
COST ACCOUNTING
16th Edition
ISBN: 9781323694008
Author: Horngren
Publisher: PEARSON C
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.40P
Cost estimation, cumulative average-time learning curve. The Pacific Boat Company, which is under contract to the U S. Navy, assembles troop deployment boats. As part of its research program, it completes the assembly of the first of a new model (PT109) of deployment boats. The Navy is impressed with the PT109. It requests that Pacific Boat submit a proposal on the cost of producing another six PT109s. Pacific Boat reports the following cost information for the first PT109 assembled and uses a 90% cumulative average-time learning model as a basis for
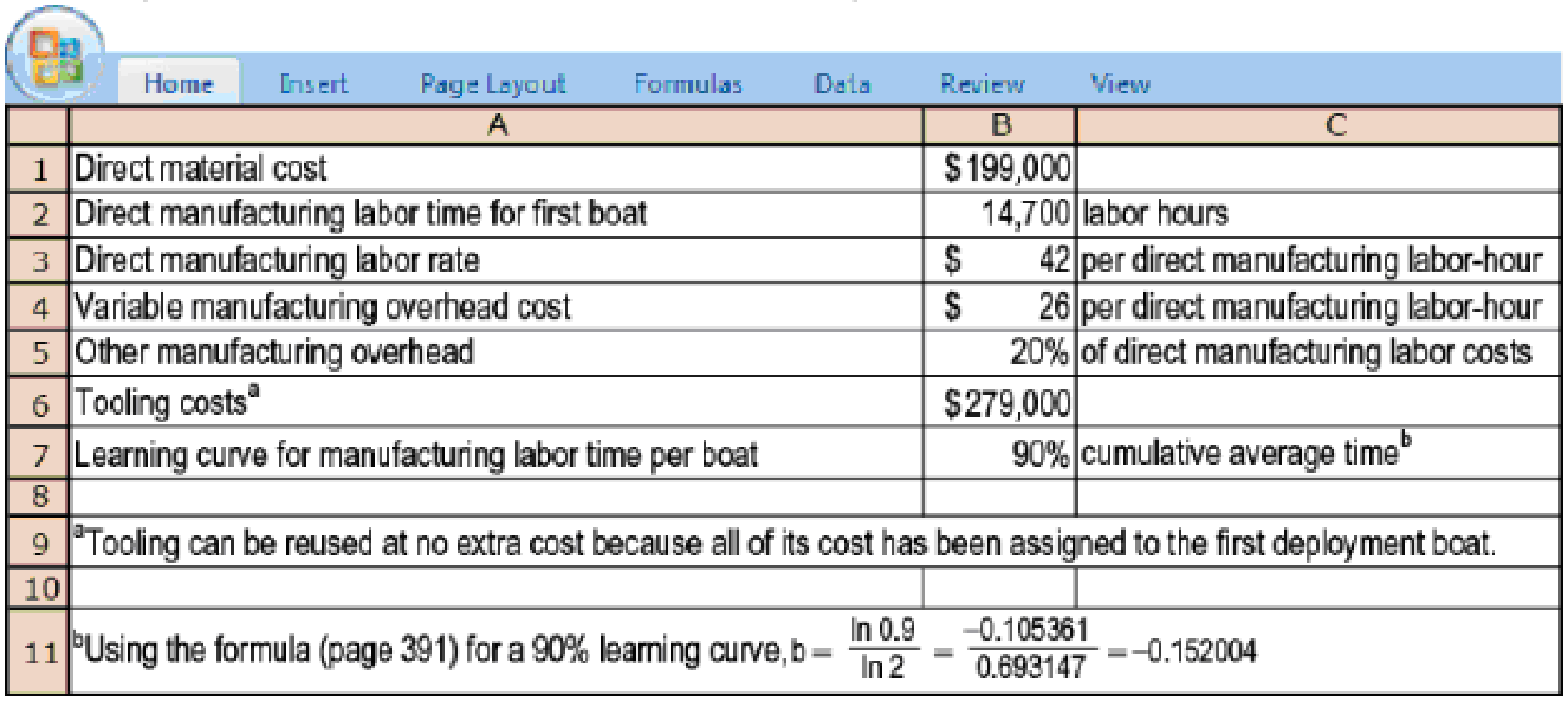
- 1. Calculate predicted total costs of producing the six PT109s for the Navy. (Pacific Boat will keep the first deployment boat assembled, costed at $1,477,600, as a demonstration model for potential customers.)
