
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The mechanism for epoxides under neutral or basic conditions consists of an
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The product of the given reaction is:
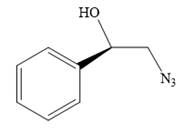
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
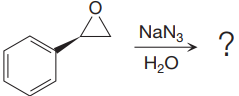
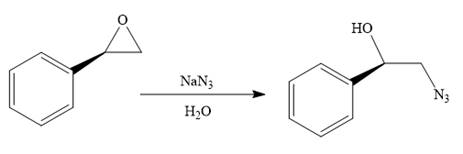
When the given epoxide is treated with sodium azide (basic conditions), the azide ion in sodium azide acts as a nucleophile and attacks the less substituted carbon atom (highlighted in red) of the epoxide. Due to this, the highly strained epoxide ring opens and the azide gets attached to the less substituted carbon atom. In the presence of a solvent such as water, the negatively charged oxygen atom is protonated resulting in the final product. The product of the reaction when the given epoxide is treated with sodium azide is as below:
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under neutral or basic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks the least substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides react readily under neutral, basic, or acidic conditions. Epoxides can undergo
The mechanism for the epoxides under neutral or basic conditions consists of an
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The product of the given reaction is:
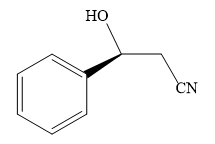
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
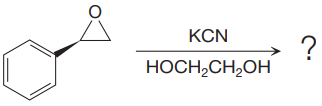
The given reaction conditions are basic as the potassium cyanide is a weak base and nucleophile.
When the given epoxide is treated with potassium cyanide (neutral conditions), the cyanide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the least substituted carbon atom of the epoxide. Due to this, the highly strained epoxide ring opens and the cyanide ion gets attached to the carbon. In the presence of a solvent such as ethanediol, the negatively charged oxygen atom is protonated resulting in the final product. The product of the reaction when the given epoxide is treated with sodium azide is as below:
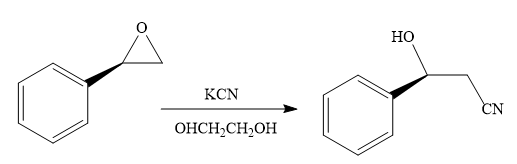
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under neutral or basic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks the least substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides react readily under neutral, basic, or acidic conditions. Epoxides can undergo
Under acidic conditions, the first step is the protonation of
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The product of the given reaction is:
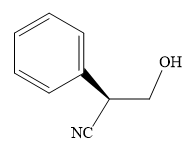
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
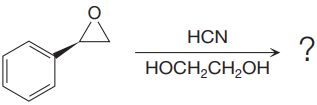
The given reaction conditions are acidic as hydrogen cyanide is a weak acid.
When the given epoxide is treated with hydrogen cyanide (acidic conditions), the first step is the protonation of the epoxide oxygen atom. Due to this, a partial positive charge is generated on both carbon atoms in the epoxide. Out of the two carbon atoms, the one that is most substituted would be able to stabilize the partially developed charge, and thus, in the second step, the nucleophile, cyanide ion attacks the most substituted carbon atom from the side opposite to the
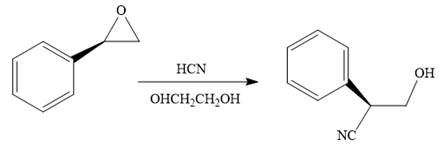
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under acidic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks the most substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides react readily under neutral, basic, or acidic conditions. Epoxides can undergo
The mechanism for the epoxides under neutral or basic conditions consists of an
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The product of the given reaction is:
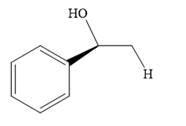
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
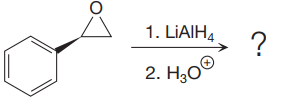
The given reaction conditions are basic as lithium aluminum hydride is a strong base.
