
Effect of Convertible Bonds on Earnings per Share
Poppy Corporation owns 60 percent of Seed Company’s common shares. Balance sheet data for the companies on December 31, 20X2, are as follows:
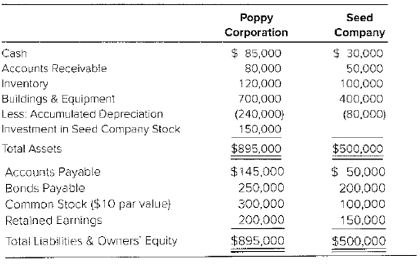
The bonds of Poppy Corporal ion and Seed Company pay annual interest of 8 percent and 10 percent, respectively. Poppy’s bonds are not convertible. Seeds bonds can be converted into 10,000 shares of its company stock any time after January 1, 20X1. An income tax rate of 40 percent is applicable to both companies. Seed reports net income of $30,000 for 20X2 and pays dividend of $15,000. Poppy reports income from its separate operations of $45,000 and pays dividends of $25,000.
Required
Compute basic and diluted EPS for the consolidated entity for 20X2.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
ADVANCED FIN. ACCT. LL W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- Please provide the accurate answer to this financial accounting problem using appropriate methods.arrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardI need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning  Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





