
(a)
Balance Sheet
This is a financial statement that shows the assets owned, and the liabilities owed to the creditors and the owners (
To Prepare: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
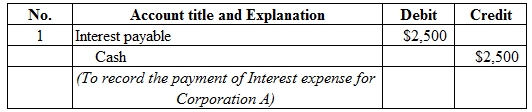
Figure (1)
Description:
- Interest payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit interest payable account for $2,500.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $2,500.

Figure (2)
Description:
- Inventory is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit inventory account for $241,100.
- Accounts payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit accounts payable account for $241,100.
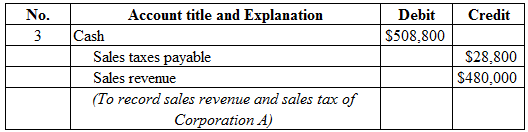
Figure (3)
Description:
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash is a current asset account for $508,800.
- Sales taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit sales taxes payable account for $28,800.
- Sales revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit sales revenue account for $480,000.
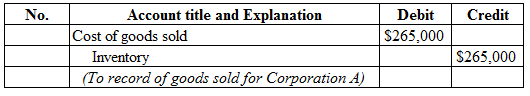
Figure (4)
Description:
- Cost of goods sold is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit cost of goods sold account for $265,000.
- Inventory is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit inventory account for $265,000.

Figure (5)
Description:
- Accounts payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit accounts payable account for $230,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $230,000.
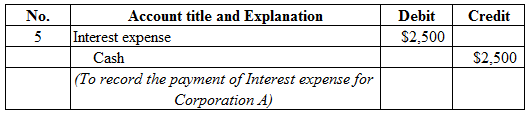
Figure (6)
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $2,500.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $2,500.
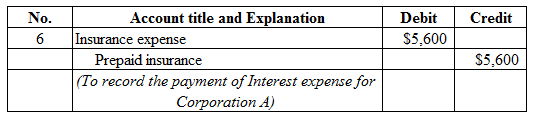
Figure (7)
Description:
- Insurance expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit insurance expense account for $5,600.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $5,600.

Figure (8)
Description:
- Prepaid insurance is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit prepaid insurance account for $10,200.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $10,200.
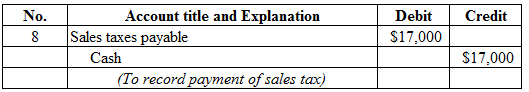
Figure (9)
Description:
- Sales taxes payable is a current liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit sales taxes payable account for $17,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $17,000.
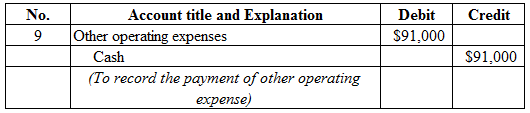
Figure (10)
Description:
- Other operating expenses are a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit other operating expenses account for $91,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $91,000.
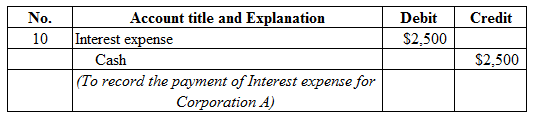
Figure (11)
Description:
- Interest expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit interest expense account for $2,500.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $2,500.
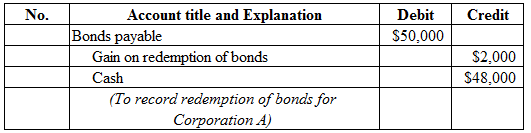
Figure (12)
Description:
- Bonds payable is a liability, and decreased. Therefore, debit bonds payable account for $50,000.
- Gain on redemption of bonds is a component of stockholders’ equity, and increased it. Therefore, credit gain on redemption of bonds account for $2,000.
- Cash is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $48,000.
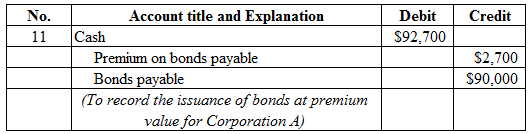
Figure (13)
Description:
- Cash is a current asset, and increased. Therefore, debit cash account for $92,700.
- Premium on bonds payable is a contra liability, and increased. Therefore, credit premium on bonds payable for $2,700.
- Bonds payable is a long-term liability, and increased. Therefore, credit bonds payable account for $90,000.
