
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The equation that shows the reaction of the given acid with water by considering the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory is to be written. All the electron pairs, formal chargers and curved arrows that represent the electron movement in the respective reaction are to be shown.
Concept introduction:
An acid is a chemical substance that readily donates protons and a base is a chemical substance that can easily accept a proton. During an acid-base reaction, the interaction between an acid and a base is taken place because of the transfer of a proton. The stronger the acid, the smaller its
Answer to Problem 63P
Solution:
a)
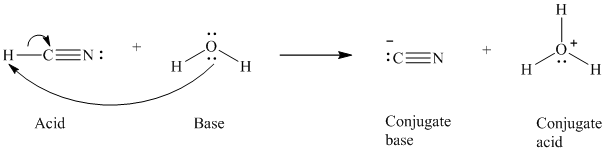
The formal charge on the the oxygen atom is
b)
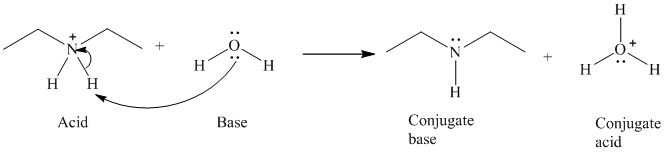
The formal charge on both the the oxygen atom and the nitrogen atom is
c)
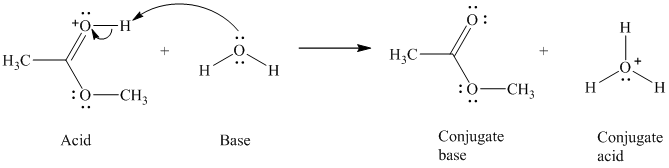 The formal charge on the oxygen atom is
The formal charge on the oxygen atom is
Explanation of Solution
a) The reaction of an acid with water.
In the respective reaction, the water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of oxygen atom present in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton, is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement is given below:
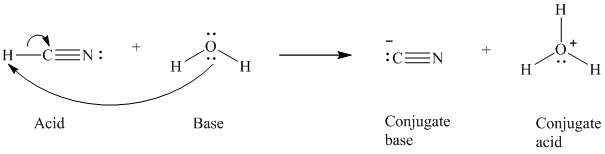
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the conjugate base is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the oxygen atom is as follows:
Substitute
b) The reaction of an acid with water.
The given acid reacts with water. So water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of the oxygen atom in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement are shown below:
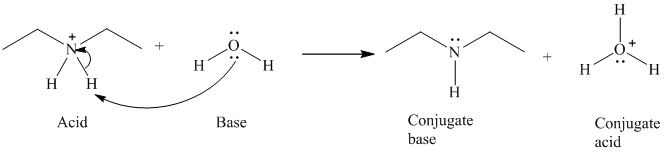
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the nitrogen atom is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the nitrogen atom is as follows:
Substitute
For calculating formal charge on the oxygen atom, recall the electron count formula:
Substitute
Recall the formula for formal charge:
Substitute
c) The given acid reacts with water.
So water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of the oxygen atom in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton, is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement are shown below:
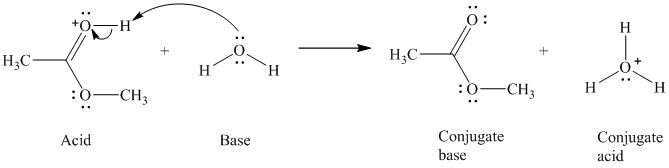
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the oxygen is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the oxygen atom is as follows:
Substitute
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF)-PACKAGE
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



