
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is generally considered as a simplified structure of any molecule or atom. Lewis structure for any atom or molecule depicts the valence electrons as dots around the element’s symbol present in the molecule along with the bonds that connect them. Every element tries to complete an octet except the hydrogen atom.
Every element in the Lewis structure tries to attain eight electrons in its valence shell by transfer or share of electrons. This rule is known as the octet rule.
To draw the Lewis structure of the molecule there are following steps:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Step 5: Convert the lone pair into bond pair.
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.76P
The Lewis structure for
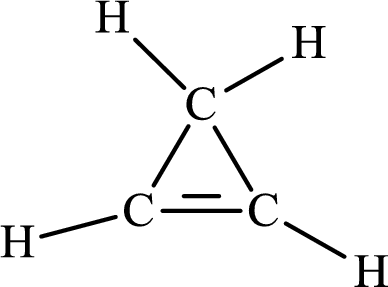
The carbon-carbon single bond has the bond order 1 and carbon-carbon double bond has the bond order 2.
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons of
Substitute 3 for the total number of
In
The Lewis structure of
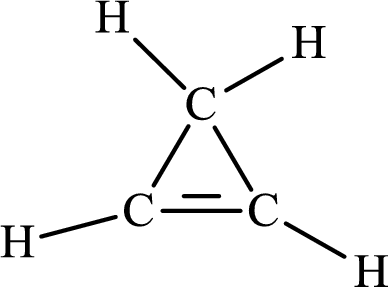
The single bond has the bond order 1 and double bond has the bond order 2. Therefore, the carbon-carbon single bond has the bond order 1 and carbon-carbon double bond has the bond order 2.
The single bond has the bond order 1, the double bond has the bond order 2 and triple bond has the bond order 3.
(b)
Interpretation:
A Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is generally considered as a simplified structure of any molecule or atom. Lewis structure for any atom or molecule depicts the valence electrons as dots around the element’s symbol present in the molecule along with the bonds that connect them. Every element tries to complete an octet except the hydrogen atom.
Every element in the Lewis structure tries to attain eight electrons in its valence shell by transfer or share of electrons. This rule is known as octet rule.
To draw the Lewis structure of the molecule there are following steps:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Step 5: Convert the lone pair into bond pair.
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.76P
The Lewis structure of
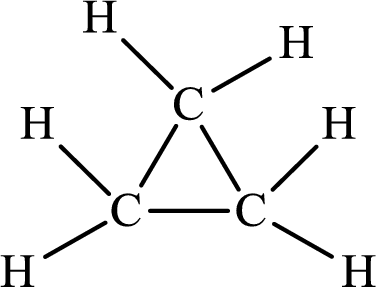
There is only single bond in
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons of
Substitute 3 for the total number of
In
The Lewis structure of
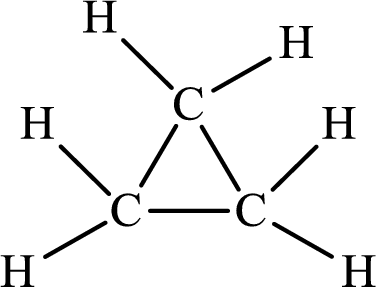
The single bond has the bond order 1 and double bond has the bond order 2. Therefore, there is only single bond in
The single bond has the bond order 1, double bond has the bond order 2 and triple bond has the bond order 3.
(c)
Interpretation:
A Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is generally considered as a simplified structure of any molecule or atom. Lewis structure for any atom or molecule depicts the valence electrons as dots around the element’s symbol present in the molecule along with the bonds that connect them. Every element tries to complete an octet except the hydrogen atom.
Every element in the Lewis structure tries to attain eight electrons in its valence shell by transfer or share of electrons. This rule is known as the octet rule.
To draw the Lewis structure of the molecule there are following steps:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Step 5: Convert the lone pair into bond pair.
