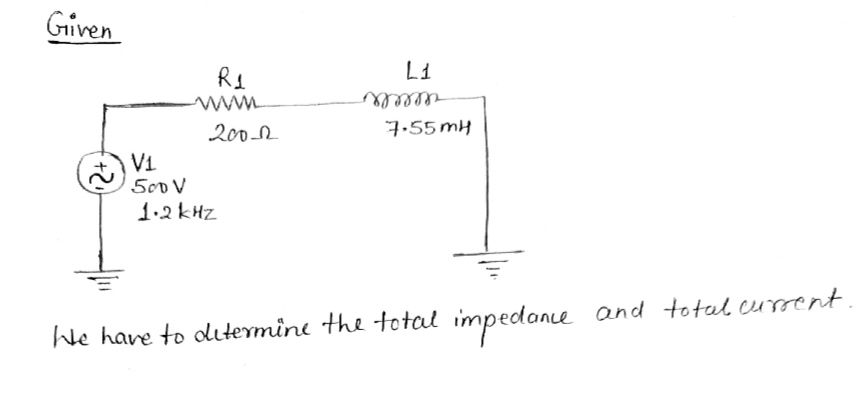
V1 500V 1.2kHz Total Impedance Trec = Tpolar = otal Current T(PK) = T(rms) R1 20092 units units units L1 7.55mH • units units
V1 500V 1.2kHz Total Impedance Trec = Tpolar = otal Current T(PK) = T(rms) R1 20092 units units units L1 7.55mH • units units
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
100%
Determine the following for the circuit below
![**Introduction to Series RL Circuit Analysis**
This educational resource aims to help you understand the analysis of a simple series RL (Resistor-Inductor) AC circuit. In this circuit, the components are connected in a single loop.
**Circuit Description**
- **Source (V1):** The circuit is powered by an AC voltage source with a magnitude of 500 V and a frequency of 1.2 kHz.
- **Resistor (R1):** The resistor in the circuit has a resistance of 200 ohms (Ω).
- **Inductor (L1):** The inductor has an inductance of 7.55 millihenrys (mH).
**Circuit Analysis**
1. **Total Impedance (Z):**
- **Rectangular Form (Zrec):** Impedance is a complex quantity. It can be expressed in rectangular form as \( Z = R + jX \), where \( R \) is the resistance and \( X \) is the reactance.
- **Polar Form (Zpolar):** Impedance can also be represented in polar form as a magnitude and angle, \( Z = |Z| \angle \theta \).
2. **Total Current (I):**
- **Peak Current (I(Tpk)):** The maximum instantaneous value of the AC current.
- **RMS Current (I(Trms)):** The effective value of the current, which is crucial for calculating average power.
**Interactive Sections**
- **Total Impedance:**
- \( Z_{\text{rec}} = \) [Enter real part] units + j [Enter imaginary part] units
- \( Z_{\text{polar}} = \) [Enter magnitude] \( \angle \) [Enter angle] ° units
- **Total Current:**
- \( I_{T(\text{Pk})} = \) [Enter peak current] units
- \( I_{T(\text{rms})} = \) [Enter RMS current] units
Understanding these parameters allows you to analyze how resistors and inductors affect AC circuits, which is fundamental in electrical engineering. Make sure to use the correct units and conversions in your calculations.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F945ae690-9b29-4664-b591-03f86d69ed48%2Fe0f3f62c-9d3a-403e-89b0-38a73b8371e3%2Fuoxypui_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Introduction to Series RL Circuit Analysis**
This educational resource aims to help you understand the analysis of a simple series RL (Resistor-Inductor) AC circuit. In this circuit, the components are connected in a single loop.
**Circuit Description**
- **Source (V1):** The circuit is powered by an AC voltage source with a magnitude of 500 V and a frequency of 1.2 kHz.
- **Resistor (R1):** The resistor in the circuit has a resistance of 200 ohms (Ω).
- **Inductor (L1):** The inductor has an inductance of 7.55 millihenrys (mH).
**Circuit Analysis**
1. **Total Impedance (Z):**
- **Rectangular Form (Zrec):** Impedance is a complex quantity. It can be expressed in rectangular form as \( Z = R + jX \), where \( R \) is the resistance and \( X \) is the reactance.
- **Polar Form (Zpolar):** Impedance can also be represented in polar form as a magnitude and angle, \( Z = |Z| \angle \theta \).
2. **Total Current (I):**
- **Peak Current (I(Tpk)):** The maximum instantaneous value of the AC current.
- **RMS Current (I(Trms)):** The effective value of the current, which is crucial for calculating average power.
**Interactive Sections**
- **Total Impedance:**
- \( Z_{\text{rec}} = \) [Enter real part] units + j [Enter imaginary part] units
- \( Z_{\text{polar}} = \) [Enter magnitude] \( \angle \) [Enter angle] ° units
- **Total Current:**
- \( I_{T(\text{Pk})} = \) [Enter peak current] units
- \( I_{T(\text{rms})} = \) [Enter RMS current] units
Understanding these parameters allows you to analyze how resistors and inductors affect AC circuits, which is fundamental in electrical engineering. Make sure to use the correct units and conversions in your calculations.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Parameters need to be determine
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,