
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337516877
Author: Das
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.11P
Refer to Figure 10.42. Due to application of line loads q1 and q2, the vertical stress increase at point A is 58 kN/m2. Determine the magnitude of q2.
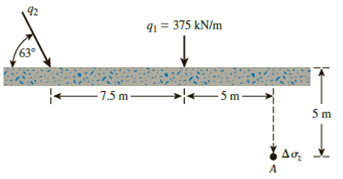
Figure 10.42
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Sketch and Describe a double bottom solid floor of a vessel
Explain the difference between a Class A and Class B bulkhead
By using the yield line theory, determine the moment (m) for an isotropic
reinforced concrete two-way slab shown in figure under a uniformly
distributed load. Use segment Equilibrium method
2.5
A
7.0m
c.g.
ㄨˋ
B
1
B
A
IA
2.5
2.0
+
2.5
5.0m
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.1PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.2PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.4PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.5PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.6PCh. 10 - Point loads of magnitude 125, 250, and 500 kN act...Ch. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.41. Determine the vertical...Ch. 10 - For the same line loads given in Problem 10.8,...Ch. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.41. Given: q2 = 3800 lb/ft, x1...
Ch. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.42. Due to application of line...Ch. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.43. A strip load of q = 1450...Ch. 10 - Repeat Problem 10.12 for q = 700 kN/m2, B = 8 m,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.14PCh. 10 - For the embankment shown in Figure 10.45,...Ch. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.46. A flexible circular area of...Ch. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.47. A flexible rectangular area...Ch. 10 - Refer to the flexible loaded rectangular area...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.19PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.20PCh. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.48. If R = 4 m and hw = height...Ch. 10 - Refer to Figure 10.49. For the linearly increasing...Ch. 10 - EB and FG are two planes inside a soil element...Ch. 10 - A soil element beneath a pave ment experiences...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given cross-classification data for the Jeffersonville Transportation Study Area in this table, develop the family of cross-classification curves. (Use high = $55,000; medium = $25,000; low = $15,000. Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen This answer has not been graded yet. Determine the number of trips produced (by purpose) for a traffic zone containing 400 houses with an average household income of $35,000. 1610 HBW HBO Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. trips 1791 NHB Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. trips 1791 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. tripsarrow_forward2.Water is siphoned from a reservoir. Determine (a) the maximum flow rate that can be achieved without cavitation occurring in the piping system (all indicated points) and (b) the maximum elevation of the highest point of the piping system to avoid cavitation. D = 20 cm, and d = 8 cm. The minimum pressure to avoid cavitation in the pipes is Pmin = 2340 Pa (absolute) for T = 20 °C. Water density = 1000 kg/m³. ✓ (1) T=20 C (4)arrow_forward3. Water flows steadily down the inclined pipe as shown. Determine (a) the difference in pressure pı-p2 and (b) the head loss between section (1) and section (2). Flow 5 ft Section (1) 6 in. 30°/ Section (2) 8 in. Mercuryarrow_forward
- 1. Streams of water from two tanks impinges upon each other as shown. If viscous effects are negligible and point A is a stagnation point, determine the height h. Free ets Air 20 ft P₁ = 25 psi 8 ftarrow_forwardProb. Design the dimensions (rectangular) and longitudinal reinforcements for the beans sham. Design the beams as SRBS. Given: fi= 21 MPa fy= 275 hPa X= 23.5 kaf. λ= 1.0arrow_forwardPlease answer the following show me how to solve in your paper dont type thank youarrow_forward
- Prob. Design the dimensions (rectangular) and longitudinal reinforcements for the beans sham. Design the beams as SRBS. Given: fi= 21 MPa fy= 275 hPa X= 23.5 kaf. λ= 1.0arrow_forwardQuestion 1Demonstrate and relate the different strategies you would use to enhance the buildingenvelope's performance in reducing heat ingress when retrofitting an existing building.Question 2There are several forms of renewable energy sources that are available for the builtenvironment.Demonstrate what some of these types of renewable energy sources are and evaluate in detailwhich type of renewable energy source is the most suitable for Singapore as well as itslimitations.Question 3Some of the broad strategies to optimize energy efficiency in existing building involve theuse of Energy Control Measures (ECMs).Demonstrate and appraise any THREE (3) Energy Control Measures for zero-cost, low-costand high-cost areas each.arrow_forwardGiven cross-classification data for the Jeffersonville Transportation Study Area in this table, develop the family of cross-classification curves. (Use high = $55,000; medium = $25,000; low = $15,000. Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen This answer has not been graded yet. Determine the number of trips produced (by purpose) for a traffic zone containing 400 houses with an average household income of $35,000. HBW 2200 HBO Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. trips 2747 NHB Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. trips 2507 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. tripsarrow_forward
- I am studying building diagnosis. Kindly help to provide the answers and example required and elaborate for explanation.arrow_forwardA simply supported rectangular RC beam is to carry a uniform factored dead load of 1.2 kip/ftand a concentrated factored live load of 16 kip at mid-span. The beam self-weight is not includedin these loads. The concrete weighs 135 pcf. The span length is 25 ft. Please find the smallestsection allowed by ACI and design accordingly. Use f c’ = 5,000 psi, f y = 75,000 psi. Theexposure is interior with no weather exposure.a. Assume an arbitrary self-weight/ft of the beam.b. Find the maximum factored bending moment in the beam.c. Set up the moment equation and solve for the beam section.d. Revise the assumption if needed.Hint: The beam section (b and h) and steel reinforcement are inversely proportional. The smallestallowable beam section will be for the largest allowable steel ration (ρmax), and vice versa. Sincethe steel ratio is fixed, two remaining variables (b, d) need to be found from the moment equations.Then, bd2 term can be solved to get an acceptable b and d combination.arrow_forwardFind: ftop and fbottom of (initial stage, construction phase, final stage)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stress Distribution in Soils GATE 2019 Civil | Boussinesq, Westergaard Theory; Author: Gradeup- GATE, ESE, PSUs Exam Preparation;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6e7yIx2VxI0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY