
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula is required for Hydrogen peroxide (
Concept Introduction:
The structure formula is the representation of the position of its atoms present in molecules along with the bonds which are present in between the atoms of molecule. There are two model which can help to detemine the sturcture of molecule: Lewis Model and VSEPR Model- The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion model.
Answer to Problem 10.17P
Following is structure formula of Hydrogen peroxide (
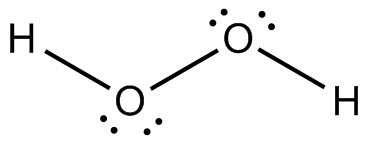
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and there are two unshared pair of electron present on each oxygen atom. Here both oxygen atoms are joined forming one single bond with hydrogen and two pairs are represnted with dots which is completing octet of oxygen.
- Hydrogen atom can form one covalent bond and there is no unshared pair of electron. Both hydrogen atoms are bonded with oxygen atoms and completing their octet.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom is prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
Following is structure formula of Hydrogen peroxide (
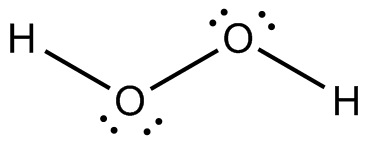
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and there are two unshared pair of electron present on each oxygen atom. Here both oxygen atoms are joined forming one single bond with hydrogen and two pairs are represnted with dots which is completing octet of oxygen.
- Hydrogen atom can form one covalent bond and there is no unshared pair of electron. Both hydrogen atoms are bonded with oxygen atoms and completing their octet.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula is required for Hydrazine (
Concept Introduction:
The structure formula is the representation of the position of its atoms present in molecules along with the bonds which are present in between the atoms of molecule. There are two model which can help to detemine the sturcture of molecule: Lewis Model and VSEPR Model- The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion model.
Answer to Problem 10.17P
Following is structural formula for Hydrazine (
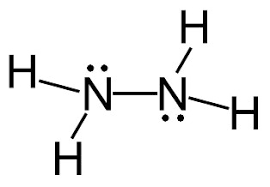
- In hydrazine, both nitrogen atoms are bonded together with single bond and have one unshared pair of electron represented as two dots on each nitrogen atom. Both nitrogen atoms has also formed single bonds with two hydrogen atoms each and completing their octet.
- All hydrogen atoms are bonded with nitrogen atoms and formed single bonds.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom is prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
Following is structural formula for Hydrazine (
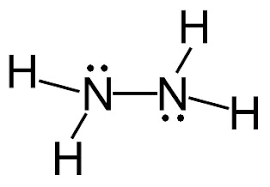
- In hydrazine, both nitrogen atoms are bonded together with single bond and have one unshared pair of electron represented as two dots on each nitrogen atom. Both nitrogen atoms has also formed single bonds with two hydrogen atoms each and completing their octet.
- All hydrogen atoms are bonded with nitrogen atoms and formed single bonds.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula is required for Methanol (
Concept Introduction:
The structure formula is the representation of the position of its atoms present in molecules along with the bonds which are present in between the atoms of molecule. There are two model which can help to detemine the sturcture of molecule: Lewis Model and VSEPR Model- The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion model.
Answer to Problem 10.17P
Following is structural formula for Methanol (
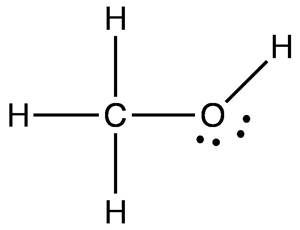
- Methanol has one oxygen atom which has two single bonds with hydrogen and carbon and two unshared pair of electrons is represented with dots over oxygen symbol.
- Three hydrogen atoms are bonded with carbon atoms and formed single bonds whereas rest hydrogen is bonded with oxygen and forming single bond.
- Carbon atom is linked with three hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom forming total four single bonds and there is no unshared pair of electron with it.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom is prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
Following is structural formula for Methanol (
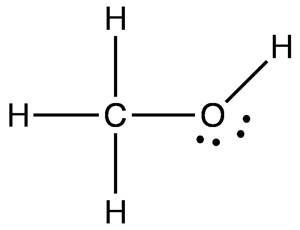
- Methanol has one oxygen atom which has two single bonds with hydrogen and carbon and two unshared pair of electrons is represented with dots over oxygen symbol.