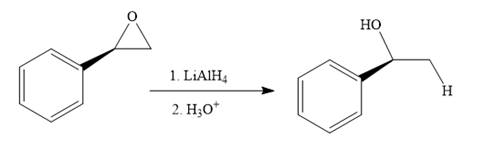
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under neutral or basic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks the least substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides react readily under neutral, basic, or acidic conditions. Epoxides can undergo
Under acidic conditions, the first step is the protonation the
Answer to Problem 10.53P
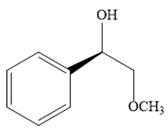
The product of the given reaction is:
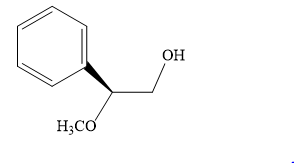
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
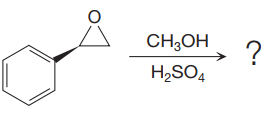
The given reaction conditions are methanol in sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid. When it is treated with methanol, it will produce protonated methanol which is a strongest known acid. When the given epoxide is treated with protonated methanol, (highly acidic conditions), the first step is the protonation of the oxygen atom in the epoxide. Due to this, a partial positive charge is generated on both the carbon atoms in the epoxide. Out of the two carbon atoms, the one that is most substituted would be able to stabilize the partially developed positive charge. Thus, in the second step, the nucleophile, methoxide ion attacks the most substituted carbon atom from the side opposite to the protonated
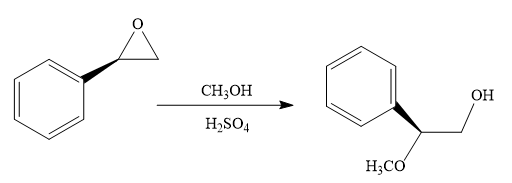
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under acidic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks on the most substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides react readily under neutral, basic, or acidic conditions. Epoxides can undergo
The mechanism for the epoxides under neutral or basic conditions consists of an
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The product of the given reaction is:
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
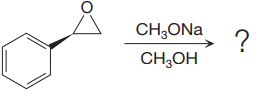
When the given epoxide is treated with sodium methoxide in methanol (basic conditions), the methoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the least substituted carbon atom of the epoxide. Due to this, the highly strained epoxide ring opens and the methoxide ion gets attached to the least substituted carbon atom. The product of the reaction when the given epoxide is treated with sodium methoxide in methanol is as below:
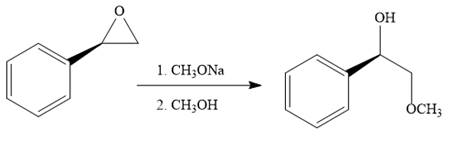
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under neutral or basic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks the least substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
(g)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides react readily under neutral, basic, or acidic conditions. Epoxides can undergo
The mechanism for the epoxides under neutral or basic conditions consists of an
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The product of the given reaction is:
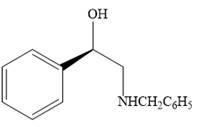
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
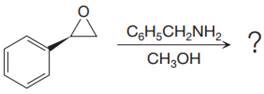
When the given epoxide is treated with benzyl
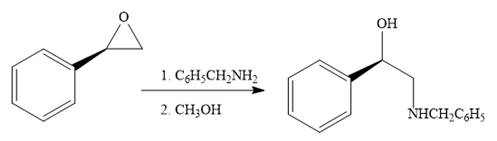
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under neutral or basic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks on the least substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
(h)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides react readily under neutral, basic, or acidic conditions. Epoxides can undergo
The mechanism for the epoxides under neutral or basic conditions consists of an
Answer to Problem 10.53P
The product of the given reaction is:
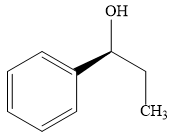
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is:
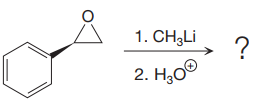
Methyl lithium is an inorganic methylating agent. When the given epoxide is treated with methyl lithium (basic conditions), the methyl anion acts as a nucleophile and attacks the least substituted carbon atom of the epoxide. Due to this, the highly strained epoxide ring opens. In the second step, acidic workup is important so as to protonate the negatively charged oxygen atom.
The product of the reaction when the given epoxide is treated with methyl lithium in the acidic workup is as below:
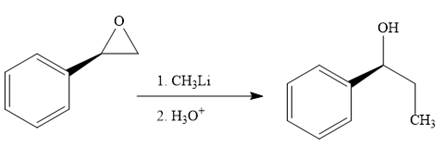
Epoxides can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions under neutral or basic conditions in which the nucleophile attacks the least substituted carbon atom in the epoxide.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forwardProvide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forward
- Identify the 'cartoon' drawing of the acceptor orbital in the first mechanistic step of an electrophilic addition reaction of butadiene with HBr. Pleasearrow_forwardH- H H H H H H Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H H H A. H H H H-C CI H H D. H H H H H H C C -H H C C H H H H B. H CI H H- C C H H H H E. H CI H C.arrow_forwardWhy doesn't this carry on to form a ring by deprotonating the alpha carbon and the negatively-charged carbon attacking the C=O?arrow_forward
- 6. A solution (0.0004 M) of Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (see the structural drawing below) in chloroform has absorption bands at: 350 nm (absorbance A = 2.34); 514 nm(absorbance A = 0.0532); Calculate the molar absorptivity values for these bands. Comment on their possible nature (charge transfer transitions or d-d S N- transitions?). (4 points)arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6], [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 4. Room temperature (20°C) measurement of molar magnetic susceptibility (Xm) for Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2×6H2O is 1.1888 x 102 cgs (Gaussian units). Calculate effective magnetic moment and provide a number of unpaired electrons for the iron ion. Use this number to rationalize the coordination geometry around iron center. (4 points)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

