What is the mechanism of chymotrypsin catalysed by enzymes without cofactors?
CHYMOTRYPSIN is a digestive enzyme of pancreatic juice acting on the duodenum where it performs functions like, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferably cleaves peptide amide bond. These amino acids contain an aromatic ring that fits into hydrophobic pocket of the enzyme. It is activated by the presence of trypsin.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Chymotrypsin is a proteolytic enzyme acting on the digestive systems of many organisms. It cleaves peptide bond by hydrolysis reaction. The main substrates of chymotrypsin are peptide bonds in which amino acid N-terminal to the bond is tryptophan, tyrosine, phenylalanine or leucine.
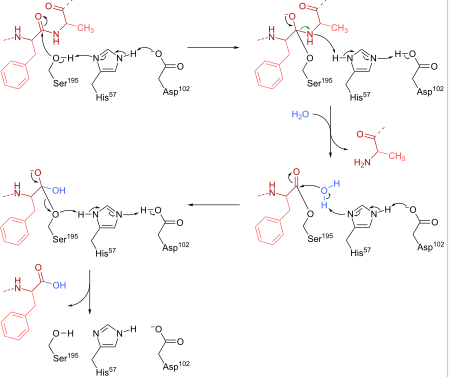
Chymotrypsin cleaves bond by attacking the unreactive carbonyl group by the strong nucleophile, the serine which becomes covalently bonded to the substrate forming enzyme-substrate intermediate.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