- Three hydrogen atoms are bonded with carbon atoms and formed single bonds whereas rest hydrogen is bonded with oxygen and forming single bond.
- Carbon atom is linked with three hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom forming total four single bonds and there is no unshared pair of electron with it.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula is required for Methanethiol (
Concept Introduction:
The structure formula is the representation of the position of its atoms present in molecules along with the bonds which are present in between the atoms of molecule. There are two model which can help to detemine the sturcture of molecule: Lewis Model and VSEPR Model- The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion model.
Answer to Problem 10.17P
Following is structural formula for Methanethiol (
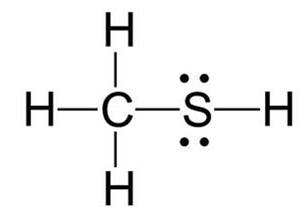
- In Methanethiol, carbon atom is linked with one sulphur and three hydrogen atoms forming four single bonds and completing its octet.
- One hydrogen atom has formed single bond with sulphur whereas three hydrogen atoms has formed single bonds with carbon and completed their octet.
- Sulphur has two unshared pair of electrons and two single bonds with hydrogen and carbon.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom is prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
Following is structural formula for Methanethiol (
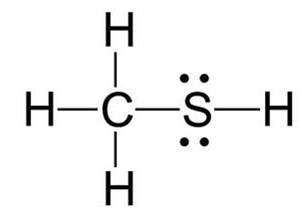
- In Methanethiol, carbon atom is linked with one sulphur and three hydrogen atoms forming four single bonds and completing its octet.
- One hydrogen atom has formed single bond with sulphur whereas three hydrogen atoms has formed single bonds with carbon and completed their octet.
- Sulphur has two unshared pair of electrons and two single bonds with hydrogen and carbon.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formula is required for Methylamine (
Concept Introduction:
The structure formula is the representation of the position of its atoms present in molecules along with the bonds which are present in between the atoms of molecule. There are two model which can help to detemine the sturcture of molecule: Lewis Model and VSEPR Model- The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion model.
Answer to Problem 10.17P
Following is structural formula for Methylamine (
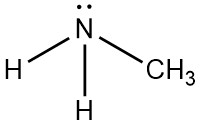
- Nitrogen atom in methylamine is linked with carbon and two hydrogen atoms through single bonds and one unshared pair of electrons is seen on symbol of atom.
- Carbon atom has one single bond with nitrogen atom and three single bonds with hydrogen atoms which results into completion of octet of carbon with no unshared pair of electron.
- Total five hydrogen atoms are present in methylamine from which two hydrogen atoms have single bonds with nitrogen atoms and three hydrogen atoms have single bond with carbon atoms and completing their octet.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom is prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
Following is structural formula for Methylamine (
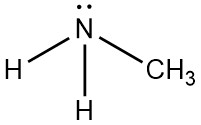
- Nitrogen atom in methylamine is linked with carbon and two hydrogen atoms through single bonds and one unshared pair of electrons is seen on symbol of atom.
- Carbon atom has one single bond with nitrogen atom and three single bonds with hydrogen atoms which results into completion of octet of carbon with no unshared pair of electron.
- Total five hydrogen atoms are present in methylamine from which two hydrogen atoms have single bonds with nitrogen atoms and three hydrogen atoms have single bond with carbon atoms and completing their octet.
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formula is required for Chloromethane (
Concept Introduction:
The structure formula is the representation of the position of its atoms present in molecules along with the bonds which are present in between the atoms of molecule. There are two model which can help to detemine the sturcture of molecule: Lewis Model and VSEPR Model- The valence-shell electron-pair repulsion model.
Answer to Problem 10.17P
Following is structural formula for Chloromethane (
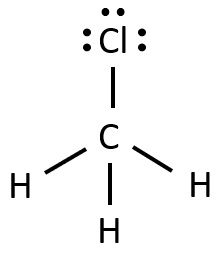
- Chloromethane has halogen atom as chlorine which is linked with carbon atom and forming single bond and has three unshared pair of electrons.
- Carbon completes its octet by forming three single bonds with three hydrogen atoms and one single bond with chlorine.