Required
- 2. What is the dollar amount of the difference between (a) the predicted total costs for producing the six PT109s in requirement 1 and (b) the predicted total costs for producing the six PT109s, assuming that there is no learning curve for direct manufacturing labor? That is, for (b) assume a linear function for units produced and direct manufacturing labor-hours.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Cost estimation, cumulative average-time learning curve. The Pacic Boat Company, which is under contract to the U.S. Navy, assembles troop deployment boats. As part of its research program, it completes the assembly of the rst of a new model (PT109) of deployment boats. The Navy is impressed with the PT109. It requests that Pacic Boat submit a proposalon the cost of producing another six PT109s. Pacic Boat reports the following cost information for the rst PT109 assembled and uses a 90% cumulative average-time learning model as a basis for forecasting direct manufacturing laborhours for the next six PT109s. (A 90% learning curve means b = −0.152004.)
An automobile spare part manufacturer has set up a project for developing a new machine
for one of its production lines. The engineering department has provided a project proposal
that estimates the following investment requirements:
) An initial investment of RM 300,000 to be paid for purchasing the new machine.
i) An additional cost is needed to install the machines and integrate it into the overall
production system and it is estimated to take one (1) year for completion. There are
three cost categories involved:
• Engineering labor cost, estimated to be 1200 hours at a cost of RM 100/hour.
• None-engineering labor cost, estimated to be 3000 hours at a cost of RM 50/hour.
Assorted material cost, estimated to be RM 100,000.
iv) The machine has to be overhauled every 2 year, and it costs RM 20.000 beginning
the third year of the project. They will not overhaul the machine in the last year of its
life.
v) The production will be started in the second year, and it will be up-to-speed by…
The engineering department have appointed you on a task purchasing new forklift to transport sheet metal part. From your research, two types of forklift have been finalized as shown in Table 1 for their material handling plan in 6 years. The company also has another option; using manual material handling with 3 workers and the salary of each worker is RM1,200 per month. Suggest TWO (2) decisions on material handling alternatives to the company with suitable assumptions.
Chapter 10 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING
Ch. 10 - What two assumptions are frequently made when...Ch. 10 - Describe three alternative linear cost functions.Ch. 10 - What is the difference between a linear and a...Ch. 10 - High correlation between two variables means that...Ch. 10 - Name four approaches to estimating a cost...Ch. 10 - Describe the conference method for estimating a...Ch. 10 - Describe the account analysis method for...Ch. 10 - List the six steps in estimating a cost function...Ch. 10 - When using the high-low method, should you base...Ch. 10 - Describe three criteria for evaluating cost...
Ch. 10 - Define learning curve. Outline two models that can...Ch. 10 - Discuss four frequently encountered problems when...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.13QCh. 10 - All the independent variables in a cost function...Ch. 10 - Multicollinearity exists when the dependent...Ch. 10 - HL Co. uses the high-low method to derive a total...Ch. 10 - A firm uses simple linear regression to forecast...Ch. 10 - In regression analysis, the coefficient of...Ch. 10 - A regression equation is set up, where the...Ch. 10 - What would be the approximate value of the...Ch. 10 - Estimating a cost function. The controller of the...Ch. 10 - Identifying variable-, fixed-, and mixed-cost...Ch. 10 - Various cost-behavior patterns. (CPA, adapted)....Ch. 10 - Matching graphs with descriptions of cost and...Ch. 10 - Account analysis, high-low. Stein Corporation...Ch. 10 - Account analysis method. Gower, Inc., a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.27ECh. 10 - Estimating a cost function, high-low method. Lacy...Ch. 10 - Linear cost approximation. Dr. Young, of Young and...Ch. 10 - Cost-volume-profit and regression analysis....Ch. 10 - Regression analysis, service company. (CMA,...Ch. 10 - High-low, regression. May Blackwell is the new...Ch. 10 - Learning curve, cumulative average-time learning...Ch. 10 - Learning curve, incremental unit-time learning...Ch. 10 - High-low method. Wayne Mueller financial analyst...Ch. 10 - High-low method and regression analysis. Market...Ch. 10 - High-low method; regression analysis. (CIMA,...Ch. 10 - Regression, activity-based costing, choosing cost...Ch. 10 - Interpreting regression results. Spirit...Ch. 10 - Cost estimation, cumulative average-time learning...Ch. 10 - Cost estimation, incremental unit-time learning...Ch. 10 - Regression; choosing among models. Apollo Hospital...Ch. 10 - Multiple regression (continuation of 10-42). After...Ch. 10 - Cost estimation. Hankuk Electronics started...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10 - Interpreting regression results, matching time...Ch. 10 - Purchasing department cost drivers, activity-based...Ch. 10 - Purchasing department cost drivers, multiple...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- United Research Associates (URA) had received a contract to produce two units of a new cruise missile guidance control. The first unit took 4,000 hours to complete and cost $30,000 in materials and equipment usage. The second took 3,200 hours and cost $22,500 in materials and equipment usage. Labor cost is charged at $20 per hour. The company expects “learning” to occur relative to labor and also the pricing of parts from suppliers. The prime contractor has now approached URA and asked to submit a bid for the cost of producing another 20 guidance controls. Use Exhibit 4A.5 and Exhibit 4A.6. a. What will the last unit cost to build? (Round your answer to the nearest dollar amount.) b. What will be the average time for the 20 missile guidance controls? (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) c. What will the average cost be for guidance control for the 20 in the contract? (Round your answer to the nearest dollar amount.)arrow_forwardYou and your team are continuing your work on the Global Treps Project. Your project sponsor, Dr. K. has asked you to refine the existing cost estimate for the project so you can evaluate supplier bids and have a solid cost baseline for evaluating project performance. Recall that your schedule and cost goals are to complete the project in six months for under $120,000. You planned to use up to $50,000 total to pay yourself and your team members, and your initial estimates were $30,000 for travel expenses, $20,000 for hardware and software, and $20,000 for organizing four events, including consultants, legal/business fees, etc.arrow_forwardAs supervisor of a facilities engineering department, you consider mobile cranes to be critical equipment. The purchase of a new, medium-sized truck-mounted crane is being evaluated. The economic estimates for the two best alternatives are shown in the following table. MARR is at 15% per year. You can use the assumption of repeatability in this case. Show that the same selection is made for the following methods: a. PW method b. FW method c. EUAC method Alternative A B Capital investment ALTERNATIVE A $272,000 ALTERNATIVE B $346,000 Annual expenses ALTERNATIVE A $28,800 1 ALTERNATIVE B $9,300 Useful life (years) ALTERNATIVE A =6 ALTERNATIVE B =9 Salvage value ALTERNATIVE A $ 25,000 ALTERNATIVE B $40,000arrow_forward
- Shrewsbury Technologies, which manufactures high-technology instruments for spacecraft, is considering the sale of a navigational unit to a private company that wishes to launch its own communications satellite. The company plans to purchase 8 units, although it would also consider buying 16 units. Shrewsbury has started a chart relating labor time required to units produced: Unit Produced (X) Time Required to Produce the Xth Unit1 5,000 hours2 4,500 hours4 4,050 hours8 ?16 ? Required: Compute the labor time required to produce 8 and 16 units. Assume that labor time costs $140 per hour. Compare the cost of producing the 1st unit to the cost of producing the 16th unit. What is the percentage of the cost of the 16th unit to the cost of the 1st unit?arrow_forwardShrewsbury Technologies, which manufactures high-technology instruments for spacecraft, is considering the sale of a navigational unit to a private company that wishes to launch its own communications satellite. The company plans to purchase 8 units, although it would also consider buying 16 units. Shrewsbury has started a chart relating labor time required to units produced: Unit Produced (X) Time Required to Produce the Xth Unit 1 18,000 hours 2 14,400 hours 4 11,520 hours 8 ? 16 ? Questions: Compute the labor time required to produce 8 and 16 units. Assume that labor time costs $153 per hour. Compare the cost of producing the 1st unit to the cost of producing the 16th unit. What is the percentage of the cost of the 16th unit to the cost of the 1st unit?arrow_forwardShrewsbury Technologies, which manufactures high-technology instruments for spacecraft, is considering the sale of a navigational unit to a private company that wishes to launch its own communications satellite. The company plans to purchase 8 units, although it would also consider buying 16 units. Shrewsbury has started a chart relating labor time required to units produced: Unit Produced (X) Time Required to Produce the Xth Unit 1 5,000 hours 2 4,500 hours 4 4,050 hours 8 ? 16 ? Required: Compute the labor time required to produce 8 and 16 units. Assume that labor time costs $140 per hour. Compare the cost of producing the 1st unit to the cost of producing the 16th unit. What is the percentage of the cost of the 16th unit to the cost of the 1st unit?arrow_forward
