
Concept explainers
1.
To identify: The effect of given transactions on the
1.
Explanation of Solution
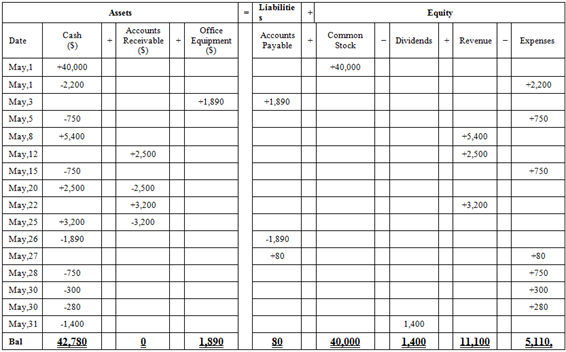
Table (1)
Hence, the cash balance is $42,780, office equipment is $1,890, accounts payable is $80, common stock is $40,000, dividend is $1,400, revenue is $11,100 and expenses is $5,110.
2.
To prepare: The income statement, statement of
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare income statement.
| G. Company | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the month ended May 31,20XX | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue: | ||
| Service Revenue | 11,100 | |
| Total Revenue | 11,100 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Advertising Expenses | 80 | |
| Cleaning Expenses | 750 | |
| Rent Expenses | 2200 | |
| Salary Expenses | 1,500 | |
| Telephone Expenses | 300 | |
| Utilities Expenses | 280 | |
| Total Expense | 5,110 | |
| Net income | 5,990 | |
Table(2)
Hence, net income of .G Company as on May 31, 20XX is $5,990.
Prepare statement of retained earnings.
| G. Company | |
| Retained Earnings Statement | |
| For the month ended May 31,20XX | |
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Opening balance | 0 |
| Net income | 5,990 |
| Total | 5,990 |
| Dividends | (1,400) |
| Retained earnings | 4,590 |
Table(3)
Hence, the retained earnings of G Company as on May 31, 20XX are $4,590.
Prepare balance sheet.
| G. Company | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As on May 31, 20XX | ||
| Particulars |
| Amount ($) |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | 42,780 | |
| Equipment | 1,890 | |
| Total assets |
| 44,670 |
| Liabilities and | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | 80 | |
| Stockholder’s equity | ||
| Common stock | 40,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 4,590 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity |
| 44,590 |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholder’s equity |
| 44,670 |
Table(4)
Hence, the total of the balance sheet of the G Company as on May 31, 20XX is of $44,670.
3.
To prepare: The statement of
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the cash flow statement.
| G. Company | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| Month Ended May 31, 20XX | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash flow from operating activities | ||
| Receipts: | ||
| Collections from customers |
| 11,100 |
| Payments: |
| |
| Cleaning Expenses | (750) | |
| Rent Expenses | (2200) | |
| Salary Expenses | (1,500) | |
| Telephone Expenses | (300) | |
| Utilities | (280) | (5,030) |
| Net cash from operating activities |
| 6,070 |
| Cash flow from investing activities |
| |
| Purchase of equipment | (1,890) | |
| Net cash from investing activities |
| (1,890) |
| Cash flow from financing activities |
| |
| Issued common stock | 40,000 | |
| Less: Payment of cash dividends | (1,400) | |
| Net cash from financing activities |
| 38,600 |
| Net increase in cash |
| 42,780 |
| Cash balance, May 1,20XX |
| 0 |
| Cash balance, May 31,20XX |
| 42,780 |
Table(5)
Hence, the cash balance of the G Company as on May 31, 20XX is $42,780.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting: Information for Decisions w Access Card, 5th edition, ACC 211 & 212, Northern Virginia Community College
- Amy is evaluating the cash flow consequences of organizing her business entity SHO as an LLC (taxed as a sole proprietorship), an S corporation, or a C corporation. She used the following assumptions to make her calculations: a) For all entity types, the business reports $22,000 of business income before deducting compensation paid to Amy and payroll taxes SHO pays on Amy's behalf. b) All entities use the cash method of accounting. c) If Amy organizes SHO as an S corporation or a C corporation, SHO will pay Amy a $5,000 annual salary (assume the salary is reasonable for purposes of this problem). For both the S and C corporations, Amy will pay 7.65 percent FICA tax on her salary and SHO will also pay 7.65 percent FICA tax on Amy's salary (the FICA tax paid by the entity is deductible by the entity). d) Amy's marginal ordinary income tax rate is 35 percent, and her income tax rate on qualified dividends and net capital gains is 15 percent. e) Amy's marginal self-employment tax rate is…arrow_forwardInformation pertaining to Noskey Corporation’s sales revenue follows: November 20X1 (Actual) December 20X1 (Budgeted) January 20X2 (Budgeted)Cash sales $ 115,000 $ 121,000 $ 74,000Credit sales 282,000 409,000 208,000Total sales $ 397,000 $ 530,000 $ 282,000Management estimates 5% of credit sales to be uncollectible. Of collectible credit sales, 60% is collected in the month of sale and the remainder in the month following the month of sale. Purchases of inventory each month include 70% of the next month’s projected total sales (stated at cost) plus 30% of projected sales for the current month (stated at cost). All inventory purchases are on account; 25% is paid in the month of purchase, and the remainder is paid in…arrow_forwardMirror Image Distribution Company expects its September sales to be 20% higher than its August sales of $163,000. Purchases were $113,000 in August and are expected to be $133,000 in September. All sales are on credit and are expected to be collected as follows: 40% in the month of the sale and 60% in the following month. Purchases are paid 20% in the month of purchase and 80% in the following month. The cash balance on September 1 is $23,000. The ending cash balance on September 30 is estimated to be:arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





