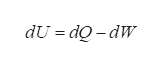An Introduction to Physical Science 14th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079137
Author: James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher: James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
1 Measurement 2 Motion 3 Force And Motion 4 Work And Energy 5 Temperature And Heat 6 Waves And Sound 7 Optics And Wave Effects 8 Electricity And Magnetism 9 Atomic Physics 10 Nuclear Physics 11 The Chemical Elements 12 Chemical Bonding 13 Chemical Reactions 14 Organic Chemistry 15 Place And Time 16 The Solar System 17 Moons And Small Solar System Bodies 18 The Universe 19 The Atmosphere 20 Atmospheric Effects 21 Structural Geology And Plate Tectonics 22 Minerals, Rocks, And Volcanoes 23 Surface Processes 24 Geologic Time Chapter5: Temperature And Heat
5.1 Temperature 5.2 Heat 5.3 Specific Heat And Latent Heat 5.4 Heat Transfer 5.5 Phases Of Matter 5.6 The Kinetic Theory Of Gases 5.7 Thermodynamics Chapter Questions Section: Chapter Questions
Problem AM Problem BM Problem CM Problem DM Problem EM Problem FM Problem GM Problem HM Problem IM Problem JM Problem KM Problem LM Problem MM Problem NM Problem OM Problem PM Problem QM Problem RM Problem SM Problem TM Problem UM Problem VM Problem WM Problem XM Problem YM Problem 1MC Problem 2MC: Which unit of the following is smaller? (5.2) (a) a degree Fahrenheit (b) a kelvin (c) a degree... Problem 3MC Problem 4MC Problem 5MC Problem 6MC Problem 7MC Problem 8MC: Which of the following has a definite volume but no definite shape? (5.5) (a) solid (b) liquid (c)... Problem 9MC: If the average kinetic energy of the molecules in an ideal gas initially at 20C doubles, what is the... Problem 10MC: When we use the ideal gas law, the temperature must be in which of the following units? (5.6) (a) C... Problem 11MC Problem 12MC Problem 1FIB: When a bimetallic strip is heated, it bends away from the metal with the ___ thermal expansion.... Problem 2FIB Problem 3FIB Problem 4FIB Problem 5FIB Problem 6FIB Problem 7FIB Problem 8FIB: The ___ phase of matter has no definite shape, and no definite volume. (5.4) Problem 9FIB Problem 10FIB: In the ideal gas law, pressure is ___ proportional to volume. (5.6) Problem 11FIB Problem 12FIB Problem 1SA: When the temperature changes during the day, which scale, Fahrenheit or Celsius, will have the... Problem 2SA Problem 3SA: The two common liquids used in liquid-in-glass thermometers are alcohol (ethanol) and mercury, which... Problem 4SA: An older type of thermostat used in furnace and heat pump control is shown in Fig. 5.21. The glass... Problem 5SA: Heat may be thought of as the middleman of energy. Why? Problem 6SA: When one drinking glass is stuck inside another, an old trick to unstick them is to put water in one... Problem 7SA Problem 8SA: What does the specific heat of a substance tell you when you compare it with the specific heat of... Problem 9SA: When eating a piece of hot apple pie, you may find that the crust is only warm but the apple filling... Problem 10SA Problem 11SA: When you exhale outdoors on a cold day, you can see your breath. Why? Problem 12SA: Compare the SI units of specific heat and latent heat and explain any differences. Problem 13SA: Give two examples each of good thermal conductors and good thermal insulators. In general, what... Problem 14SA Problem 15SA Problem 16SA: Thermal underwear is made to fit loosely. ( Fig. 5.23). What is the purpose of this? Figure 5.23... Problem 17SA: What determines the phase of a substance? Problem 18SA: Give descriptions of a solid, a liquid, and a gas in terms of shape and volume. Problem 19SA Problem 20SA: How does the kinetic theory describe a gas? Problem 21SA Problem 22SA Problem 23SA Problem 24SA: In terms of kinetic theory, explain why a basketball stays inflated. Problem 25SA Problem 26SA Problem 27SA Problem 28SA Problem 29SA: What can be said about the total entropy of the universe? Why is it true? Problem 30SA Problem 31SA Problem 1VC Problem 1AYK Problem 2AYK Problem 3AYK Problem 4AYK Problem 5AYK Problem 6AYK Problem 7AYK: When you freeze ice cubes in a tray, there is a decrease in entropy because there is more order in... Problem 8AYK Problem 1E Problem 2E Problem 3E Problem 4E Problem 5E: Researchers in the Antarctic measure the temperature to be 40F. What is this temperature (a) on the... Problem 6E Problem 7E: A college student produces about 100 kcal of heat per hour on the average. What is the rate of... Problem 8E Problem 9E: A pound of body fat stores an amount of chemical energy equivalent to 3500 Cal. When sleeping, the... Problem 10E Problem 11E: On a brisk walk, a person burns about 325 Cal/h. At this rate, how many hours of brisk walking would... Problem 12E Problem 13E: How much heat in kcal must be added to 0.50 kg of water at room temperature (20C) to raise its... Problem 14E Problem 15E: (a) How much energy is necessary to heat 1.0 kg of water from room temperature (20C) to its boiling... Problem 16E: Equal amounts of heat are added to equal masses of aluminum and iron at the same initial... Problem 17E: How much heat is necessary to change 500 g of ice at 10C to water at 20C? Problem 18E: A quantity of steam (300 g) at 110C is condensed, and the resulting water is frozen into ice at 0C.... Problem 19E Problem 20E: A fire breaks out and increases the Kelvin temperature of a cylinder of compressed gas by a factor... Problem 21E: A cylinder of gas is at room temperature (20C). The air conditioner breaks down, and the temperature... Problem 22E: A cylinder of gas at room temperature has a pressure p1. To what temperature in degrees Celsius... Problem 23E: A quantity of gas in a piston cylinder has a volume of 0.500 m3 and a pressure of 200 Pa. The piston... Problem 24E: If the gas in Exercise 23 is initially at room temperature (20C) and is heated in an isobaric... Problem 26SA
Related questions
What is significance of first law of thermodynamics ?
Science that deals with the amount of energy transferred from one equilibrium state to another equilibrium state.
Expert Solution
The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of the system is equal to the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system. It is based on the principle of conservation of energy.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images
UNLOCK THE REST