(c)
Answer to Problem 10.76P
The Lewis structure of
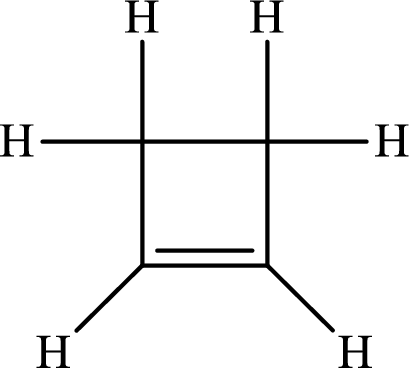
The carbon-carbon single bond has the bond order 1 and carbon-carbon double bond has the bond order 2.
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons of
Substitute 4 for the total number of
In
The Lewis structure of
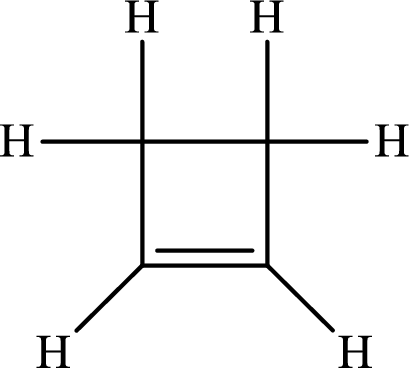
The single bond has the bond order 1 and double bond has the bond order 2. Therefore, the carbon-carbon single bond has the bond order 1 and carbon-carbon double bond has the bond order 2.
The single bond has the bond order 1, the double bond has the bond order 2 and triple bond has the bond order 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
A Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is generally considered as a simplified structure of any molecule or atom. Lewis structure for any atom or molecule depicts the valence electrons as dots around the element’s symbol present in the molecule along with the bonds that connect them. Every element tries to complete an octet except the hydrogen atom.
Every element in the Lewis structure tries to attain eight electrons in its valence shell by transfer or share of electrons. This rule is known as the octet rule.
To draw the Lewis structure of the molecule there are following steps:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Step 5: Convert the lone pair into bond pair.
(d)
Answer to Problem 10.76P
The Lewis structure of
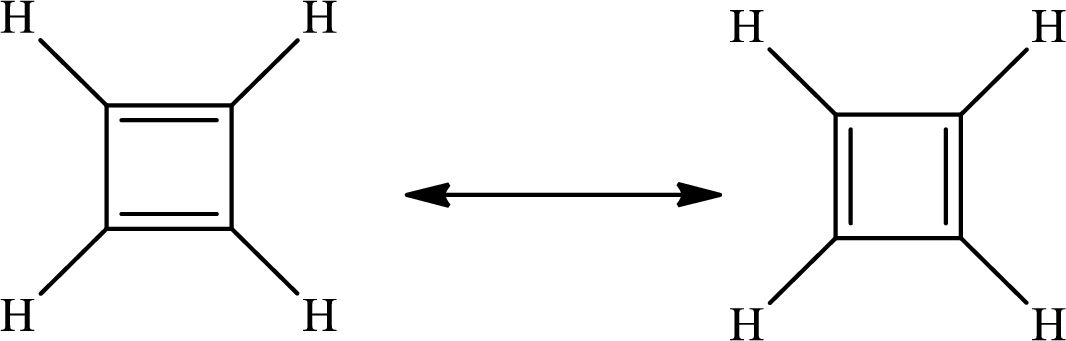
The average bond order in
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons of
Substitute 4 for the total number of
In
There is alternate single and double present in the ring so the molecule will show resonance.
The Lewis structure of
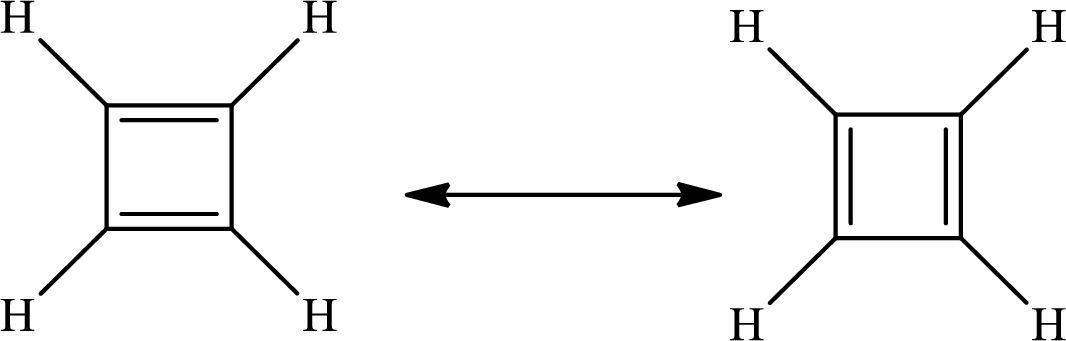
There are 4 single bonds and 2 double bonds in
The formula to calculate the average bond order in
Substitute 6 for the number of shared electron pair and 4 for the number of bonded atoms in equation (5).
The single bond has the bond order 1, the double bond has the bond order 2 and triple bond has the bond order 3.
(e)
Interpretation:
A Lewis structure for
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure is generally considered as a simplified structure of any molecule or atom. Lewis structure for any atom or molecule depicts the valence electrons as dots around the element’s symbol present in the molecule along with the bonds that connect them. Every element tries to complete an octet except the hydrogen atom.
Every element in the Lewis structure tries to attain eight electrons in its valence shell by transfer or share of electrons. This rule is known as the octet rule.
To draw the Lewis structure of the molecule there are following steps:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Step 5: Convert the lone pair into bond pair.
(e)
Answer to Problem 10.76P
The Lewis structure of
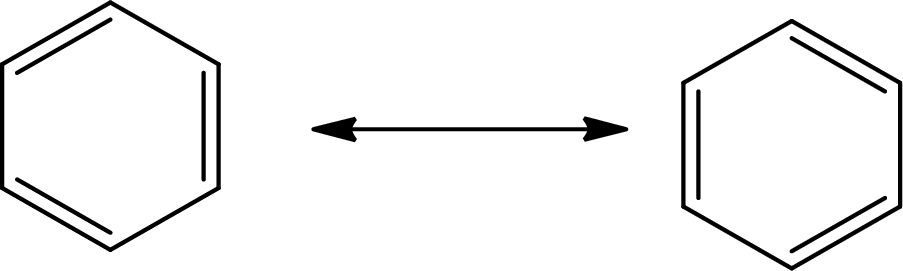
The average bond order in
Explanation of Solution
The total number of valence electrons of
Substitute 6 for the total number of
In
There is alternate single and double present in the ring so the molecule will show resonance.
The Lewis structure of
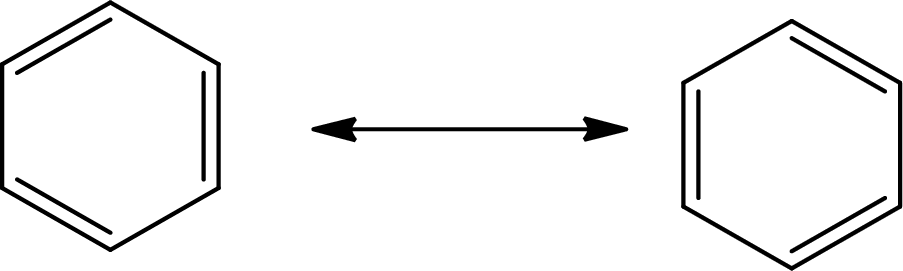
There are 6 single bonds and 3 double bonds in
The formula to calculate the average bond order in
Substitute 9 for the number of shared electron pair and 6 for the number of bonded atoms in equation (7).
The single bond has the bond order 1, the double bond has the bond order 2 and triple bond has the bond order 3.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





