selling price of $102.
(c-1)
Answer to Problem 10.8AP
Prepare the balance sheet presentation for issuance of bonds at December 31, 2017 using the selling price of $102 as shown below:
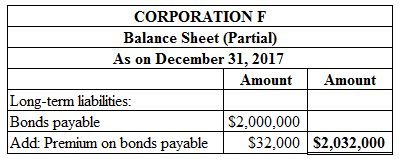
Figure (1)
Explanation of Solution
Premium on bonds payable for the year 2017 is $32,000 which is calculated by deducting from premium on amortize of bond for the year 2017 is $8,000 from premium on bonds payable on January 1, 2017 is $40,000.
(c-2)
To Prepare: The balance sheet presentation for issuance of bonds at December 31, 2017 using the selling price of $97.
(c-2)
Answer to Problem 10.8AP
Prepare the balance sheet presentation for issuance of bonds at December 31, 2017 using the selling price of $97 as shown below:
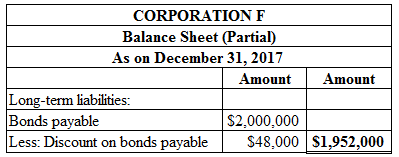
Figure (2)
Explanation of Solution
Discount on bonds payable for the year 2017 is $48,000 which is calculated by deducting from discount on amortization of bond for the year 2017 for $12,000, from discount on bonds payable on January 1, 2017 for $60,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 8th Edition
- Greenfield Corporation budgeted 3,500 pounds of material costing $6.80 per pound to produce 1,500 units. The company actually used 4,200 pounds which cost $7.10 per pound to produce 1,500 units. What is the direct materials price variance?arrow_forwardCan you solve this financial accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardUsing the retail method, what is the estimated cost of the merchandise inventory on October 31?arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning


