The pulley of Fig. wheel that fits loosely over a t in.-diameter shaft. A rope passes over the pulley and is attached to a 50-lb weight. The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the consists of a 4-in.-diameter pulley and the shaft are 0.35 and 0.25, respectively. The weight of the pulley is 2 lb. The rope being pulled makes an angle 8 = 90° with the horizontal. Determine the force necessary to Raise the weight at a constant speed. P
The pulley of Fig. wheel that fits loosely over a t in.-diameter shaft. A rope passes over the pulley and is attached to a 50-lb weight. The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the consists of a 4-in.-diameter pulley and the shaft are 0.35 and 0.25, respectively. The weight of the pulley is 2 lb. The rope being pulled makes an angle 8 = 90° with the horizontal. Determine the force necessary to Raise the weight at a constant speed. P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The pulley of Fig.
wheel that fits loosely over a t in.-diameter shaft. A rope
passes over the pulley and is attached to a 50-lb weight.
The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the
consists of a 4-in.-diameter
pulley and the shaft are 0.35 and 0.25, respectively. The
weight of the pulley is 2 lb. The rope being pulled makes
an angle 8 = 90° with the horizontal. Determine the force
necessary to
Raise the weight at a constant speed.
P
Expert Solution
Step 1
The free-body diagram for the problem is shown below:
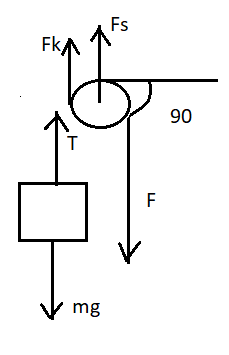
From the free-body diagram, we can write the equation for net force. Since the body moves with constant velocity, the acceleration of the body is zero.
The equation for the force is given by
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images