- The Chief Operations Officer (COO) of a manufacturing firm recommends one of the manufacturing sites to undergo a process improvement initiative. He claims that this project will enable the company to realize a net savings of at least $3.25 Mln. The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) of the company tasked you to conduct a financial analysis to verify the claims of the COO. After performing cost analysis, you estimated that the project will require an initial investment of $2 Mln today and $1 Mln in Year 1. Afterwards, the initiative will yield an annual cost savings of $850k from Year 2 to Year 10. You assume that these cost savings are realized at the end of each year. (a) Suppose that you use a discount rate of 5%. Will the resulting net savings support the claim of the COO? (b) Determine the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the process improvement initiative. (c) Show the NPV profile of the project.arrow_forwardAs the supervisor of a facilities engineering department, you consider mobile cranes to be critical equipment. The purchase of a new medium-sized, truck-mounted crane is being evaluated. The economic estimates for the two best alternatives are shown in the following table. You have selected the longest useful life (nine years) for the study period and would lease a crane for the final three years under Alternative A. On the basis of previous experience, the estimated annual leasing cost at that time will be $66,000 per year (plus the annual expenses of $28,800 per year). The MARR is 15% per year. Show that the same selection is made with Solve, a. the PW method. b. the IRR method. c. the ERR method. d. Would leasing crane A for nine years, assuming the same costs per year as for three years, be preferred over your present selection? (∈ = MARR = 15%).arrow_forwardA process control manager is considering two robots to improve materials-handling capacity in the production of rigid shaft couplings that make dissimilar drive components. Robot X has a first cost of $74,000, an annual M&O cost of $31,000, and $35,000 salvage value, and it will improve revenues by $96,000 per year. Robot Y has a first cost of $146,000, an annual M&O cost of $28,000, and $47,000 salvage value, and it will increase revenues by $120,000 per year. The company's MARR is 10% per year, and it uses a 3-year study period for economic evaluations. Calculate the incremental ROR, and identify the robot the manager should select. The incremental ROR is %. The manager should select robot (Click to select) ♥arrow_forward
- Alyeski Tours operates day tours of coastal glaciers in Alaska on its tour boat the Blue Glacier. Management has identified two cost drivers the number of cruises and the number of passengers that it uses in its budgeting and performance reports. The company publishes a schedule of day cruises that it may supplement with special sailings if there is sufficient demand. Up to 85 passengers can be accommodated on the tour boat. Data concerning the company's cost formulas appear below: Vessel operating costs Advertising Administrative costs Insurance Fixed Cost per Month $6,600 $2,200 $5,900 $3,100 Required: Complete the company's planning budget for July. For example, vessel operating costs should be S6,600 per month plus $471.00 per cruise plus $3.10 per passenger. The company's sales should average $34.00 per passenger. The company's planning budget for July is based on 55 cruises and 3,150 passengers. Alyeski Tours Planning Budget For the Month Ended July 31 Revenue Expenses: Vessel…arrow_forwardAMT, Inc., is considering the purchase of a digital camera for the maintenance of design specifications by feeding digital pictures directly into an engineering workstation where computer-aided design files can be superimposed over the digital pictures. Differences between the tw images can be noted, and corrections, as appropriate, can then be made by design engineers. The capital investment requirement is $345,000 and the estimated market value of the system after a six-year study period is $115,000. Annual revenues attributable to the new camera system will be $120,000, whereas additional annual expenses will be $22,000. You have been asked by management to determine the IRR of this project and to make a recommendation. The corporation’s MARR is 20% per year. Solve first by using linear interpolation and then by using a spreadsheet.arrow_forwardBorges Machine Shop, Inc., has a 1-year contract for the production of 75,000 gear housings for a new off-road vehicle. Owner Luis Borges hopes the contract will be extended and the volume increased next year. Borges has developed costs for three alternatives. They are general-purpose equipment (GPE), flexible manufacturing system (FMS), and expensive, but efficient, dedicated machine (DM) The cost data follow General Purpose Equipment (GPE) Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) 75,000 $125,000 $15.00 Annual contracted units Annual fixed cost Per unit vanable cost Based on the total cost, the process that is best suited for the current contracted volume is Suppose the contracted volume changes to 275,000 gear housings. Based on the total cost, the process that is best suited for the new volume is Suppose the contracted volume changes to 375,000 gear housings. Based on the total cost, the process that is best suited for the new volume is Dedicated Machine (DM) 75,000 $225,000 $14.00…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Relevant Costing Explained; Author: Kaplan UK;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hnsh3hlJAkI;License: Standard Youtube License