
a.
The
a.
Answer to Problem 27PSA
Option 1
Calculation of income statement of Company CM is as follows:
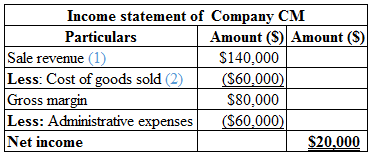
Table (1)
Hence, the net income of Company CM is $20,000.
Calculation of balance sheet of Company CM is as follows:
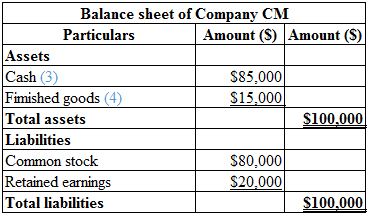
Table (2)
Option 2
Calculation of income statement of Company CM is as follows:
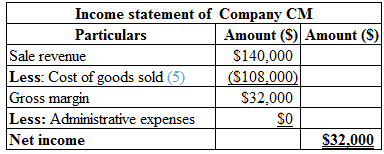
Table (3)
Hence, the net income of Company CM is $32,000.
Calculation of balance sheet of Company CM is as follows:
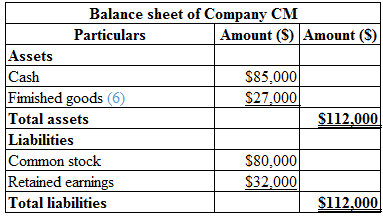
Table (4)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
It is the financial statement of a company that shows all the incomes earned and expenditures incurred by the company for a particular period of time.
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet is one of the financial statements that summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Working notes:
Calculate the sale revenue:
Sales revenue=Number of units sold×Price of each =4000 units×$35=$140,000
Hence, the sales revenue is $140,000.
(1)
Calculate the cost per unit:
Cost per unit=Materials+Labor+Overheads Total number of units produced=$75,0005000 units=$15
Hence, the cost per unit is $15.
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold=Cost per unit×Number of goods sold=$15×4,000 units=$60,000
Hence, the cost of goods sold is $60,000.
(2)
Calculate the total cash:
Total cash=Acquired capital+Sales revenue−Product cost−Planning cost=$80,000+$140,000−$75,000−$60,000 =$220,000−135,000=$85,000
Hence, the total cash is $85,000.
(3)
Calculate the total finished goods:
Finished goods=Cost per unit×Completed goods−Number of goods sold=$15×5,000 units−4,000 units=$15×1,000 units=$15,000
Hence, the finished goods is $15,000.
(4)
Calculate the cost per unit:
Cost per unit=Materials+Labor+Overheads+Planning cost Total number of units produced=$75,000+$60,0005000 units=$135,0005000 units=$27
Hence, the cost per unit is $27.
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold=Cost per unit×Number of goods sold=$27×4,000 units=$108,000
Hence, the cost of goods sold is $108,000.
(5)
Calculate the total finished goods:
Finished goods=Cost per unit×Completed goods−Number of goods sold=$27×5,000 units−4,000 units=$27×1,000 units=$27,000
Hence, the finished goods is $27,000.
(6)
b.
The option in the financial statement that gives a favourable image to the creditors and investors.
b.
Answer to Problem 27PSA
Option 2 is the financial statement that gives a favorable impression to creditors and investors with a greater net income of $12,000 than option 1’s net income.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is the financial statement of a company that shows all the incomes gained and expenditures incurred by the company for a time period.
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet is one of the financial statements that summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
The option that gives the favorable image to the creditors and investors is as follows:
Option 2 provides the financial statement that gives a favorable image to the creditors and investors because the net income in option 2 is greater than the net income in option 1.
c.
The amount of bonus under each option and recognize the option that provides a higher bonus.
c.
Answer to Problem 27PSA
Option 2 provides the president with a higher bonus of $6,400.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is the financial statement of a company that shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
Balance sheet:
Balance sheet is one of the financial statements that summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Calculation of bonus under option 1 is as follows:
Bonus=Net income×20% on net income=$20,000×20%=$4,000
Hence, the bonus received by the president under option 1 is $4,000.
Calculation of bonus under option 2 is as follows:
Bonus=Net income×20% on net income=$32,000×20%=$6,400
Hence, the bonus received by the president under option 2 is $6,400.
d.
The amount of tax rate under each option and recognize which option pays less tax.
d.
Answer to Problem 27PSA
Option 1 minimizes the cost of income tax expenses for the company by $6,000.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of income tax under option 1 is as follows:
Bonus=Net income×30% income tax rate=$20,000×30%=$6,000
Hence, the income tax expenses under option 1 is $6,000.
Calculation of income tax under option 2 is as follows:
Bonus=Net income×30% income tax rate=$32,000×30%=$9,600
Hence, the bonus received by the president under option 2 is $9,600
e.
Comment on the conflict among the company’s president as determined in requirement c and the owner-based requirement d, and define an incentive compensation plan that will neglect the conflict.
e.
Explanation of Solution
The conflicts between the owner and the president are as follows:
Option 2 provides the president with a higher bonus of $6,400. Option 1 minimizes the cost of income tax expenses for the company by $6,000. These are the two conflicts between the owner and the president.
The reasons to avoid these conflicts are as follows:
- The bonus plans of the company can be tied up with the company’s stock price, instead of net income.
Market efficiency increases; as a result, the performance of the company increases, which creates a value to the company’s stock price.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Fundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts
- Please show me how to solve this financial accounting problem using valid calculation techniques.arrow_forwardCould you help me solve this financial accounting question using appropriate calculation techniques?arrow_forwardCan you explain this general accounting question using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
- how much overhead cost would be assigned to product G98X using the activity based costing system ?arrow_forwardThe closing price of a stock is $74.55, and the net earnings per share are $3.50. The stock's P/E ratio is .arrow_forwardI need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





