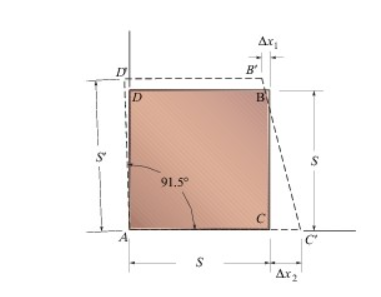
The square deforms into the position shown by the dashed lines in. The dimensions are S=49 mm, S′=54 mm, Δx1=5 mm, and Δx2=9 mm. Side D'B' remains horizontal. A)Determine the shear strain at A relative to the x, y axes. B) Determine the shear strain at B relative to the x, y axes. C) Determine the shear strain at C relative to the x, y axes.
The square deforms into the position shown by the dashed lines in. The dimensions are S=49 mm, S′=54 mm, Δx1=5 mm, and Δx2=9 mm. Side D'B' remains horizontal. A)Determine the shear strain at A relative to the x, y axes. B) Determine the shear strain at B relative to the x, y axes. C) Determine the shear strain at C relative to the x, y axes.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
The square deforms into the position shown by the dashed lines in. The dimensions are S=49 mm, S′=54 mm, Δx1=5 mm, and Δx2=9 mm. Side D'B' remains horizontal.
A)Determine the shear strain at A relative to the x, y axes.
B) Determine the shear strain at B relative to the x, y axes.
C) Determine the shear strain at C relative to the x, y axes.

Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a deformed square, illustrating shear deformation. The original square, labeled as ABCD, transforms into a parallelogram with dashed lines indicating the deformation.
Key Elements:
1. **Original Shape (Square ABCD):**
- Side AB is parallel to side DC and both have a length denoted as \( S \).
- Side AD is parallel to side BC and also has a length of \( S \).
2. **Deformation:**
- The square tilts to the right, forming a parallelogram.
- The angle \(\angle DAB\) increases slightly to 91.5°, indicating shear strain.
3. **Displacement:**
- Point B moves to \( B' \), introducing a horizontal shift \(\Delta x_1\).
- Point C moves to \( C' \), with a horizontal shift of \(\Delta x_2\).
4. **Measurements:**
- Vertical displacement remains constant at \( S \) for points D and D', as well as A and C.
- The horizontal displacement between initial and deformed positions is shown as \(\Delta x_1\) and \(\Delta x_2\).
This diagram serves as a visual explanation for shear deformation, where the internal angle change and horizontal displacements show how forces might act on a material to distort its shape while retaining the same vertical dimension.
Expert Solution
Step 1: all given data, figures and determining parts are written here.
Given data- S=49 mm, S′=54 mm, Δx1=5 mm, and Δx2=9 mm
Determine-
A) the shear strain at A relative to the x, y axes.
B) the shear strain at B relative to the x, y axes.
C) the shear strain at C relative to the x, y axes.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY