
Modern Physics
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781111794378
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 30P
An observer in a rocket moves toward a mirror at speed v relative to the reference frame labeled by S in Figure P1.30. The mirror is stationary with respect to S. A light pulse emitted by the rocket travels toward the mirror and is reflected back to the rocket. The front of the rocket is a distance d from the mirror (as measured by observers in S) at the moment the light pulse leaves the rocket. What is the total travel time of the pulse as measured by observers in (a) the S frame and (b) the front of the rocket?
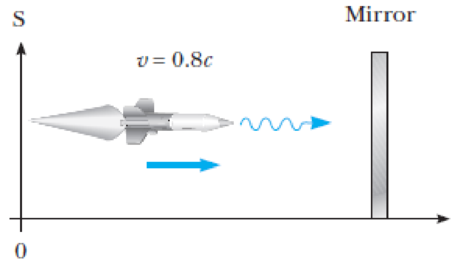
Figure P1.30
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
A pendulum has a 0.4-m-long cord and is given a tangential velocity of 0.2 m/s toward the
vertical from a position 0 = 0.3 rad.
Part A
Determine the equation which describes the angular motion.
Express your answer in terms of the variable t. Express coefficients in radians to three significant figures.
ΜΕ ΑΣΦ
vec
(t)=0.3 cos (4.95t) + 0.101 sin (4.95t)
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining
Part A
■Review
The uniform 150-lb stone (rectangular block) is being turned over on its side by pulling the
vertical cable slowly upward until the stone begins to tip.
(Figure 1)
If it then falls freely (T = 0) from an essentially balanced at-rest position, determine the speed at which the corner A strikes the pad at B. The stone does not slip at its corner C as it falls. Suppose that height of the stone is
L = 1.2 ft.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
?
ft
VA 10.76
S
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. The battery has emf ε = 69 volts and negligible internal resistance. The inductance is L = 0.4 H and the resistances are R 1 = 12 Ω and R 2 = 9.0 Ω. Initially the switch S is open and no currents flow. Then the switch is closed. After leaving the switch closed for a very long time, it is opened again. Just after it is opened, what is the current in R 1?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Modern Physics
Ch. 1.2 - Prob. 1ECh. 1.2 - Exercise 2 Conservation of Linear Momentum Is...Ch. 1.5 - If the speed of the observer is increased by 5.0%,...Ch. 1.5 - If the ship moves past the observer at 0.01000c,...Ch. 1.6 - Prob. 5ECh. 1 - What two measurements will two observers in...Ch. 1 - A spaceship in the shape of a sphere moves past an...Ch. 1 - An astronaut moves away from Earth at a speed...Ch. 1 - Two identically constructed clocks are...Ch. 1 - Two lasers situated on a moving spacecraft are...
Ch. 1 - Prob. 6QCh. 1 - When we speak of time dilation, do we mean that...Ch. 1 - Prob. 8QCh. 1 - Prob. 9QCh. 1 - It is said that Einstein, in his teenage years,...Ch. 1 - Prob. 11QCh. 1 - What happens to the density of an object as its...Ch. 1 - In a lab frame of reference, an observer finds...Ch. 1 - Prob. 2PCh. 1 - Prob. 3PCh. 1 - An airplane flying upwind, downwind, and crosswind...Ch. 1 - Prob. 5PCh. 1 - Prob. 6PCh. 1 - A clock on a moving spacecraft runs 1 s slower per...Ch. 1 - A meter stick moving in a direction parallel to...Ch. 1 - A spacecraft moves at a speed of 0.900c. If its...Ch. 1 - The average lifetime of a pi meson in its own...Ch. 1 - An atomic clock is placed in a jet airplane. The...Ch. 1 - An astronaut at rest on Earth has a heartbeat rate...Ch. 1 - The muon is an unstable particle that...Ch. 1 - A rod of length L0 moves with a speed v along the...Ch. 1 - The classical Doppler shift for light. A light...Ch. 1 - Calculate, for the judge, how fast you were going...Ch. 1 - Prob. 17PCh. 1 - Prob. 18PCh. 1 - Two spaceships approach each other, each moving...Ch. 1 - Prob. 20PCh. 1 - An observer on Earth observes two spacecraft...Ch. 1 - Speed of light in a moving medium. The motion of a...Ch. 1 - An observer in frame S sees lightning...Ch. 1 - As seen from Earth, two spaceships A and B are...Ch. 1 - Prob. 25PCh. 1 - The proper length of one spaceship is three times...Ch. 1 - Prob. 27PCh. 1 - Prob. 28PCh. 1 - A spaceship moves away from Earth at a speed v and...Ch. 1 - An observer in a rocket moves toward a mirror at...Ch. 1 - A physics professor on Earth gives an exam to her...Ch. 1 - A yet-to-be-built spacecraft starts from Earth...Ch. 1 - Suppose our Sun is about to explode. In an effort...Ch. 1 - Two powerless rockets are on a collision course....Ch. 1 - Prob. 35PCh. 1 - Suzanne observes two light pulses to be emitted...Ch. 1 - An observer in reference frame S sees two events...Ch. 1 - A spacecraft is launched from the surface of the...Ch. 1 - An Earth satellite used in the Global Positioning...Ch. 1 - Prob. 40P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.95×10−5 F is charged by connecting it to a 12.5 −V battery. The capacitor is then disconnected from the battery and connected across an inductor with an inductance of L = 1.55 H . At the time 2.35×10−2 s after the connection to the inductor is made, what is the current in the inductor? At that time, how much electrical energy is stored in the inductor?arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question. Thanks.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Time Dilation - Einstein's Theory Of Relativity Explained!; Author: Science ABC;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yuD34tEpRFw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY