Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
ChapterP: Preliminary Concepts
SectionP.CT: Test
Problem 1CT
Related questions
Question
1. Use the

Transcribed Image Text:The image is a table designed for educational purposes, structured to help students organize information logically.
**Table Structure:**
- **Columns:**
- The table has two main columns.
1. **Statement:** This column is meant for assertions, propositions, or hypotheses that learners are examining or proving.
2. **Justification:** This column is used to provide the reasoning, evidence, or proof behind each statement.
- **Rows:**
- The table contains multiple rows, each intended to hold a distinct statement and its corresponding justification.
**Design Details:**
- The headers for each column are prominently displayed and styled in green.
- There are several horizontally aligned black lines separating each row, ensuring clarity and organization.
- The background of the table is light blue, which visually distinguishes the fields where text is to be entered.
This table format is useful for subjects that require critical thinking and detailed reasoning, such as mathematics, science, or philosophy. It helps in systematically breaking down complex ideas into clear and understandable components.

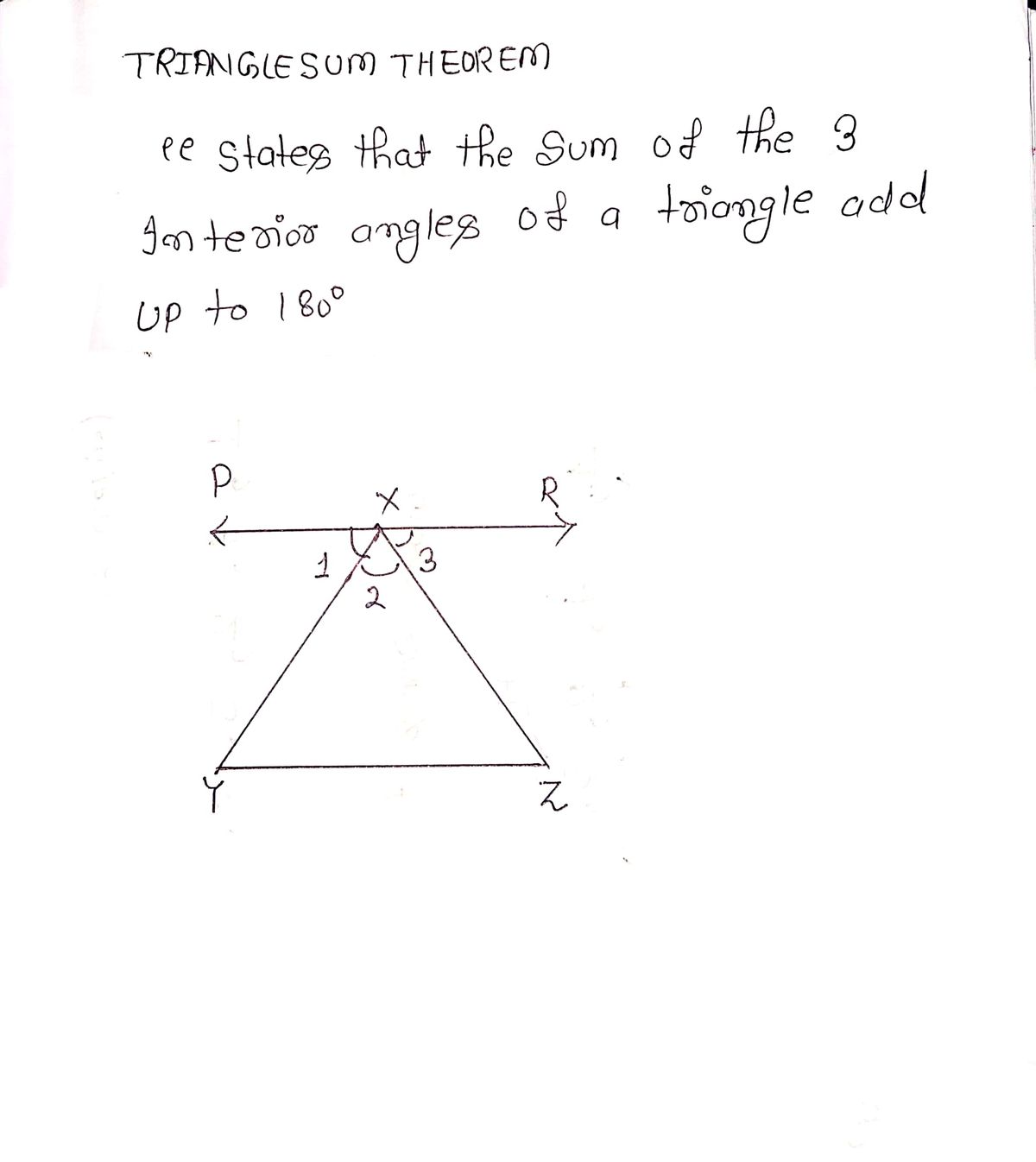
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a green equilateral triangle labeled with vertices X, Y, and Z.
### Diagram Explanation:
- **Shape:** Equilateral Triangle
- **Vertices:**
- Vertex X is located at the top of the triangle.
- Vertex Y is at the bottom-left corner.
- Vertex Z is at the bottom-right corner.
- **Color:** The triangle is filled with a solid green color, and the outlines are black.
- **Properties:** In an equilateral triangle, all three sides are of equal length, and each interior angle measures 60 degrees. This geometric shape is symmetrical and balanced.
This triangle can be used to demonstrate various geometric principles, including symmetry, angles, and the properties of equilateral triangles.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning