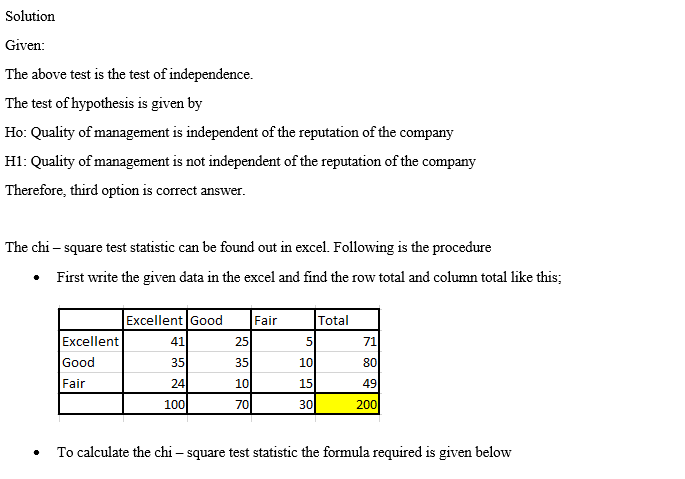
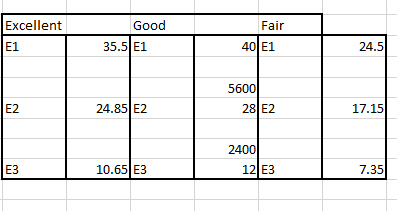
The Wall Street Journal Corporate Perceptions Study 2011 surveyed readers and asked how each rated the quality of management and the reputation of the company for over 250 worldwide corporations. Both the quality of management and the reputation of the company were rated on an excellent, good, and fair categorical scale. Assume the sample data for 200 respondents below applies to this study. Reputation of Company Quality of Management Excellent Good Fair Excellent 41 25 5 Good 35 35 10 Fair 24 10 15 (a) Use a 0.05 level of significance and test for independence of the quality of management and the reputation of the company. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company. H: The proportion of companies with excellent management is not equal across companies with differing reputations. O Ho: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company. H: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company. O Hg: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company. H: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company. O Ho: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company. H: The proportion of companies with excellent management is equal across companies with differing reputations. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value = State your conclusion. Do not reject Hg. We cannot conclude that the rating for the quality of management is independent of the rating of the reputation of the company. Reject Hg. We conclude that the rating for the quality of management is not independent of the rating for the reputation of the company. O Do not reject Hg. We cannot conclude that the ratings for the quality of management and the reputation of the company are not independent. Reject Hg. We conclude that the rating for the quality of management is independent of the rating for the reputation of the company. (b) If there is a dependence or association between the two ratings, discuss and use probabilities to justify your answer. For companies with an excellent reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to --Select-- v with a fair reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to -Select- v management quality. Since these highest probabilities correspond to Select--- v ratings of quality of management and reputation, the two ratings are ---Select- v. management quality. For companies with a good reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to --Select-- management quality. For companies
The Wall Street Journal Corporate Perceptions Study 2011 surveyed readers and asked how each rated the quality of management and the reputation of the company for over 250 worldwide corporations. Both the quality of management and the reputation of the company were rated on an excellent, good, and fair categorical scale. Assume the sample data for 200 respondents below applies to this study. Reputation of Company Quality of Management Excellent Good Fair Excellent 41 25 5 Good 35 35 10 Fair 24 10 15 (a) Use a 0.05 level of significance and test for independence of the quality of management and the reputation of the company. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company. H: The proportion of companies with excellent management is not equal across companies with differing reputations. O Ho: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company. H: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company. O Hg: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company. H: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company. O Ho: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company. H: The proportion of companies with excellent management is equal across companies with differing reputations. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) p-value = State your conclusion. Do not reject Hg. We cannot conclude that the rating for the quality of management is independent of the rating of the reputation of the company. Reject Hg. We conclude that the rating for the quality of management is not independent of the rating for the reputation of the company. O Do not reject Hg. We cannot conclude that the ratings for the quality of management and the reputation of the company are not independent. Reject Hg. We conclude that the rating for the quality of management is independent of the rating for the reputation of the company. (b) If there is a dependence or association between the two ratings, discuss and use probabilities to justify your answer. For companies with an excellent reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to --Select-- v with a fair reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to -Select- v management quality. Since these highest probabilities correspond to Select--- v ratings of quality of management and reputation, the two ratings are ---Select- v. management quality. For companies with a good reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to --Select-- management quality. For companies
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The Wall Street Journal Corporate Perceptions Study 2011 surveyed readers and asked how each rated the quality of management and the reputation of the company for over 250 worldwide corporations. Both the quality of management and the reputation of the company
were rated on an excellent, good, and fair categorical scale. Assume the sample data for 200 respondents below applies to this study.
Reputation of Company
Quality of Management
Excellent
Good
Fair
Excellent
41
25
5
Good
35
35
10
Fair
24
10
15
(a) Use a 0.05 level of significance and test for independence of the quality of management and the reputation of the company.
State the null and alternative hypotheses.
O Ho: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company.
H: The proportion of companies with excellent management is not equal across companies with differing reputations.
O Ho: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company.
H: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company.
O Ho: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company.
H: Quality of management is not independent of the reputation of the company.
O Ho: Quality of management is independent of the reputation of the company.
H: The proportion of companies with excellent management is equal across companies with differing reputations.
Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
Find the p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
p-value =
State your conclusion.
O Do not reject H.. We cannot conclude that the rating for the quality of management is independent of the rating of the reputation of the company.
O Reject Ho. We conclude that the rating for the quality of management is not independent of the rating for the reputation of the company.
O Do not reject Ho: We cannot conclude that the ratings for the quality of management and the reputation of the company are not independent.
O Reject Ho. We conclude that the rating for the quality of management is independent of the rating for the reputation of the company.
(b) If there is a dependence or association between the two ratings, discuss and use probabilities to justify your answer.
For companies with an excellent reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to --Select- v management quality. For companies with a good reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to --Select--- v management quality. For companies
with a fair reputation, the largest column probability corresponds to ---Select-- v management quality. Since these highest probabilities correspond to --Select-- v ratings of quality of management and reputation, the two ratings are ---Select--- v.
Expert Solution
Step 1
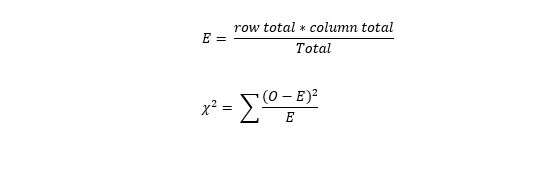
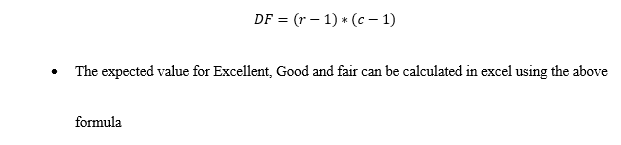
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman