
Concept explainers
As depicted in Fig. P1.22, a spherical particle settling through a quiescent luid is subject to three forces: the downward force of gravity
where
(a) Use a force balance for the particle to develop the differential equation for
(b) At steady-state, use this equation to solve for the particle's terminal velocity.
(c) Employ the result of (b) to compute the particle's terminal velocity in m/s for a spherical silt particle settling in water:
(d) Check whether low is laminar.
(e) Use Euler's method to compute the velocity from
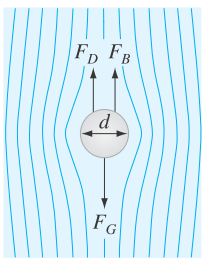
FIGURE P1.22
(a)
The differential equation for
Answer to Problem 22P
Solution:
The differential equation for
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The drag force is given as
Where,
The mass of the particle,
The mass of the displaced fluid,
The volume of sphere is
The figure,
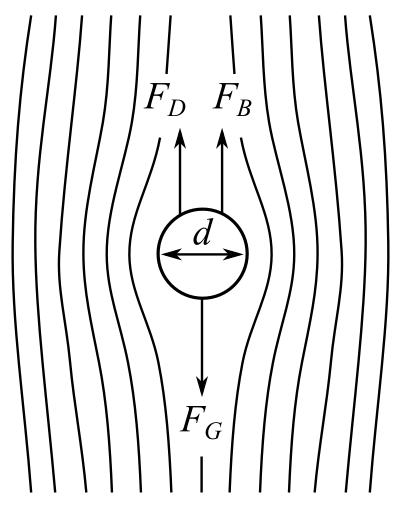
From the provided figure, the drag force and buoyancy force are against the gravitational force.
Therefore, the force balance on the sphere is given as,
Here,
And,
And,
And,
Thus, the force balance on the sphere is,
Divide the both sides of the above equation by m,
Now, the mass of the particle
Substitute
The volume of the sphere is
Substitute
Hence, the differential equation for
(b)
The particle’s terminal velocity at the steady state by the use of the differential equation
Answer to Problem 22P
Solution:
The particle’s terminal velocity at the steady state is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The differential equation
At the steady state, the change in the velocity is zero. Therefore,
Now, solve the above equation for particle’s terminal velocity v as below,
Simplify furthermore,
Hence, the particle’s terminal velocity at the steady state is,
(c)
To calculate: The value of particle’s terminal velocity in m/secif the particle’s terminal velocity is given as
Answer to Problem 22P
Solution:
The value of particle’s terminal velocity in m/sec is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The particle’s terminal velocity is given as
The values,
Formula used:
The conversions,
Calculation:
The particle’s terminal velocity at the steady state is,
Convert the provided values in to the required units as below,
And,
And,
And,
Substitute
Simplify furthermore,
Hence, the value of the particle’s terminal velocity in m/sec is
(d)
Whether the flow is laminar or not if the Reynolds number is given as
Answer to Problem 22P
Solution:
The flow is laminar.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The Reynolds number is given as
The values,
The flow is laminar if the value of Reynolds number is less than 1.
Now, consider the Reynolds number as,
From part (c),
And,
Substitute the values
Since, the Reynolds number is less than 1.
Hence, the flow is laminar.
(e)
To calculate: The velocity from
Answer to Problem 22P
Solution:
The velocity from
| t | v | dv/dt |
| 0 | 0 | 6.10771 |
| 3.8147E-06 | 2.32991E-05 | 3.891969 |
| 7.6294E-06 | 3.81457E-05 | 2.480049 |
| 1.1444E-05 | 4.76064E-05 | 1.580343 |
| 1.5259E-05 | 5.36349E-05 | 1.00703 |
| 1.9073E-05 | 5.74764E-05 | 0.641702 |
| 2.2888E-05 | 5.99243E-05 | 0.408907 |
| 2.6703E-05 | 6.14842E-05 | 0.260564 |
| 3.0518E-05 | 6.24782E-05 | 0.166037 |
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The values,
The initial condition
Formula used:
Euler’s method for
Where, h is the step size.
Calculation:
From part (a), the differential equation is,
Convert the provided values in to the standard MKS units as below,
And,
And,
And,
Substitute
The iteration formula for Euler’s method with step size
Use excel to find all the iteration with step size
Step 1: Name the column A as t and go to column A2 and put 0 then go to column A3and write the formula as,
=A2+2^(-18)
Then, Press enter and drag the column up to the
Step 2: Now name the column B as v and go to column B2 and write 0 and then go to the column B3 and write the formula as,
=B3+2^(-18)*(6.10771-95100*B3)
Step 3: Press enter and drag the column up to the
Step 4. Now name the column C as dv/dt and go to column C2 and write the formula as,
=6.10771-95100*B2
Step 5. Press enter and drag the column up to the
Thus, all the iterations are as shown below,
| t | v | dv/dt |
| 0 | 0 | 6.10771 |
| 3.8147E-06 | 2.32991E-05 | 3.891969 |
| 7.6294E-06 | 3.81457E-05 | 2.480049 |
| 1.1444E-05 | 4.76064E-05 | 1.580343 |
| 1.5259E-05 | 5.36349E-05 | 1.00703 |
| 1.9073E-05 | 5.74764E-05 | 0.641702 |
| 2.2888E-05 | 5.99243E-05 | 0.408907 |
| 2.6703E-05 | 6.14842E-05 | 0.260564 |
| 3.0518E-05 | 6.24782E-05 | 0.166037 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
- PROBLEM 3.46 The solid cylindrical rod BC of length L = 600 mm is attached to the rigid lever AB of length a = 380 mm and to the support at C. When a 500 N force P is applied at A, design specifications require that the displacement of A not exceed 25 mm when a 500 N force P is applied at A For the material indicated determine the required diameter of the rod. Aluminium: Tall = 65 MPa, G = 27 GPa. Aarrow_forwardFind the equivalent mass of the rocker arm assembly with respect to the x coordinate. k₁ mi m2 k₁arrow_forward2. Figure below shows a U-tube manometer open at both ends and containing a column of liquid mercury of length l and specific weight y. Considering a small displacement x of the manometer meniscus from its equilibrium position (or datum), determine the equivalent spring constant associated with the restoring force. Datum Area, Aarrow_forward
- 1. The consequences of a head-on collision of two automobiles can be studied by considering the impact of the automobile on a barrier, as shown in figure below. Construct a mathematical model (i.e., draw the diagram) by considering the masses of the automobile body, engine, transmission, and suspension and the elasticity of the bumpers, radiator, sheet metal body, driveline, and engine mounts.arrow_forward3.) 15.40 – Collar B moves up at constant velocity vB = 1.5 m/s. Rod AB has length = 1.2 m. The incline is at angle = 25°. Compute an expression for the angular velocity of rod AB, ė and the velocity of end A of the rod (✓✓) as a function of v₂,1,0,0. Then compute numerical answers for ȧ & y_ with 0 = 50°.arrow_forward2.) 15.12 The assembly shown consists of the straight rod ABC which passes through and is welded to the grectangular plate DEFH. The assembly rotates about the axis AC with a constant angular velocity of 9 rad/s. Knowing that the motion when viewed from C is counterclockwise, determine the velocity and acceleration of corner F.arrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