To Prepare: The
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjustment entries of Corporation as shown below:
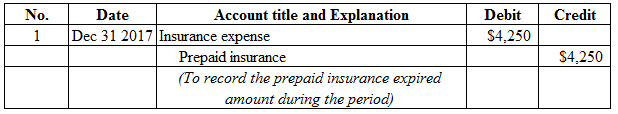
Figure (14)
Working note:
Calculate interest expense as shown below:
Description:
Insurance expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit insurance expense account for $4,250.
Prepaid insurance is a current asset, and decreased. Therefore, credit cash account for $4,250.
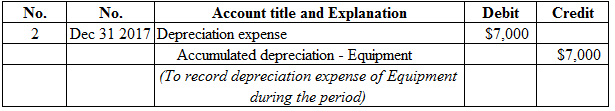
Figure (15)
Description:
Depreciation expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit depreciation expense account for $7,000.Accumulated depreciation – equipment is a contra asset, and increased. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation - equipment account for $7,000.
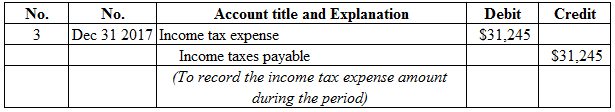
Figure (16)
Working note:
Calculate income tax expense as shown below:
Description:
- Income tax expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and decreased it. Therefore, debit income tax expense account for $31,245.
- Income taxes payable is a current liability, and increased. Therefore, credit income taxes payable account for $31,245.
To Prepare: The T-Accounts of Corporation A.
Answer to Problem 10.1CACR
| Cash | |||
| Bal. | $30,000 | $2,500 | |
| $508,800 | $230,000 | ||
| $92,700 | $2,500 | ||
| $10,200 | |||
| $17,000 | |||
| $91,000 | |||
| $2,500 | |||
| $48,000 | |||
| Bal. | $227,800 | ||
Table (1)
| Inventory | |||
| Bal. | $30,750 | $265,000 | |
| $241,100 | |||
| Bal. | $6,850 | ||
Table (2)
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| Bal. | $5,600 | $5,600 | |
| $10,200 | $4,250 | ||
| Bal. | $5,950 | ||
Table (3)
| Equipment | |||
| Bal. | $38,000 | ||
Table (4)
| Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment | |||
| $7,000 | |||
Table (5)
| Accounts Payable | |||
| $230,000 | Bal. | $13,750 | |
| $241,100 | |||
| Bal. | $24,850 | ||
Table (6)
| Other Operating Expenses | |||
| $91,000 | |||
Table (7)
| Interest Expense | |||
| $2,500 | |||
| $2,500 | |||
| Bal. | $5,000 | ||
Table (8)
| Income Tax Expense | |||
| $31,245 | |||
Table (9)
| Interest Payable | |||
| $2,500 | Bal. | $2,500 | |
| Bal. | $0 | ||
Table (10)
| Sales Taxes Payable | |||
| $17,000 | $28,800 | ||
| Bal. | $11,800 | ||
Table (11)
| Income Taxes Payable | |||
| $31,245 | |||
Table (12)
| Bonds Payable | |||
| $50,000 | Bal. | $50,000 | |
| $90,000 | |||
| Bal. | $90,000 | ||
Table (13)
| Premium on Bonds Payable | |||
| $2,700 | |||
Table (14)
| Common Stock | |||
| Bal. | $25,000 | ||
Table (15)
| Bal. | $13,100 | ||
Table (16)
| Sales Revenue | |||
| $480,000 | |||
Table (17)
| Cost of Goods sold | |||
| $265,000 | |||
Table (18)
| Depreciation Expense | |||
| $7,000 | |||
Table (19)
| Insurance Expense | |||
| $5,600 | |||
| $4,250 | |||
| Bal. | $9,850 | ||
Table (20)
| Gain on Redemption of Bonds | |||
| Bal. | $2,000 | ||
Table (21)
Explanation of Solution
Normal balance of assets account, expenses, losses account is debit balance. Hence, a debit increases these accounts and credit decreases these accounts.
Normal balance of liabilities account, capital account, revenue account and gains is credit balance. Hence, a debit decreases these accounts and credit increases these accounts.
(b)
To Prepare: The adjusted trail balance of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjusted trail balance of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
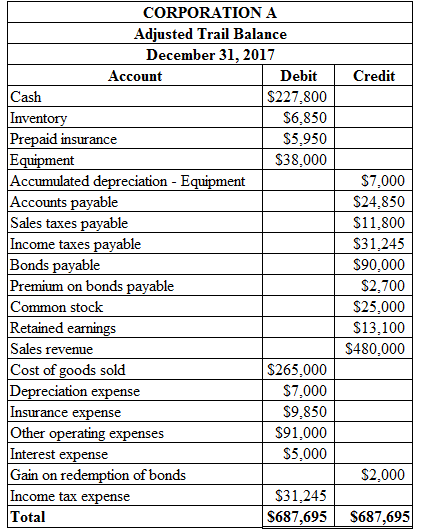
Figure (17)
(c)
To Prepare: The income statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.1CACR
Prepare the income statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
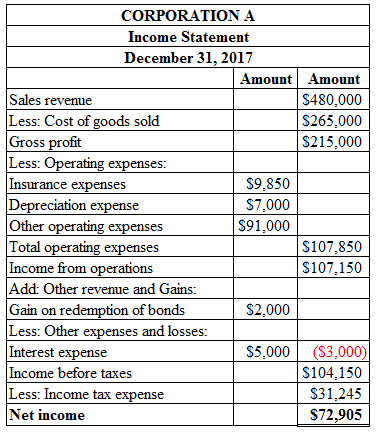
Figure (18)
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is calculated by deducting cost of goods sold from sales revenue. Total operating expenses are calculated by adding insurance expense, depreciation expense, and other operating expenses. Income from operations is calculated by deducting total operating expenses from gross profit. Income before taxes is calculated by deducting interest expenses and adding gain on redemption of bonds from income from operations. Income tax expense is calculated by multiplying income from operations with tax rate. Net income is calculated by deducting income tax expense from income before taxes.
To Prepare: The retained earnings statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
Answer to Problem 10.1CACR
Prepare retained earnings statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
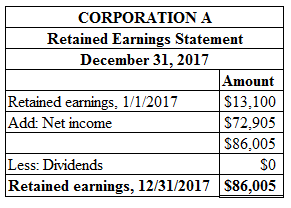
Figure (19)
Explanation of Solution
Ending retained earnings is calculated by adding opening retained earnings and net income and then deducting the dividends. Therefore, ending retained earnings is $86,005.
To Prepare: The classified balance sheet statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare classified balance sheet statement of Corporation A on December 31, 2017 as shown below:
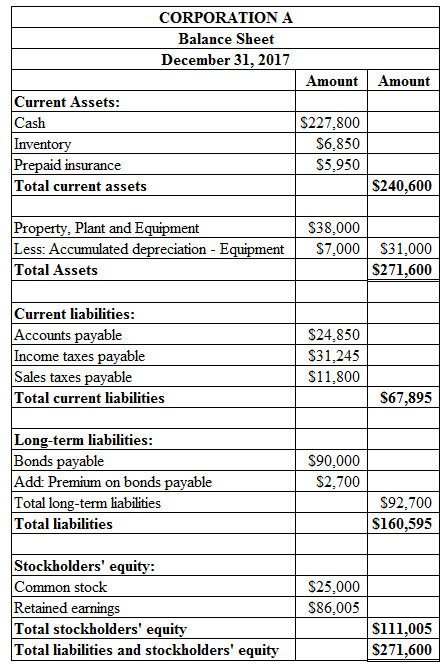
Figure (20)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Financial Accounting: Tools for Business Decision Making, 8th Edition
- Calculate the net sales revenuearrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardCariman contracts delivery drivers to service customers. Cariman owns the vans and pays for the gas. With reference to the following independent situations for Cariman, determine where (a) responsibility and (b) controllability lie. Suggest what might be done to solve the problem or to improve the situation: (20 marks)a) In the manufacturing plant the production manager is not happy with the material that the purchasing manager has been purchasing. In May the production manager stops requesting materials from the supply warehouse, and starts purchasing them directly from a different materials supplier. Actual materials costs in May are higher than budgeted.b) Overhead costs in the manufacturing plant for June are much higher than budgeted. Investigation reveals a utility rate hike in effect that was not figured into the budget.arrow_forward
- General accounting questionarrow_forwardThe Snape Corporation has the following data for 2014: Selling price per unit $10 Variable costs per unit $6 Fixed costs Units sold $20,000 12,000 Snape's 2014 operating leverage is: a) 0.50 b) 2.00 c) 4.00 d) 1.71arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





