
Define these terms: system, surroundings, thermal energy, chemical energy.
Interpretation: The terms system, surroundings, thermal energy and chemical energy has to be defined.
Concept Introduction:
The terms system, surroundings, thermal energy and chemical energy are involved in thermodynamic process.
System can be defined as portion of universe and surrounding can be defined as rest of the universe other than the system.
Thermal energy can be defined as internal energy that is seen in the system because of its temperature.
Chemical energy can be defined as the energy that is seen in the chemical bonds of atoms and molecules. The chemical energy occurs as energy released during a chemical reaction
Answer to Problem 10.1QP
System can be defined as portion of universe.
Surrounding can be defined as rest of universe other than the system.
Thermal energy can be defined as internal energy that is seen in the system because of its temperature.
Chemical energy can be defined as the energy that is seen in the chemical bonds of atoms and molecules. The chemical energy occurs as energy released during a chemical reaction
Explanation of Solution
System can be defined as portion of universe. The physical and chemical changes of substance generally constitute a system.
There are types of system in thermodynamics namely,
- 1. Open system
- 2. Closed system
- 3. Isolated system
Open system: The free exchange of matter and energy with its surroundings is called as open system. The exchange of matter in open system takes place either by addition of matter or removal of matter. The exchange of energy is much more complicated than exchange of heat. The exchange of energy takes place through heat and through work.
The figure below shows the transfer of energy and matter.
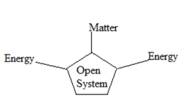
Figure 1
Closed system: The exchange of energy with its surroundings and not matter is called as closed system. The transfer of energy is similar to that of open system
The figure below shows the transfer of energy in close system
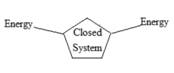
Figure 2
Isolated system: Either exchange of energy or matter takes place with the surroundings is called isolated system.
To define surroundings
Surrounding can be defined as rest of universe other than the system.
Explanation:
Any part of the universe other than the system is called as surroundings.
Consider, the example of acid-base neutralization reaction,
The reactants
To define thermal energy
Thermal energy can be defined as internal energy that is seen in the system because of its temperature.
Explanation:
Thermal energy can be defined as internal energy that is seen in the system because of its temperature. Thermal energy deals the unsystematic motion of atoms and molecules.
Its type of kinetic energy that is due to motion. Thermal energy results in substance possessing an internal temperature, which can be measured.
Consider, the example below
Thermometer having degrees in Celsius or Fahrenheit, the particles move faster within an object or system, higher the temperature is recorded.
To define chemical energy
Chemical energy can be defined as the energy that is seen in the chemical bonds of atoms and molecules. The chemical energy occurs as energy released during a chemical reaction.
Explanation:
The form of energy that is stored in chemical bonds of atoms and molecules are called as chemical energy. The chemical energy occurs as energy released during a chemical reaction called as exothermic energy
Examples of matter containing chemical energy are,
- 1) Coal- Chemical energy is converted into light and heat.
- 2) Wood- Chemical energy is converted into light and heat. Etc
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry Atoms First, Second Edition
- b. CH3 H3C 'N' H3C CH3 CN Ph 1. OH N 2. H2O2, Pyridinearrow_forwardFor each of the Followin, moleaks draw all OF The Resonance contributing stuluctures and compare these three molecules in terms of Resonance stabilization 1-C-1 a. b. H A-C+ О 112-1 C. F-C-F Farrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groupe tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures 6. Explain why -ll is an ortho -pura drccton evon though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward
- Question 1. Please predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Donnan potential.arrow_forwardIndicate what the Luther equation is used for?arrow_forward
- Indicate one aspect that benefits and another that makes it difficult to use the hydroquinone electrode to measure pH.arrow_forwardAt an electrified interface according to the Gouy-Chapman model, what types of interactions do NOT occur between the ions and the solvent according to this theory?arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. Hint: In this case you must choose the best answer to demonstrate the stereochemistry of H2 addition. 1.03 2. (CH3)2S BIZ CH₂OH 2. DMS KMnO4, NaOH ΖΗ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) HO H-SO HC 12 11 10 BH, THE 2. H2O2, NaOH Brz cold HI 19 18 17 16 MCPBA 15 14 13 A Br H₂O BH3⚫THF Brz EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) 1. Os04 2. H2O2 CH3CO3H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* H B + H H H "H C H H Darrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





