
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the dew condensing on a leaf can be reversed by changing the temperature or not is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. Physical change brings change in physical properties only. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The physical change can be represented as follows:
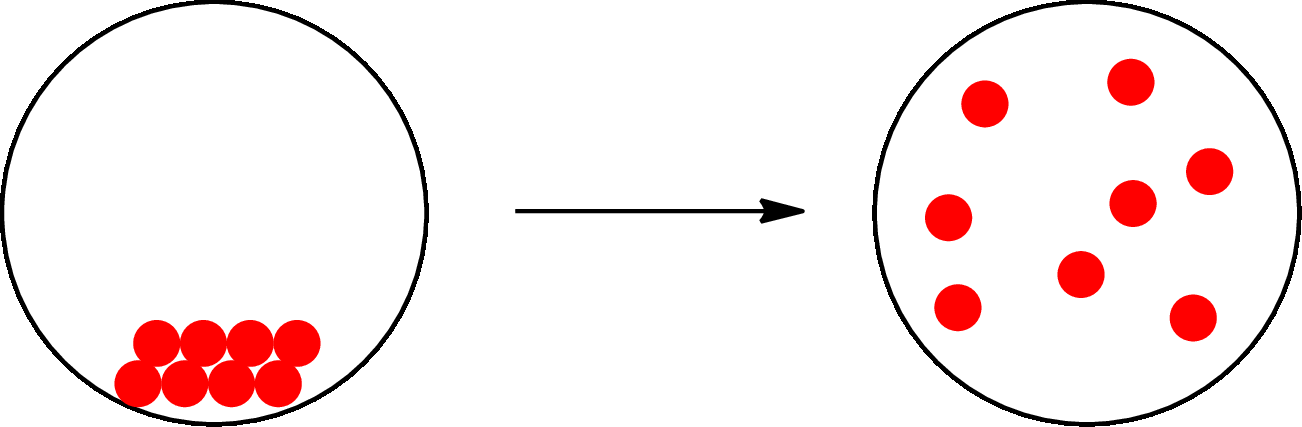
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. A chemical change can change physical as well as chemical properties of a substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
The representation of chemical change is as follows:
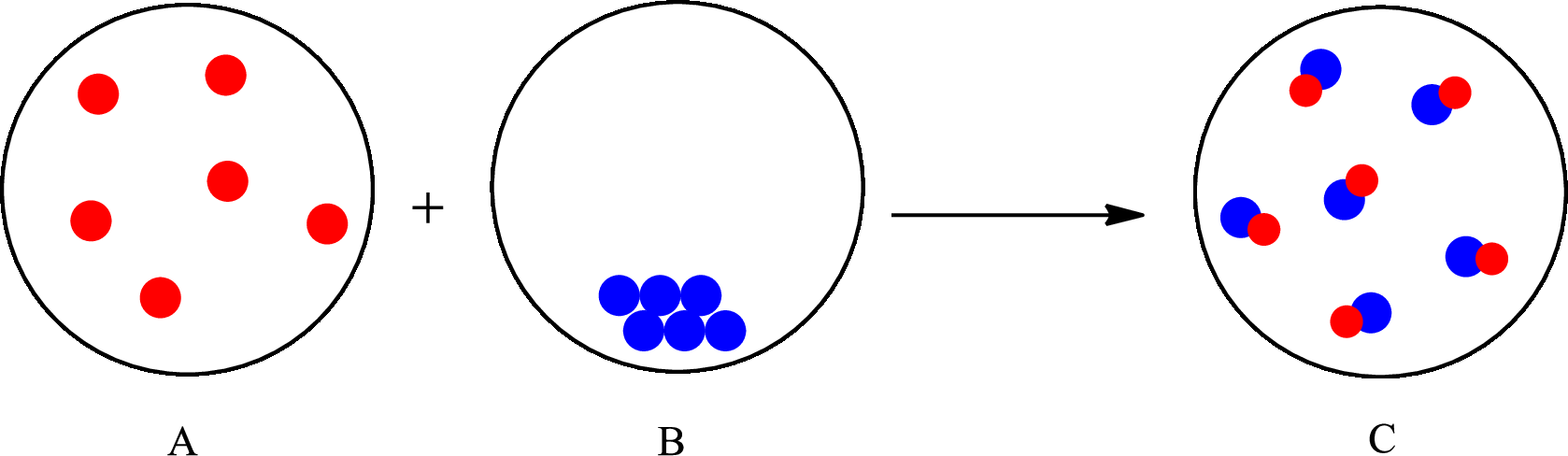
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether an egg turning hard due to boiling can be reversed by changing the temperature or not is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. Physical change brings change in physical properties only. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The physical change can be represented as follows:
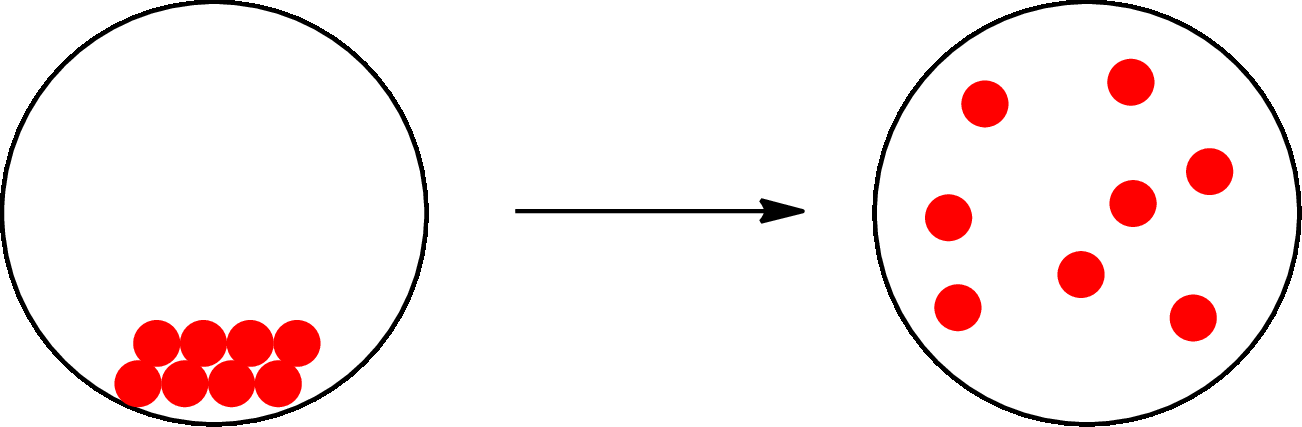
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. A chemical change can change physical as well as chemical properties of a substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
The representation of chemical change is as follows:
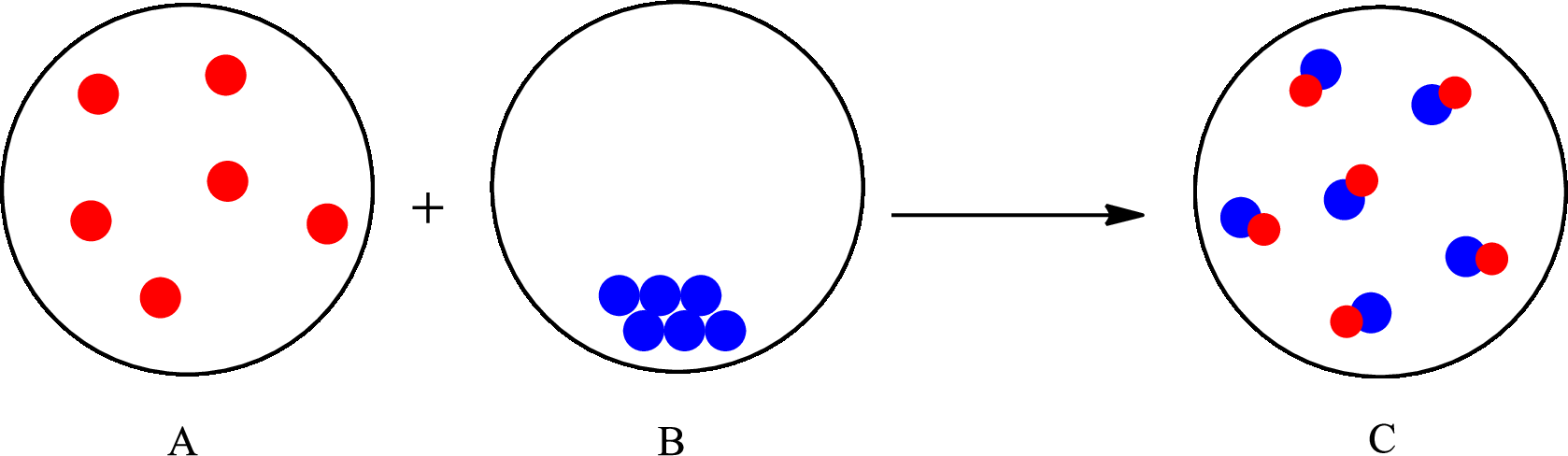
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the melting of ice cream can be reversed by changing the temperature or not is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. Physical change brings change in physical properties only. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The physical change can be represented as follows:
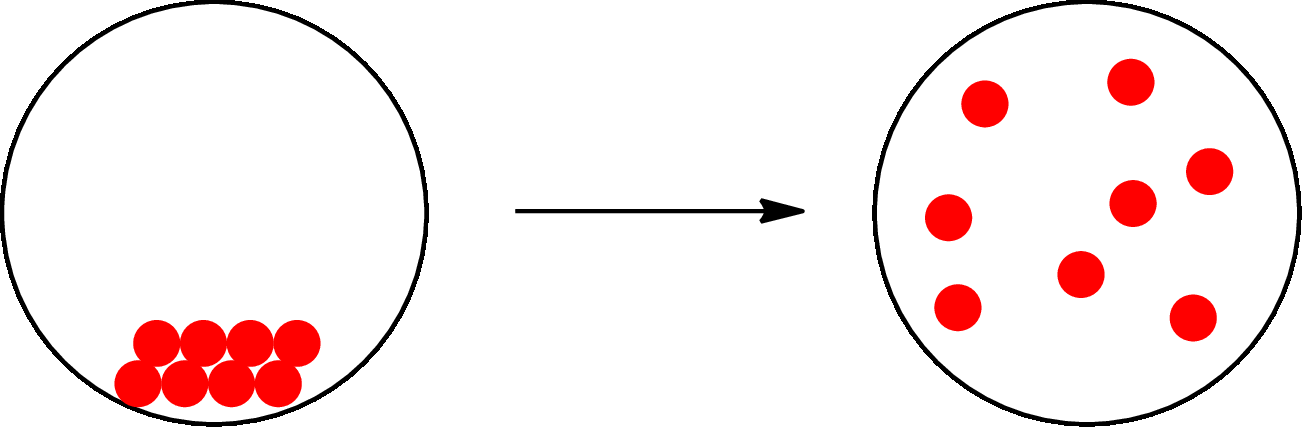
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. A chemical change can change physical as well as chemical properties of a substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
The representation of chemical change is as follows:
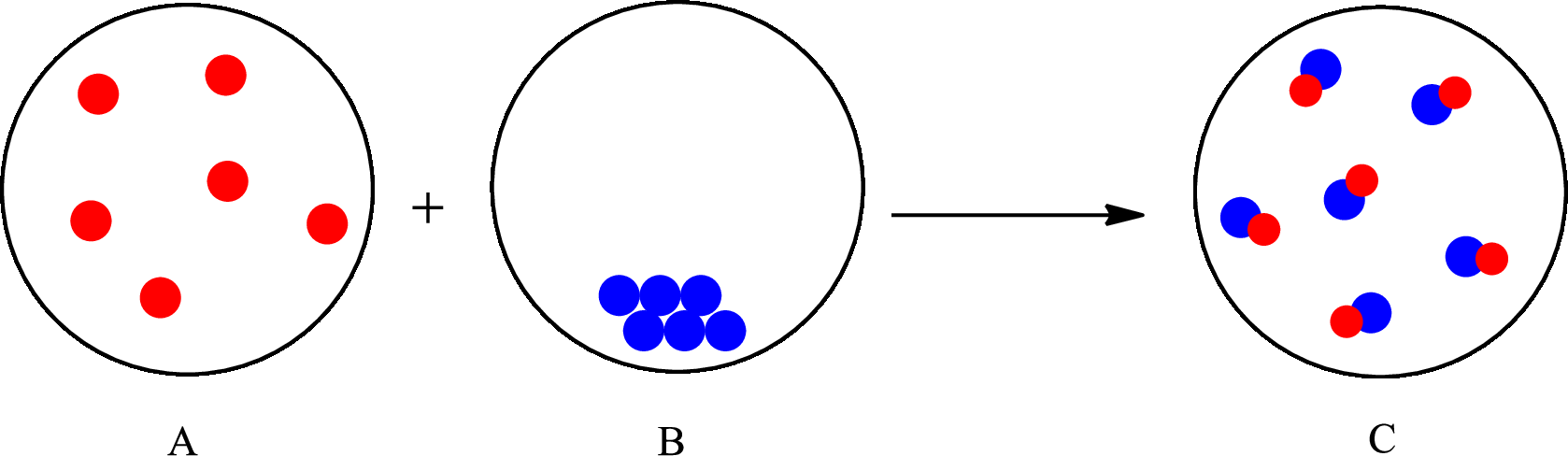
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether a spoonful of the batter cooking on a hot griddle can be reversed by changing the temperature or not is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The change that takes place only in state or appearance and not in the composition is known as physical change. The atoms or the molecules of a substance do not change their identity when a substance undergoes a physical change. The substance remains the same before and after the change. Physical change brings change in physical properties only. For example, the melting of ice is a physical change.
The physical change can be represented as follows:
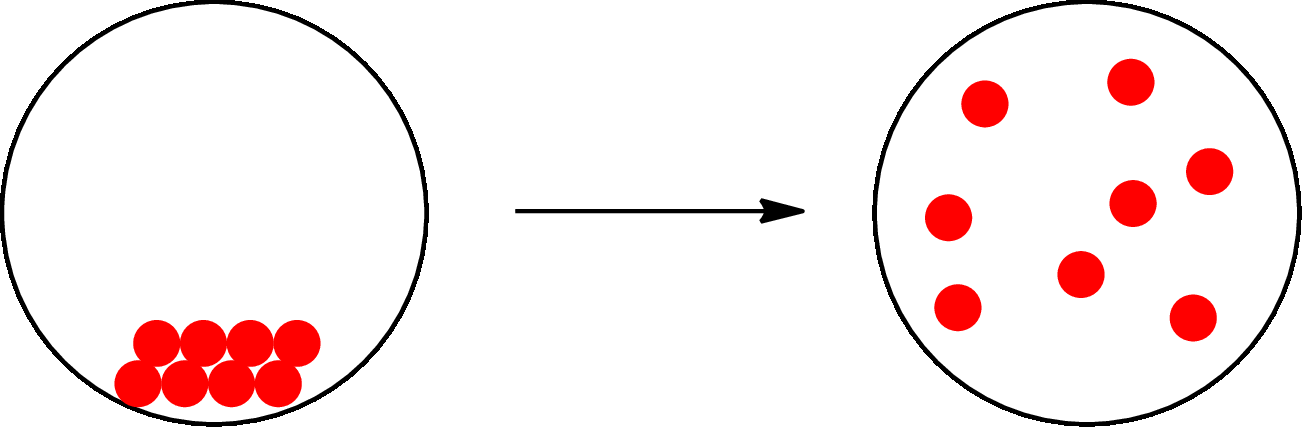
The change that takes place in the composition is known as chemical change. The atoms or the molecules of the substance rearrange and transformed into a new substance. A chemical change can change physical as well as chemical properties of a substance. For example, the burning of paper is a chemical change.
The representation of chemical change is as follows:
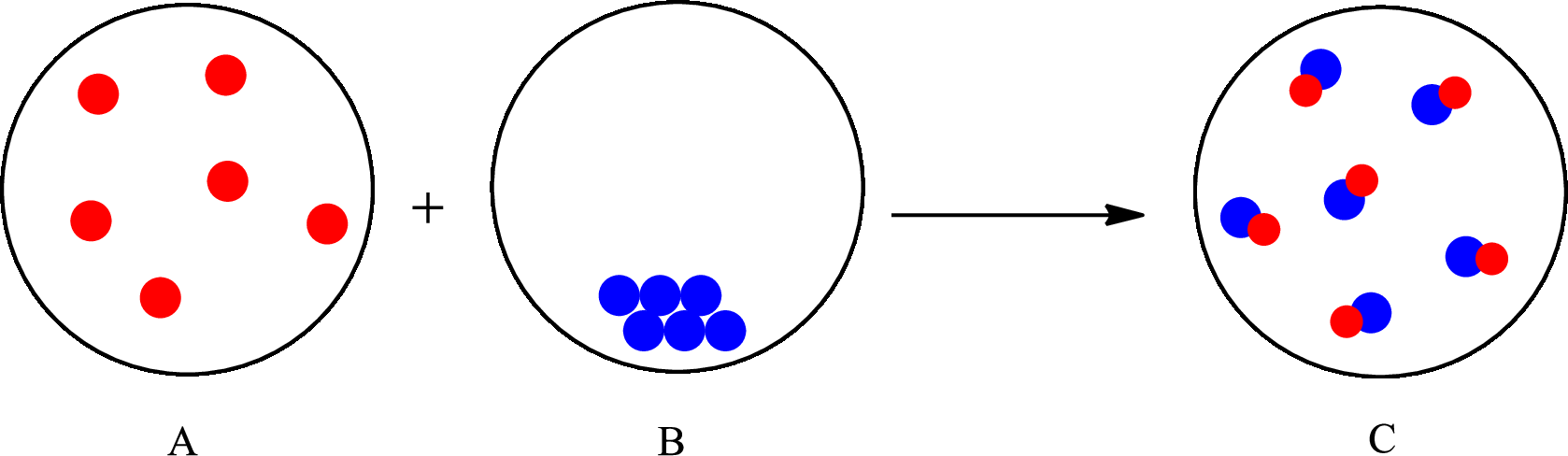
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change
- Using what we have learned in CHEM 2310 and up through class on 1/31, propose a series of reaction steps to achieve the transformation below. Be sure to show all reagents and intermediates for full credit. You do not need to draw mechanism arrows, but you do need to include charges where appropriate. If you do not put your group name, you will get half credit at most. ? Brarrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the formation of 2-bromovanillin using bromonium ion as the reactive electrophile.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





