
Concept explainers
For the function
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g)
(h)
(i)
(a)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
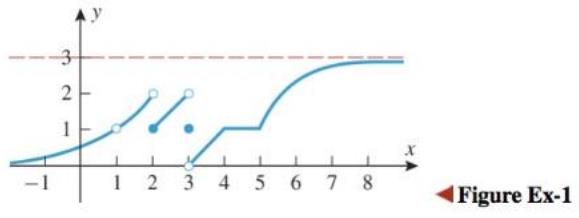
Consider the graph.
It is clear from the graph that the function is continuous at
This implies,
Hence, the value of
(b)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
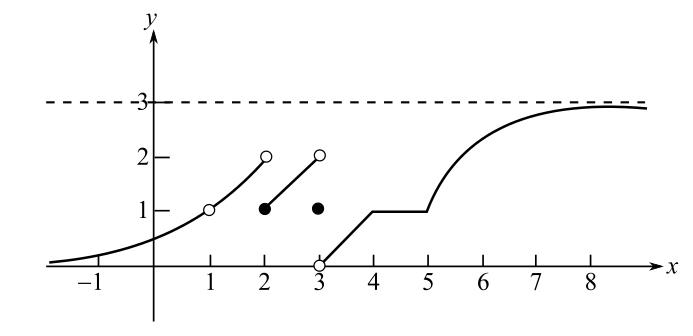
Consider the figure.
It is clear from the graph that the function approaches to 2 as
This implies that the left hand limit is not equal to right hand limit.
Therefore,
(c)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
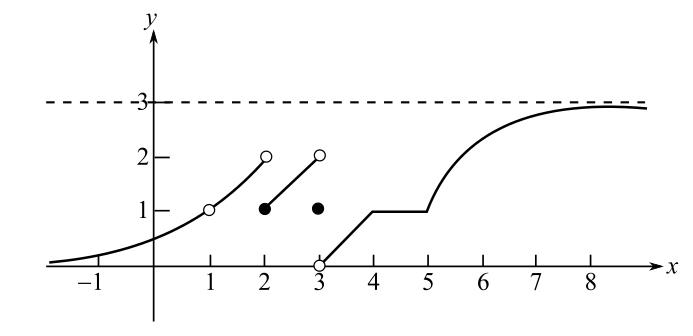
Consider the given figure.
It is clear from the graph that the function approaches to 2 as
Hence,
(d)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
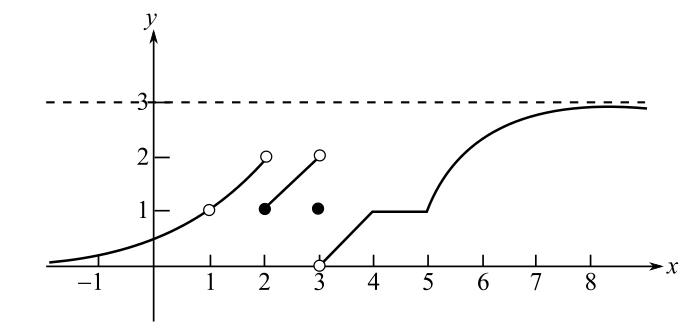
Consider the given figure.
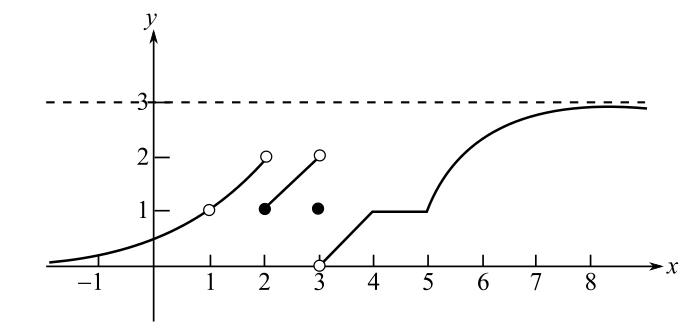
It can be seen from the graph that the function
This implies,
Hence, the value of
(e)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Consider the figure.
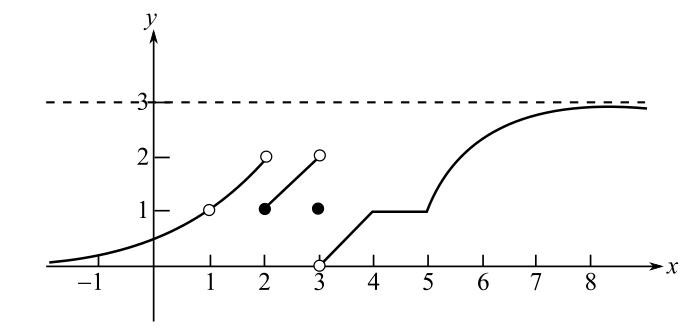
It can be observed from the graph that the function
This implies,
Hence, the value of
(f)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Consider the figure.
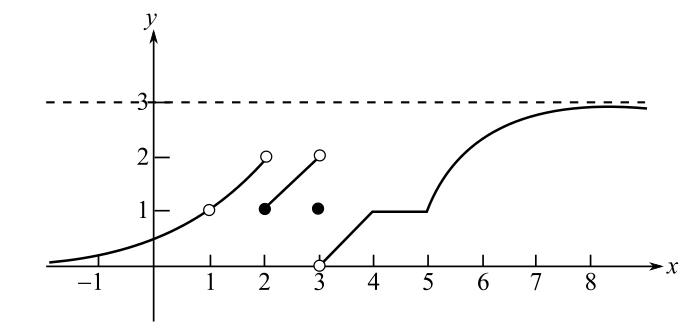
It can be observed from the graph that the minimum value that function can approach to is 0. Therefore, the function approaches to 0 for sufficiently small
This implies,
Hence, the value of
(g)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Consider the figure.
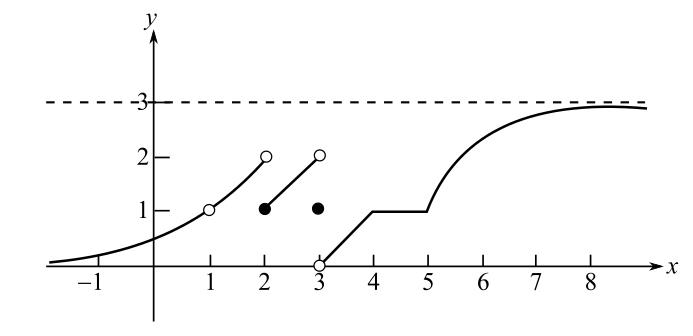
It can be clearly seen from the graph, the function approaches to 0 as
This implies,
Hence, the value of
(h)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Consider the figure.
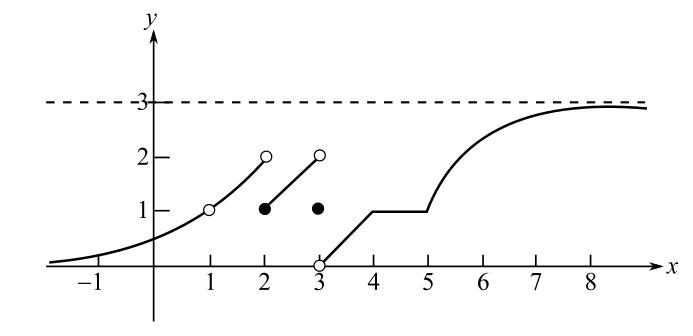
It can be observed from the graph that the function approaches to 2 as
This implies,
Hence, the value of
(i)
The value of
Answer to Problem 1RE
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Consider the given figure.
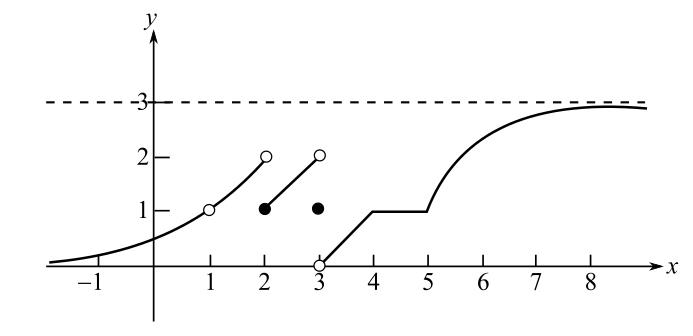
It can be seen from the graph that the function
This implies,
Hence, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Calculus Early Transcendentals, Binder Ready Version
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward3. True False. If false create functions that prove it is false. Note: f(x) = g(x). a) If_lim ƒ(x) = ∞ and_lim g(x) = ∞,then_lim [ƒ(x) − g(x)] = 0 x→ 0+ x→0+ x→0+ b) If h(x) and g(x) are continuous at x = c, and if h(c) > 0 and g(c) = 0, then h(x) lim. will = x→c g(x) c) If lim f(x) = 0 and lim g(x) = 0 then lim f(x) does not exist. x-a x-a x→a g(x)arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- 15. a) Consider f(x) = x-1 3x+2 and use the difference quotient to determine the simplified expression in terms of x, for the slope of any tangent to y = f(x). Also, determine the slope at x = 2. 15 b) Determine the equation of the tangent to f(x) at x = 2. Final answer in Standard Form Ax + By + C = 0, A ≥ 0, with no fractions or decimals.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- Determine whether the series is convergent or divergent. Justify your answer. If the series is convergent, you do not have to find its sum. n=0 (-1) 72n+1 (2n)!arrow_forward+ Find the first five non-zero terms of the Taylor series for f(x) = sin(2x) centered at 4π. + + + ...arrow_forward+ + ... Find the first five non-zero terms of the Taylor series for f(x) centered at x = 4. = 1 x + + +arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





