Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
100%

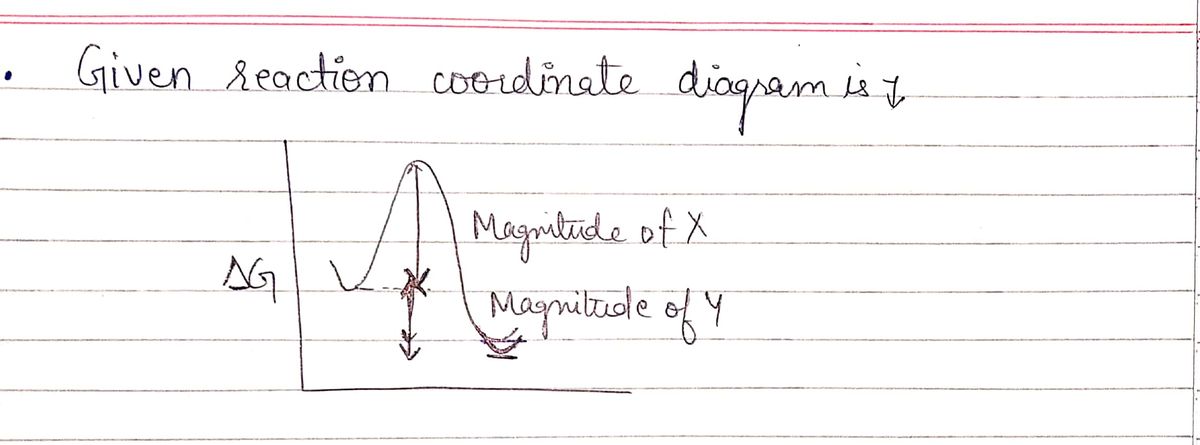
Transcribed Image Text:### Reaction Coordinate Diagram Analysis
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram illustrates a reaction coordinate graph with two significant features labeled as Magnitude X and Magnitude Y. The y-axis represents the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG), while the x-axis depicts the reaction progress. A curve on the graph shows the energy profile of the reaction, rising to a peak (activation energy) and then dropping to a lower energy level.
- **Magnitude X:** Represents the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed from reactants to products.
- **Magnitude Y:** Represents the overall change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) from reactants to products.
**Statements Analysis:**
A) This reaction will favor the starting materials.
B) The reverse reaction is faster than the forward reaction.
C) Increasing Y will make the starting materials more favored.
D) A catalyst would make X smaller.
Each statement pertains to different aspects of the reaction energetics, such as favorability, reaction rates, and the effects of catalysts. Understanding these elements can provide insight into reaction mechanisms and conditions.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY