
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for a resonance form of each ion of
Concept introduction:
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Formula to calculate the formal charge of the atom is as follows:
The formula to calculate the oxidation number of an atom is as follows:
(a)
Answer to Problem 10.17P
The possible Lewis structures for a resonance form of each ion of
The oxidation numbers of
Explanation of Solution
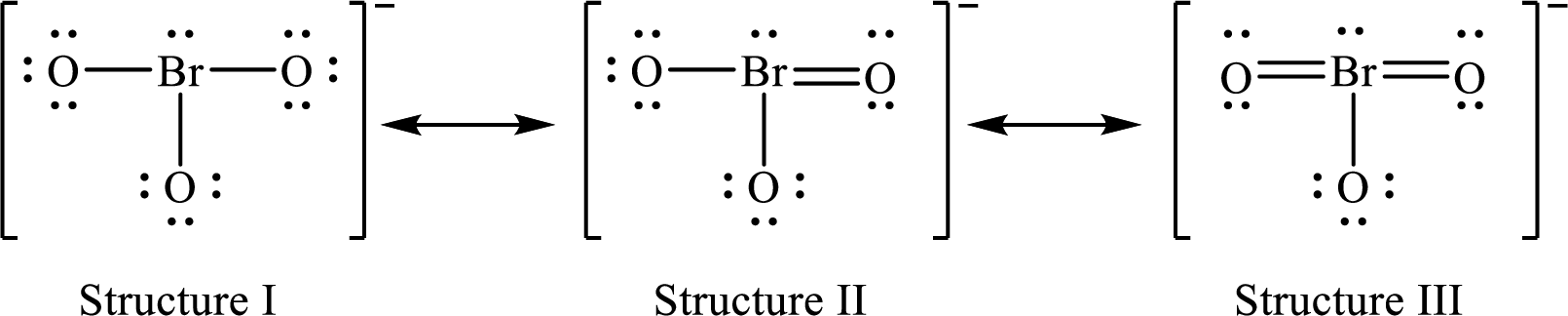
Lewis structures for a resonance form of
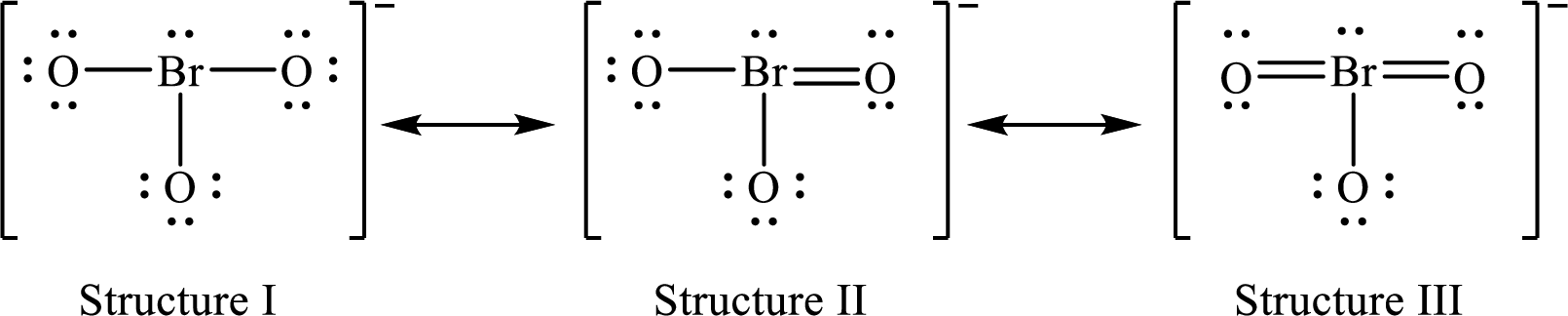
For structure I:
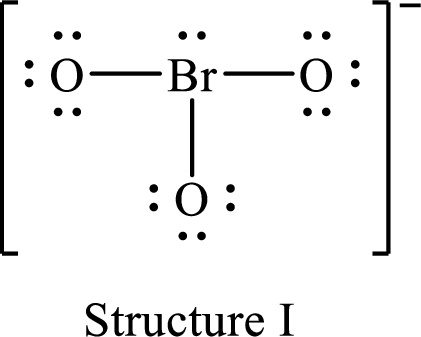
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 6 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each oxygen atom.
For structure II:
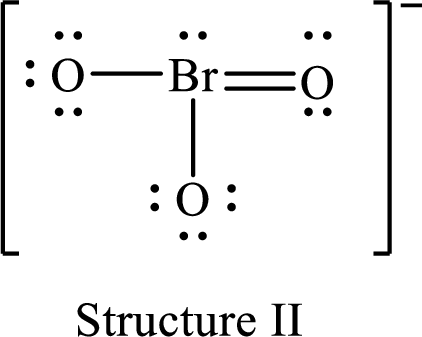
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 8 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each single bonded oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for the value of valence electrons, 4 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on the double bonded oxygen atom.
For structure III:
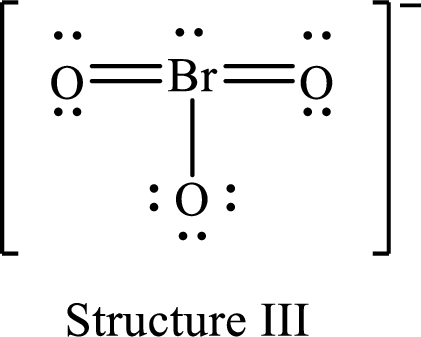
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 10 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for nonbonded electrons and 2 for number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on the single bonded oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for the value of valence electrons, 4 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each double bonded oxygen atom.
Therefore, structure II has the more acceptable and reasonable distribution of formal charges.
The oxidation numbers of
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for a resonance form of each ion of
Concept introduction:
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound which has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Calculate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
Formula to calculate the formal charge of the atom is as follows:
The formula to calculate the oxidation number of an atom is as follows:
(b)
Answer to Problem 10.17P
The possible Lewis structures for a resonance form of each ion of
The oxidation numbers of.
Explanation of Solution
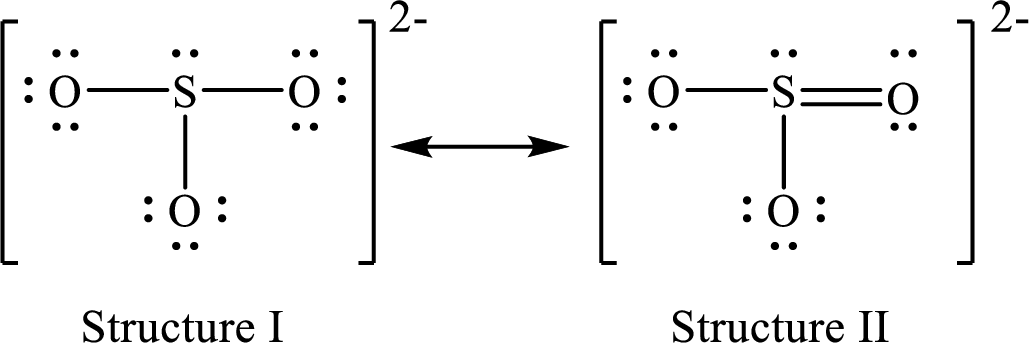
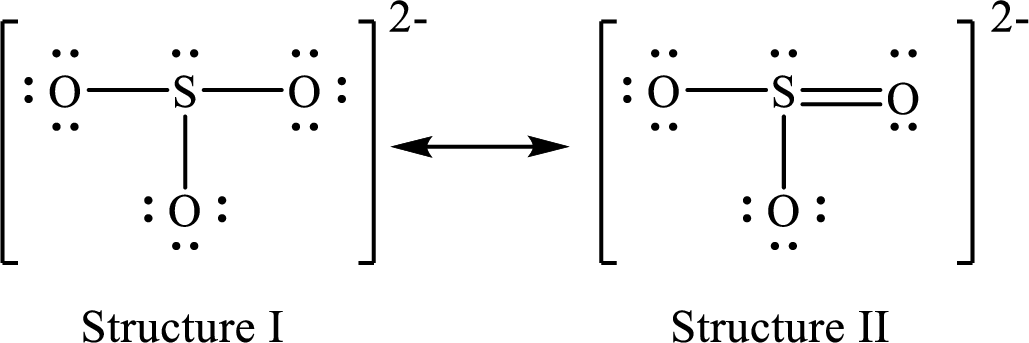
Lewis structure for a resonance form of
For structure I:
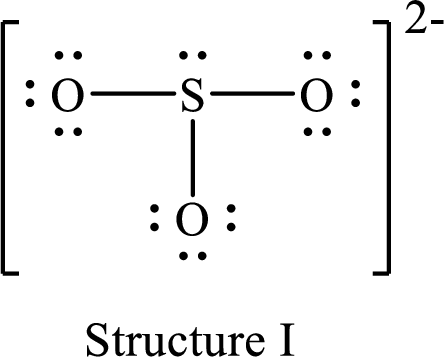
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 6 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each oxygen atom.
For structure II:
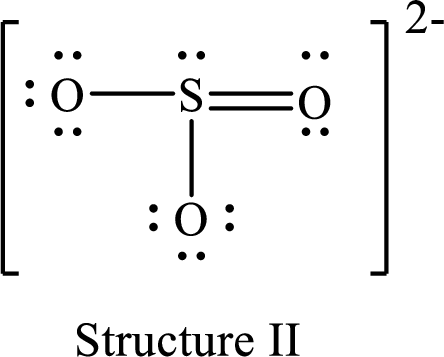
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 2 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 8 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for nonbonded electrons and 2 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on each single bonded oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for the value of valence electrons, 4 for the number of nonbonded electrons and 4 for the number of bonding electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on the double bonded oxygen atom.
Therefore, structure II has the more acceptable and reasonable distribution of formal charges.
The oxidation numbers of.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
- Draw the mechanism for the substitution reaction converting an alcohol into an alkyl halide. If chirality is important to the reaction include it.arrow_forwardWrite, in words three different reactions we can use to make an alcohol.arrow_forwardDraw the reduction mechanism for the reduction of the aldehyde.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the reaction of XeF4 with H2O? Group of answer choices H2XeF2 H2XeF4 XeO3 H2XeOarrow_forwardWhile noble gas exerts the strongest London (dispersion) forces on neighboring atoms? Group of answer choices Xe Ar Kr Nearrow_forwardWhich of the following elements is corrosive to your skin due to that element breaking down C=C bonds? Group of answer choices fluorine iodine bromine chlorinearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





