Using the web, find one example each of a functional, matrix, and project-oriented organization_ Pre asgenisations.
Critical Path Method
The critical path is the longest succession of tasks that has to be successfully completed to conclude a project entirely. The tasks involved in the sequence are called critical activities, as any task getting delayed will result in the whole project getting delayed. To determine the time duration of a project, the critical path has to be identified. The critical path method or CPM is used by project managers to evaluate the least amount of time required to finish each task with the least amount of delay.
Cost Analysis
The entire idea of cost of production or definition of production cost is applied corresponding or we can say that it is related to investment or money cost. Money cost or investment refers to any money expenditure which the firm or supplier or producer undertakes in purchasing or hiring factor of production or factor services.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is the process or system of handling all the goods that an organization owns. In simpler terms, inventory management deals with how a company orders, stores, and uses its goods.
Project Management
Project Management is all about management and optimum utilization of the resources in the best possible manner to develop the software as per the requirement of the client. Here the Project refers to the development of software to meet the end objective of the client by providing the required product or service within a specified Period of time and ensuring high quality. This can be done by managing all the available resources. In short, it can be defined as an application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet the objective of the Project. It is the duty of a Project Manager to achieve the objective of the Project as per the specifications given by the client.
Question 4.

There are basically 4 types of organizational structures are-
- Functional
- Project
- Matrix
- Composite
Functional
Most associations are partitioned along utilitarian lines, that is, every "division" is coordinated by work type, for example, designing, creation, or deals.
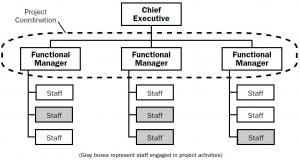
In the practical authoritative construction, projects are started and executed by the divisional supervisors, who expect the project manager duties notwithstanding their ordinary, useful, roles. They are frequently given auxiliary titles, for example, "Organizer of Project X."
In this construction, project administrators for the most part don't have alot of power to obtain resources or to manage schedules and budgets. They should get endorsements to use assets from different offices, which can be a complex undertaking. This is on the grounds that the useful association is intended to zero in on the arrangement of the divisional administrations as opposed to project deliverables.
Example- A vehicle sales center needs to start another business cycle. It allocates the plan and execution to the project supervisor, who uses a portion of the deals just as support staff to build up the essential records and actualize the arrangement. This is a functional hierarchical construction.
Project-Oriented
On the opposite finish of the scale is the undertaking focused organization. These organizations do the greater part of their work on a venture premise and are accordingly organized around projects. This incorporates development workers for hire, design firms, and experts.
Task supervisors are normally full time in the role, and for little undertakings they may deal with a few ventures on the double.
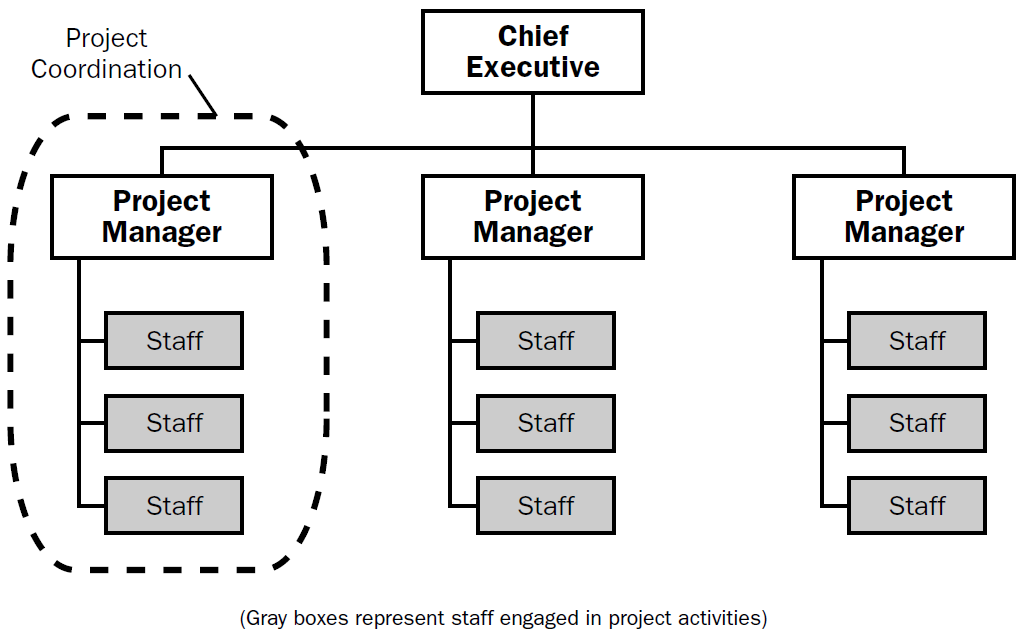
In this design project supervisors typically have a lot of freedom and authority. They can draw on assets with minimal required endorsement.
Indeed, the majority of these kinds of associations have some type of practical divisions which are placeholders for resources that can be used by all projects. They are typically called "offices."
For instance, at a designing firm the geotechnical office is accessible as a specialist asset to all ventures inside the firm.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images









