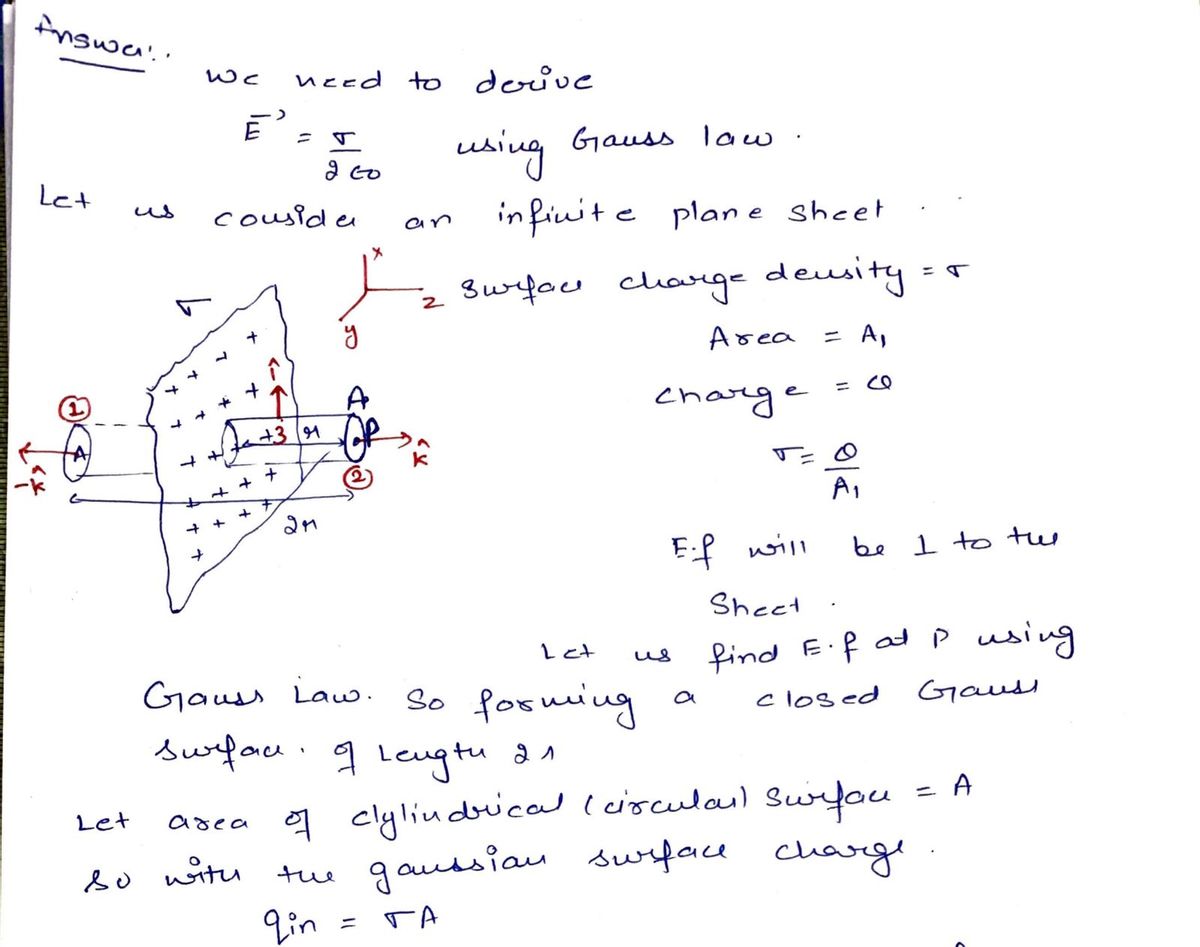
Then, we took the limit as the radius a tends toward infinity to obtain the much simpler expression E =k. 200 This same simpler equation can be very easily obtained by applying Gauss' Law using an appropriate Gaussian surface that extends above and below a small part of the charged sheet. Find this derivation (in a book or online) and rewrite it by hand below. Add verbal explanations to take the reader through the derivation, equation by equation.
Then, we took the limit as the radius a tends toward infinity to obtain the much simpler expression E =k. 200 This same simpler equation can be very easily obtained by applying Gauss' Law using an appropriate Gaussian surface that extends above and below a small part of the charged sheet. Find this derivation (in a book or online) and rewrite it by hand below. Add verbal explanations to take the reader through the derivation, equation by equation.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:3. The electric field near a charged, large, thin, flat sheet of (let's say plastic) was obtained in
Exercise 01 by solving a source charge integration problem. The electric field above a
charged, flat disk of radius a was found to be:
Ē =
ok
2€
1
√(a/z)² +1²°
Then, we took the limit as the radius a tends toward infinity to obtain the much simpler
expression E Ē =
ok.
2€
280
This same simpler equation can be very easily obtained by applying Gauss' Law using an
appropriate Gaussian surface that extends above and below a small part of the charged
sheet. Find this derivation (in a book or online) and rewrite it by hand below. Add verbal
explanations to take the reader through the derivation, equation by equation.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