- All three hydrogen forms single-single bonds with carbon and fills their octet.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of any atom is prepared with the help of Lewis model which explains guideline for bonding of atom. It guides about the covalent bonds which are formed in various combinations of single, double and triple bonds.
For several covalent bonds in organic compound containing carbon bonded to hydrogen, nitrogen, chlorine and oxygen shows some important points to be noted for structure are as follow:
- Carbon forms four covalent bonds while hydrogen form one covalent bond and both has no unshared pair of electrons.
- Three covalent bonds are formed in nitrogen atom with only one unshared pair of electron left behind.
- Oxygen can form two covalent bonds and have further more two unshared pair of electron.
- Iodine, chlorine, bromine and fluorine like halogens can form only one covalent bond like hydrogen but they have three unshared pair of electrons.
Following is structural formula for Chloromethane (
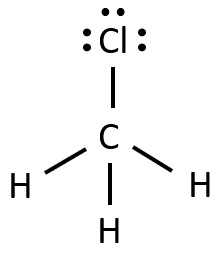
- Chloromethane has halogen atom as chlorine which is linked with carbon atom and forming single bond and has three unshared pair of electrons.
- Carbon completes its octet by forming three single bonds with three hydrogen atoms and one single bond with chlorine.
- All three hydrogen forms single-single bonds with carbon and fills their octet.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Bettelheim/Brown/Campbell/Farrell/Torres' Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry, 11th
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardCalculate the packing factor of CaTiO3. It has a perovskite structure. Data: ionic radii Co²+ = 0.106 nm, Ti4+ = 0.064 nm, O² = 0.132 nm; lattice constant is a = 2(rTi4+ + ro2-). Ca2+ 02- T14+ Consider the ions as rigid spheres. 1. 0.581 or 58.1% 2. -0.581 or -58.1 % 3. 0.254 or 25.4%arrow_forwardGeneral formula etherarrow_forward
- Please provide the retrosynthetic analysis and forward synthesis of the molecule on the left from the starting material on the right. Please include hand-drawn structures! will upvote! Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease provide the retrosynthetic analysis and forward synthesis of the molecule on the left from the starting material on the right. Please include hand-drawn structures! will upvote!arrow_forward(please correct answer and don't used hand raiting) Please provide the retrosynthetic analysis and forward synthesis of the molecule on the left from the starting material on the right. Please include hand-drawn structures! will upvote!arrow_forward
- CaTiO3 has a perovskite structure. Calculate the packing factor.Data: ionic radii Co+2 = 0.106 nm, Ti+4 = 0.064 nm, O-2 = 0.132 nm; lattice constant is a = 2(rTi4+ + rO-2).(a) 0.581(b) -0.581(c) 0.254(d) -0.254arrow_forwardIn the initial linear section of the stress-strain curve of a metal or alloy. Explain from the point of view of atomic structure?(a) No, the atomic level properties of the material can never be related to the linear section.(b) The elastic zone is influenced by the strength of the bonds between atoms.(c) The stronger the bond, the less rigid and the lower the Young's Modulus of the material tested.(d) The stronger the bond, the less stress is necessary to apply to the material to deform it elastically.arrow_forwardThe degree of polymerization of polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon) is 7500 (mers/mol). If all polymer chains have equal length, state the molecular weight of the polymer and the total number of chains in 1000 g of the polymer(a) 50 000 g/mol; 0.03·1020 chains(b) 100 000 g/mol; 1.03·1020 chains(c) 750 000 g/mol; 8.03·1020 chainsarrow_forward
- In natural rubber or polyisoprene, the trans isomer leads to a higher degree of crystallinity and density than the cis isomer of the same polymer, because(a) it is more symmetrical and regular.(b) it is less symmetrical.(c) it is irregular.arrow_forwardMost ceramic materials have low thermal conductivities because:(a) Electron mobility is strongly restricted due to their strong ionic-covalent bonding.(b) False, in general they are excellent thermal conductors (they are used in ovens).(c) Electron mobility is dependent on T and therefore they are poor conductors at high temperatures.(d) Electron mobility is very restricted by secondary bonds.arrow_forwardResistivity and electrical conductivity.(a) In metals, resistivity decreases.(b) In metals, resistivity decreases and conductivity in semiconductors also decreases with increasing temperature.(c) With increasing temperature, resistivity in metals and conductivity in semiconductors also increases.(d) None of the above.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

