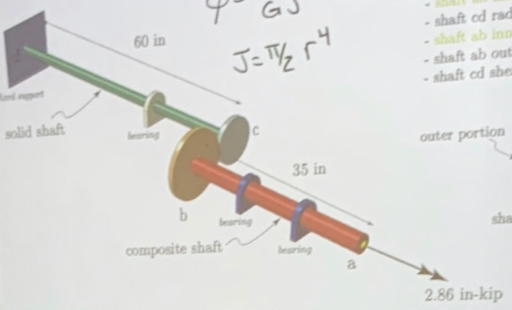
Two solid circular shafts are connected by two rigid ab is a composite shaft. Determine the angle of twist at point 'a' in degrees to two decimal places. solid shaft 60 in b 4= 11-3535 TL GJ J= π/₂2r4 composite shaft C 35 in Notes:- gear b radius = 6.0 in - gear c radius= 4.0 in - shaft ab outer radius = 1.5 in - shaft ab inner radius= 1.1 in shaft cd radius= 1.0 in -shaft ab inner shear modulus = 12000 k -shaft ab outer shear modulus = 3000 ksi shaft ed shear modulus = 12000 ksi outer portion inner portion shaft ab cross-section 2.86 in-kip
Two solid circular shafts are connected by two rigid ab is a composite shaft. Determine the angle of twist at point 'a' in degrees to two decimal places. solid shaft 60 in b 4= 11-3535 TL GJ J= π/₂2r4 composite shaft C 35 in Notes:- gear b radius = 6.0 in - gear c radius= 4.0 in - shaft ab outer radius = 1.5 in - shaft ab inner radius= 1.1 in shaft cd radius= 1.0 in -shaft ab inner shear modulus = 12000 k -shaft ab outer shear modulus = 3000 ksi shaft ed shear modulus = 12000 ksi outer portion inner portion shaft ab cross-section 2.86 in-kip
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
![**Determining the Angle of Twist in a Composite Shaft**
**Problem Statement:**
Two solid circular shafts are connected by two rigid gears. Shaft AB is a composite shaft. Determine the angle of twist at point 'a' in degrees to two decimal places.
**Equation:**
\[
\phi = \frac{TL}{GJ}
\]
\[
J = \frac{\pi}{2} r^4
\]
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a composite shaft system with a solid shaft connected to a composite shaft. Key components are:
- **Fixed Support:** Located at the left end of the solid shaft.
- **Solid Shaft:** 60 inches long.
- **Composite Shaft:** Consists of an outer portion and an inner portion, 35 inches long, leading to point 'a'.
- **Bearings:** Located at transition points, labeled along the shaft.
**Shaft AB Cross-Section:**
- The shaft consists of an outer portion and an inner portion.
**Given Parameters:**
- **Gear B radius:** 6.0 inches
- **Gear C radius:** 4.0 inches
- **Shaft AB outer radius:** 1.5 inches
- **Shaft AB inner radius:** 1.1 inches
- **Shaft CD radius:** 1.0 inch
- **Shaft AB inner shear modulus:** 12000 ksi
- **Shaft AB outer shear modulus:** 3000 ksi
- **Shaft CD shear modulus:** 12000 ksi
**Applied Torque:**
2.86 in-kip at the end of shaft AB.
This problem involves calculating the angle of twist, which combines understanding of mechanical principles like torque and materials engineering to evaluate the behavior of composite shafts under load.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe8988a1a-5625-4af8-94a1-38513bb2393c%2F255e5a41-5eb6-4d60-9f1f-e335999cf3a9%2F3jkln5_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Determining the Angle of Twist in a Composite Shaft**
**Problem Statement:**
Two solid circular shafts are connected by two rigid gears. Shaft AB is a composite shaft. Determine the angle of twist at point 'a' in degrees to two decimal places.
**Equation:**
\[
\phi = \frac{TL}{GJ}
\]
\[
J = \frac{\pi}{2} r^4
\]
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a composite shaft system with a solid shaft connected to a composite shaft. Key components are:
- **Fixed Support:** Located at the left end of the solid shaft.
- **Solid Shaft:** 60 inches long.
- **Composite Shaft:** Consists of an outer portion and an inner portion, 35 inches long, leading to point 'a'.
- **Bearings:** Located at transition points, labeled along the shaft.
**Shaft AB Cross-Section:**
- The shaft consists of an outer portion and an inner portion.
**Given Parameters:**
- **Gear B radius:** 6.0 inches
- **Gear C radius:** 4.0 inches
- **Shaft AB outer radius:** 1.5 inches
- **Shaft AB inner radius:** 1.1 inches
- **Shaft CD radius:** 1.0 inch
- **Shaft AB inner shear modulus:** 12000 ksi
- **Shaft AB outer shear modulus:** 3000 ksi
- **Shaft CD shear modulus:** 12000 ksi
**Applied Torque:**
2.86 in-kip at the end of shaft AB.
This problem involves calculating the angle of twist, which combines understanding of mechanical principles like torque and materials engineering to evaluate the behavior of composite shafts under load.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given
The radius of gear B is
The radius of gear C is
The outer radius of AB is
The inner radius of AB is
The radius of CD is
The outer shear modulus of CD is .
The shear modulus of AB is .
The inner shear modulus of CD is .
The torque at end A is
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 16 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY