What is the energy structure of metals, semiconductors and insulators?
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:What is the energy structure of metals, semiconductors and insulators?
Expert Solution
Step 1
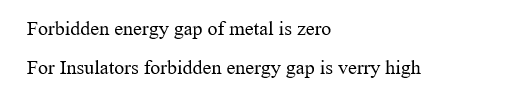
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
