You have to do thermal analysis of a building near an arctic observatory, which has a footprint of 8-m×12-m and height of 4-m and oriented as shown. Because the wind direction and velocities are different on each side wall, the convection coefficient for each wall and roof are different. They are as follows hNorth hwest indicate the corresponding wall/roof (for example, hNorth is the convection coefficient for the North-facing wall). The ambient air temperature is = 15 W/m².K, hsouth 12 W/m².K, and hRoof W/m²-K, hEast 20 W/m².K, = 30 W/m².K, where the subscript NORTH 12 m SOUTH -15°C. The sky temperature is –20°C. The solar irradiation is 350 W/m², which can be considered to be falling only on the roof and not on the walls. The surface temperature of the building is 10°C. Neglect heat transfer through the ground. What is the total heat transfer to/from the building? Is the building losing or gaining heat? What is the dominant mode of heat WEST
You have to do thermal analysis of a building near an arctic observatory, which has a footprint of 8-m×12-m and height of 4-m and oriented as shown. Because the wind direction and velocities are different on each side wall, the convection coefficient for each wall and roof are different. They are as follows hNorth hwest indicate the corresponding wall/roof (for example, hNorth is the convection coefficient for the North-facing wall). The ambient air temperature is = 15 W/m².K, hsouth 12 W/m².K, and hRoof W/m²-K, hEast 20 W/m².K, = 30 W/m².K, where the subscript NORTH 12 m SOUTH -15°C. The sky temperature is –20°C. The solar irradiation is 350 W/m², which can be considered to be falling only on the roof and not on the walls. The surface temperature of the building is 10°C. Neglect heat transfer through the ground. What is the total heat transfer to/from the building? Is the building losing or gaining heat? What is the dominant mode of heat WEST
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Please. Answer parts please. Attempt Once

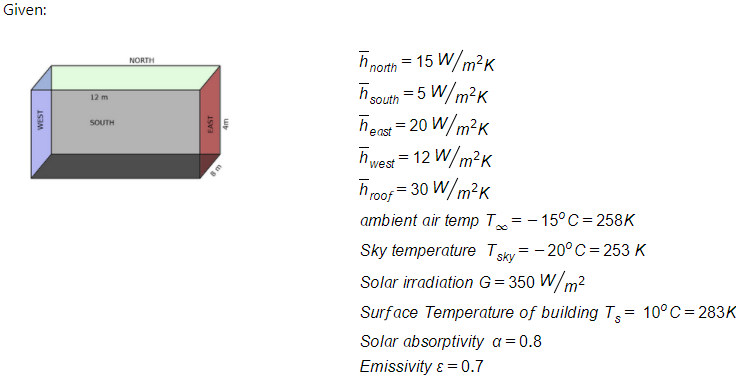
Transcribed Image Text:You have to do thermal analysis of a building near an arctic observatory,
which has a footprint of 8-mx12-m and height of 4-m and oriented as
shown. Because the wind direction and velocities are different on each side
wall, the convection coefficient for each wall and roof are different. They are
as follows hNorth
hw est
15 W/m².K, hsouth
= 12 W/m².K, and hRoof
5 W/m².K, hEast
20 W/m².K,
30 W/m2.K, where the subscript
indicate the corresponding wall/roof (for example, hNorth is the convection
NORTH
coefficient for the North-facing wall). The ambient air temperature is
12 m
-15°C. The sky temperature is –20°C. The solar irradiation is 350 W/m²,
SOUTH
which can be considered to be falling only on the roof and not on the walls.
The surface temperature of the building is 10°C. Neglect heat transfer
8 m
through the ground. What is the total heat transfer to/from the building?
Is the building losing or gaining heat? What is the dominant mode of heat
transfer? What is the ratio between the heat fluxes through the roof and
through the East wall? The solar absorptivity is 0.8, the emissivity of the
wall and roof is 0.7.
WEST
EAST
Expert Solution
Step 1

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY